Edwards syndrome, or trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 18, is a genetic syndrome caused by the presence of an extra chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 18. The extra chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics is either from 3 full copies of chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 18 or an additional segment of chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 18. As the 2nd most common trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations, Edwards syndrome is seen in 1 out of every 5,500 live births and increases with maternal age. Many cases are detected prenatally with maternal screening Screening Preoperative Care and ultrasound findings. Abnormalities include intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), overlapping fingers, typical craniofacial features, rocker-bottom feet, and congenital heart defects. Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 18 frequently results in fetal loss. For term pregnancies, most deaths occur during the 1st 6 months of life. Delivery in a specialized center is recommended for full-term pregnancies and intervention is based on associated abnormalities.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Edwards syndrome, or trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 18, is defined as the presence of 3 copies of chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 18.
Mnemonic for Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18): “At 18 you can vote in an election.”
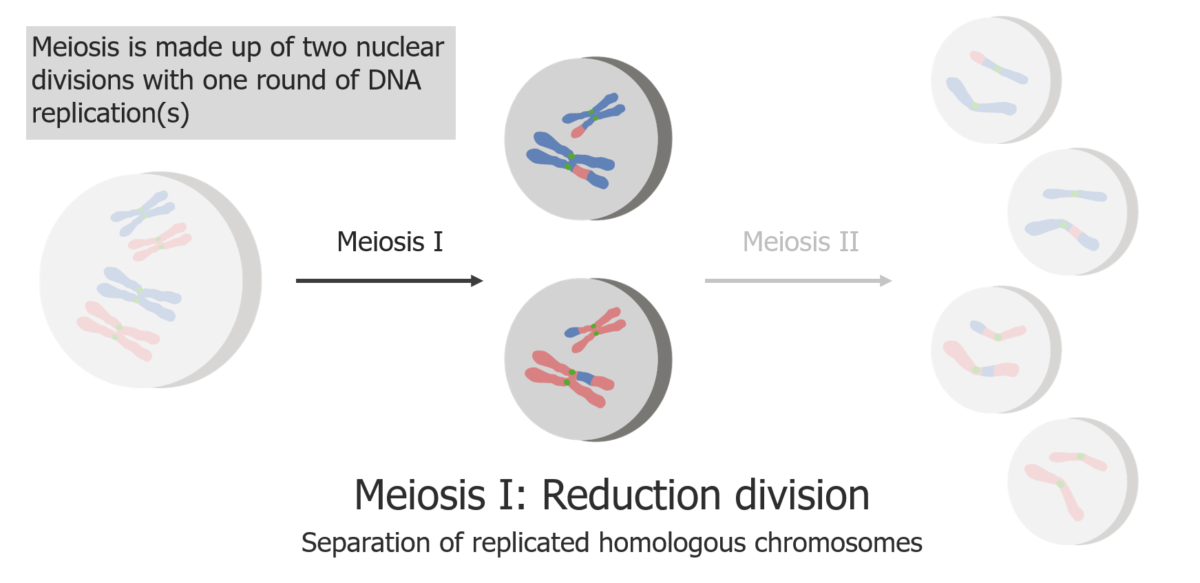
Meiosis I is a separation of replicated sister chromatids.
Image by Lecturio.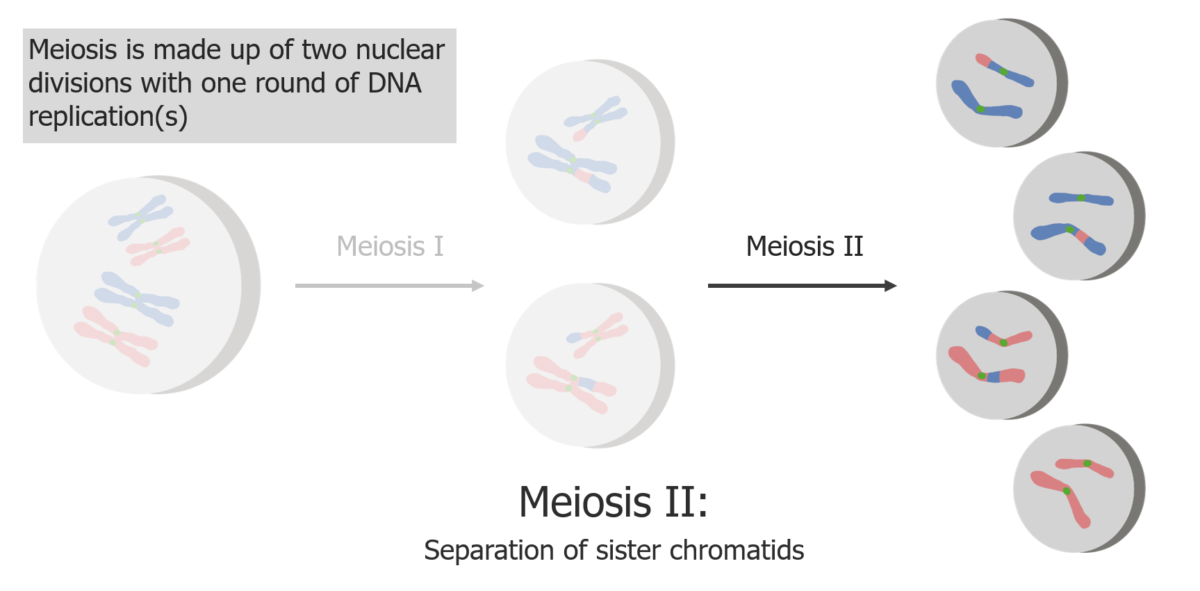
Meiosis II is a separation of sister chromatids, producing 4 haploid cells/gametes.
