The electron transport chain (ETC) sends electrons through a series of proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis, which generate an electrochemical proton gradient that produces energy in the form of adenosine Adenosine A nucleoside that is composed of adenine and d-ribose. Adenosine or adenosine derivatives play many important biological roles in addition to being components of DNA and RNA. Adenosine itself is a neurotransmitter. Class 5 Antiarrhythmic Drugs triphosphate (ATP). Proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis generate energy through redox reactions that create the proton gradient. The complete aerobic catabolism of 1 molecule of glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance yields between 36 and 38 ATPs, mostly through energy obtained as the reduced coenzymes Coenzymes Small molecules that are required for the catalytic function of enzymes. Many vitamins are coenzymes. Basics of Enzymes NADH and FADH2 are conveyed through the electron transport system. Three of the 4 respiratory complexes that make up the mitochondrial respiratory chain, as well as ATP synthase, are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Coenzyme Q and cytochrome c transfer electrons between complexes, which will ultimately meet oxygen and generate H2O.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
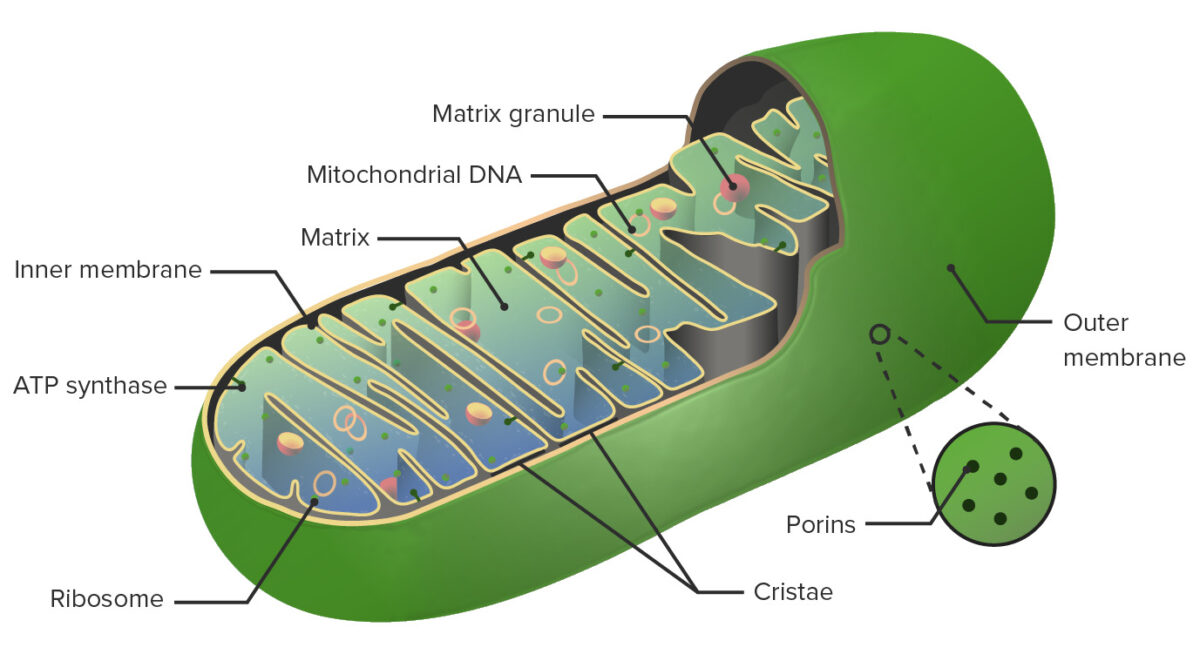
Anatomy of the mitochondrion:
The important structures of the mitochondrion include the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, and matrix.
