Ewing sarcoma (ES) is a primary bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax derived from primitive round cells affecting primarily children and teenagers. Ewing sarcoma commonly presents with a painful mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast, swelling Swelling Inflammation, and pathologic bone fractures Bone fractures Breaks in bones. Bones: Remodeling and Healing. Diagnosis is established with imaging and biopsy. Treatment involves systemic chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma and local control of the tumor Tumor Inflammation with surgical resection or radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma. With proper treatment, the overall 5-year survival is over 70%.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Ewing sarcoma (ES) is a primary bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax derived from undifferentiated primitive round cells.
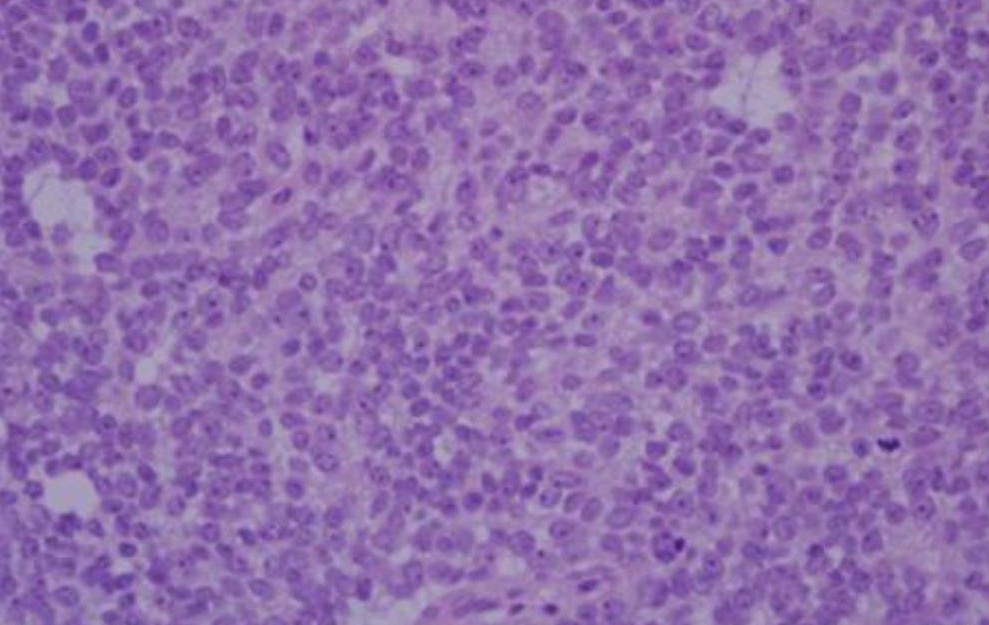
A hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained section from an Ewing sarcoma tumor magnified at 400x:
Sheets of small round cells with a high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio
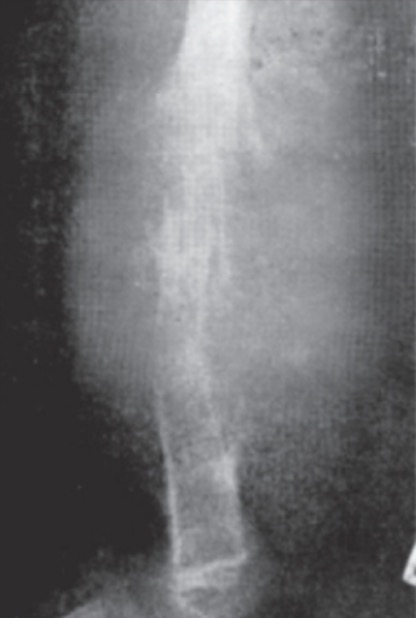
X-ray of Ewing sarcoma of the femur (large destructive lesion)
Image: “Ewing’s sarcoma of the femur” by Vyankat G Vohar. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.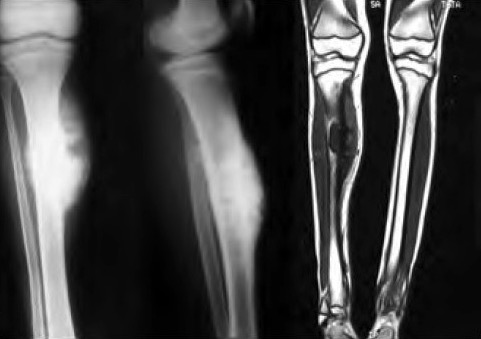
Ewing sarcoma:
Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs with T1-weighted coronal section of MRI showing involvement of proximal ⅓ diaphysis of the right tibia
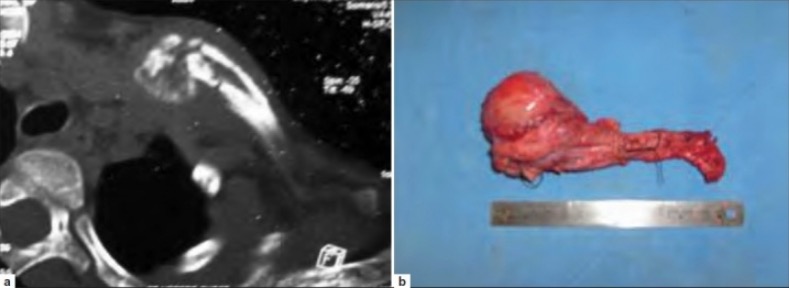
Ewing sarcoma:
a: Axial section of noncontrast CT scan showing Ewing sarcoma of the right clavicle
b: Photograph showing the resected right clavicle with tumor in situ