Failure to thrive (FTT), or faltering growth, describes suboptimal weight gain and growth in children. The majority of cases are due to inadequate caloric intake; however, genetic, infectious, and oncological etiologies are also common. A thorough history and physical examination guide the work-up to uncover the underlying cause. The causes of FTT are divided into nonorganic and organic. A multidisciplinary approach is taken in the management of nonorganic causes of FTT; organic causes require management of the underlying cause. Recognition and treatment of FTT are important to avoid developmental delay.
Last updated: Mar 6, 2023
Failure to thrive (FTT) describes suboptimal weight gain and growth in children. Failure to thrive is measured as a drop below the 5th percentile for age and sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria, or a drop in weight that crosses 2 major percentile lines on standardized growth charts in a 6-month period.
Multiple definitions exist and are considered valid:
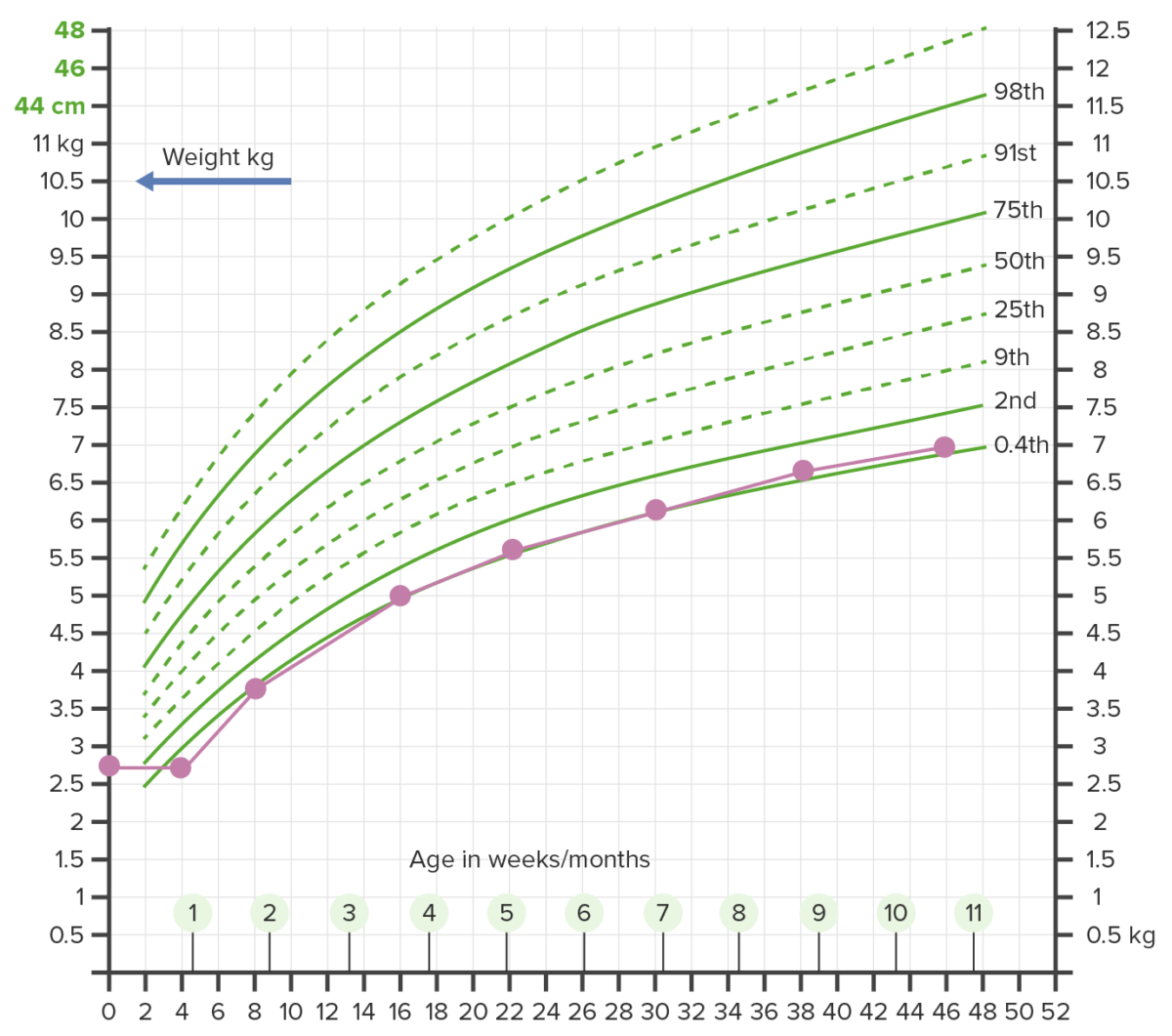
Growth chart showing failure to thrive (FTT):
Weight beneath the 2nd percentile on more than 2 occasions warrants further investigation.
Failure to thrive (FTT) is an indicator Indicator Methods for assessing flow through a system by injection of a known quantity of an indicator, such as a dye, radionuclide, or chilled liquid, into the system and monitoring its concentration over time at a specific point in the system. Body Fluid Compartments of underlying pathology or psychosocial impairment. Causes of FTT are grouped by inadequate caloric intake, malabsorption Malabsorption General term for a group of malnutrition syndromes caused by failure of normal intestinal absorption of nutrients. Malabsorption and Maldigestion, increased metabolic demand, or inefficiency in caloric use.
Because diagnosis is ascertained through growth chart comparison, cases are often detected during a well-child visit or an ED visit for dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration and lethargy Lethargy A general state of sluggishness, listless, or uninterested, with being tired, and having difficulty concentrating and doing simple tasks. It may be related to depression or drug addiction. Hyponatremia.
Diagnosis is clinical: History and physical examination guide confirmatory lab testing and direct to the underlying etiology.
A multidisciplinary approach is taken to manage FTT, especially in nonorganic causes.
Refeeding syndrome may occur in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship treated for severe chronic malnutrition Malnutrition Malnutrition is a clinical state caused by an imbalance or deficiency of calories and/or micronutrients and macronutrients. The 2 main manifestations of acute severe malnutrition are marasmus (total caloric insufficiency) and kwashiorkor (protein malnutrition with characteristic edema). Malnutrition in children in resource-limited countries.
The following conditions can present similarly to FTT and must be considered on presentation:
Insufficient caloric intake:
Malabsorptive causes:
Increased caloric demand: