Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance inherited genetic disorder that presents with numerous adenomatous polyps Adenomatous polyps Benign neoplasms derived from glandular epithelium. Colorectal Cancer in the colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy. Familial adenomatous polyposis is the most common of the polyposis syndromes, which is a group of inherited or acquired conditions characterized by the growth of polyps in the GI tract, associated with other extracolonic features. These syndromes are caused by mutations in specific genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure associated with tumor Tumor Inflammation suppression Suppression Defense Mechanisms or cell cycle Cell cycle The phases of the cell cycle include interphase (G1, S, and G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase). The cell's progression through these phases is punctuated by checkpoints regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor suppressors, and their antagonists. Cell Cycle regulation. All patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with FAP will develop colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy cancer by age 35–40 years if left untreated. Management is with a surveillance Surveillance Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth program and colectomy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance disorder that is associated with the development of numerous colorectal adenomas.
Pathogenic mutations in the tumor Tumor Inflammation suppressor gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) in chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 5 on band 5q21:
There are 4 syndromes from the germline mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the APC gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics:
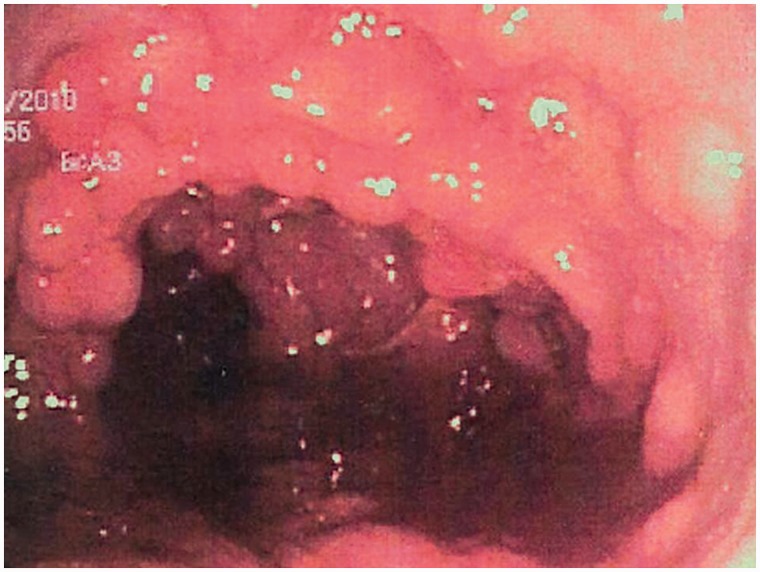
Colonic mucosa carpeted by adenomatous polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis
Image: “Colonic mucosa carpeted with adenomatous polyps in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis” by Shussman, N., Wexner, S.D. License: CC BY 3.0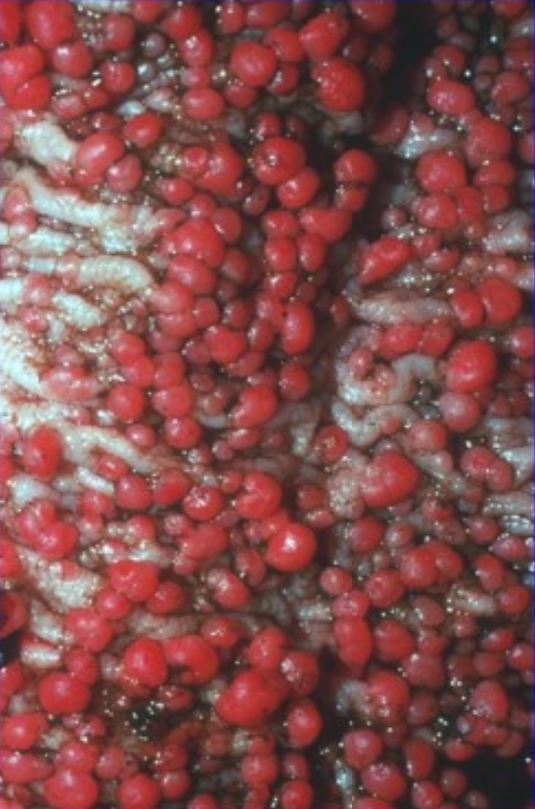
Endoscopic view of established, multiple FAP adenomas
Image: “Familial adenomatous polyposis” by Half, E., Bercovich, D., Rozen, P. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.