Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. The underlying etiology varies and may be associated with infection, drug exposure, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, or malignancy. The lesions often self-resolve within 8 weeks without scarring. Management focuses on identifying and treating the underlying cause.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Epidemiology[1‒4]
Etiology[2‒6]
| Classification | Etiologies | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious causes | Bacterial |
|
| Viral |
|
|
| Fungal |
|
|
| Parasitic |
|
|
| Noninfectious causes | Drugs |
|
| Malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax |
|
|
| IBD |
|
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
An immune-mediated reaction to various antigens results in subcutaneous fat Subcutaneous fat Fatty tissue under the skin throughout the body. Erythema Nodosum inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation (septal panniculitis Panniculitis General term for inflammation of adipose tissue, usually of the skin, characterized by reddened subcutaneous nodules. Erythema Nodosum).[1‒3]
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may present with:[1,2,5,7]
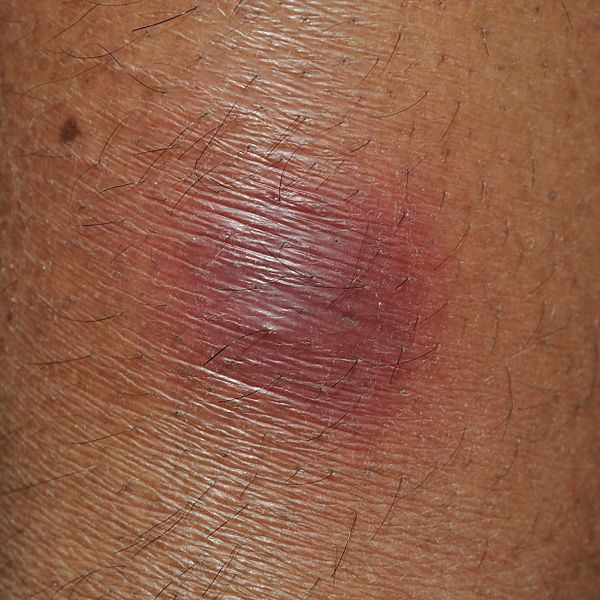
Erythema nodosum is an inflammation of the fat cells under the skin (panniculitis) characterized by tender red nodules or lumps that are usually seen on both shins.
Image: “Erythema nodosum” by Biswarup Ganguly. License: CC BY 3.0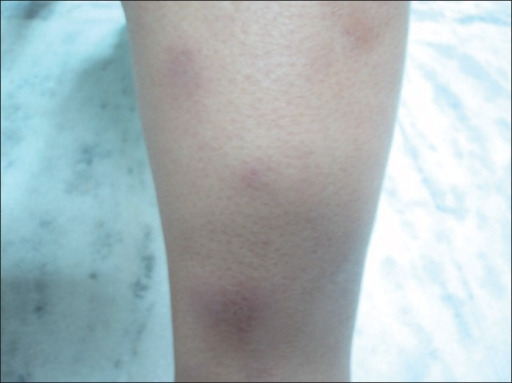
Erythema nodosum: atypical presentation of common disease
Image: “Erythematous, papulo-nodular skin lesions over the shin” by Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. License: CC BY 2.0Diagnostic and management criteria may vary depending on practice location. The following information on diagnosis and management is based on US and UK medical society recommendations.
Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion nodosum is usually diagnosed clinically by history and physical examination. Acute onset of tender nonulcerated nodules or plaques on both shins Shins Erythema Nodosum is typical.
Skin biopsy Skin Biopsy Secondary Skin Lesions:[1‒3,5]
Evaluate for an underlying cause:[1‒3,5,7]
Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion nodosum is self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children and usually resolves within 8 weeks.
Symptomatic treatment includes:[1‒4,7]
Antiinflammatory medications:[1,7]
Identify and manage the underlying cause, such as:[1‒4,7]
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose
Erythema
Erythema
Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes.
Chalazion Nodosum, an inflammatory condition of the
subcutaneous fat
Subcutaneous fat
Fatty tissue under the skin throughout the body.
Erythema Nodosum (
panniculitis
Panniculitis
General term for inflammation of adipose tissue, usually of the skin, characterized by reddened subcutaneous nodules.
Erythema Nodosum) that presents as tender red nodules, typically on the
shins
Shins
Erythema Nodosum.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | L52 | Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion nodosum |
| SNOMED CT | 36011006 | Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion nodosum (disorder) |
Evaluation & Workup:
Erythema
Erythema
Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes.
Chalazion nodosum is often a reaction to an underlying systemic condition. This code is for a chest
X-ray
X-ray
Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source.
Pulmonary Function Tests, a key part of the workup to screen for common triggers like
sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly.
Sarcoidosis or
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes.
Tuberculosis.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 71046 | Radiologic examination, chest; 2 views |
| CPT | 87880 | Infectious agent antigen detection Antigen detection Respiratory Syncytial Virus by immunoassay with direct optical observation; Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus, group A |