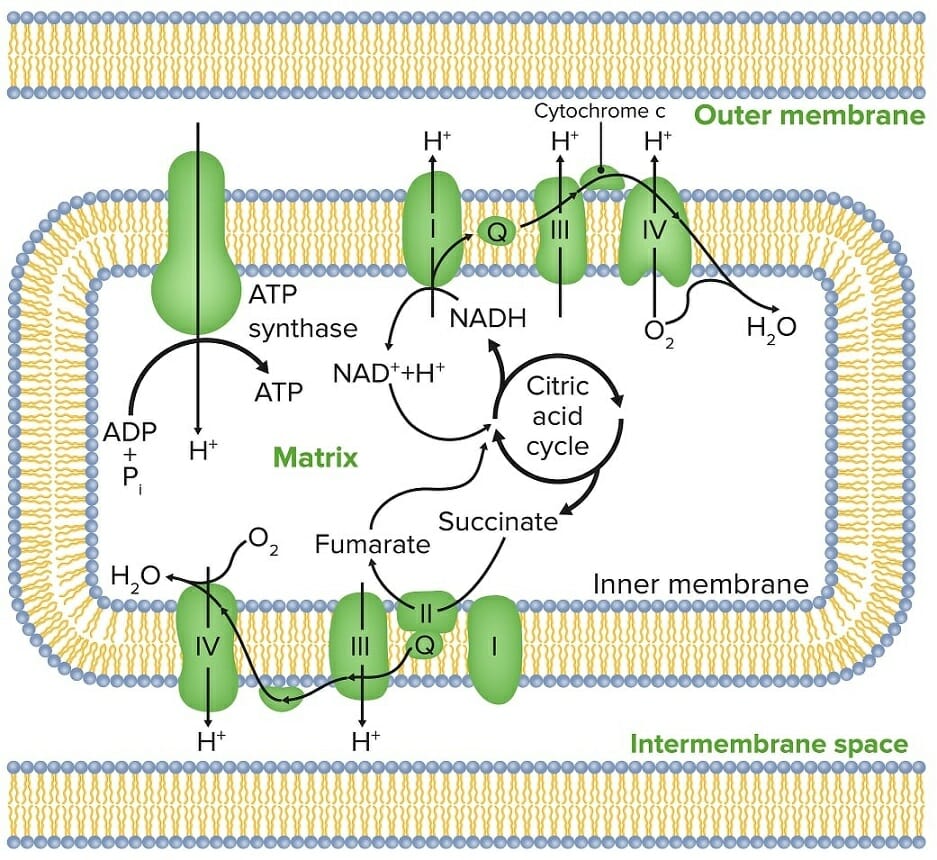
Mitochondrial membranes:
Key proteins are shown within the inner membrane. The citric acid cycle is crucial to the process, as it provides NADH for the electron transport chain (ETC).
| Enzyme catalyzing oxidation step | Number of NADH or FADH2 formed | Number of protons ultimately translocated into intermembrane space |
|---|---|---|
| Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase A flavoprotein oxidoreductase that has specificity for medium-chain fatty acids. It forms a complex with electron transferring flavoproteins and conveys reducing equivalents to ubiquinone. Fatty Acid Metabolism | 7 FADH2 | 42 |
| Beta-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 7 NADH | 70 |
| Isocitrate dehydrogenase Isocitrate dehydrogenase An enzyme of the oxidoreductase class that catalyzes the conversion of isocitrate and NAD+ to yield 2-ketoglutarate, carbon dioxide, and nadh. It occurs in cell mitochondria. The enzyme requires mg2+, mn2+; it is activated by adp, citrate, and Ca2+, and inhibited by nadh, NADPH, and ATP. The reaction is the key rate-limiting step of the citric acid (tricarboxylic) cycle. Citric Acid Cycle | 8 NADH | 80 |
| Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase | 8 NADH | 80 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase Succinate dehydrogenase A flavoprotein containing oxidoreductase that catalyzes the dehydrogenation of succinate to fumarate. In most eukaryotic organisms this enzyme is a component of mitochondrial electron transport complex II. Citric Acid Cycle | 8 FADH2 | 48 |
| Malate dehydrogenase | 8 NADH | 80 |
| Total | 400 |