Image by Lecturio.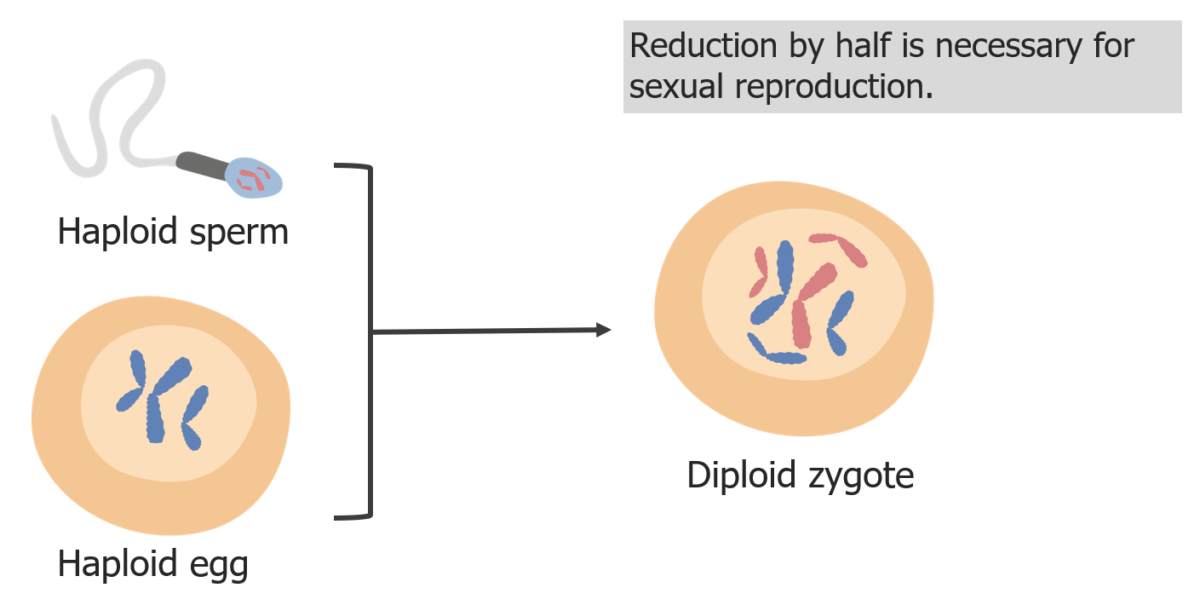
Chromosome reduction is necessary so the zygote is diploid in fertilization.
Image by Lecturio.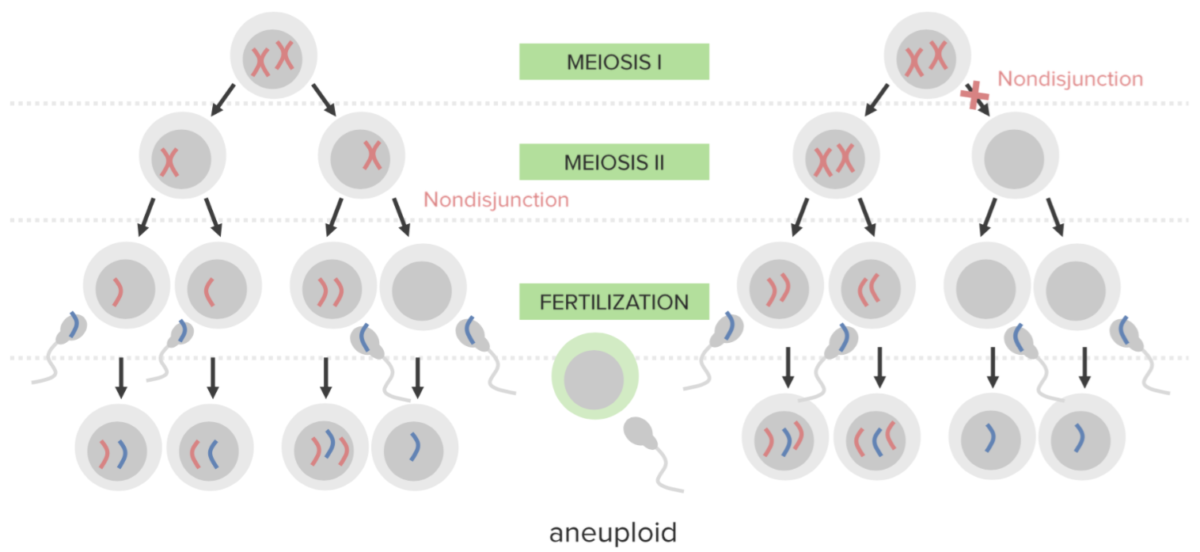
Nondisjunction:
The failure to properly separate 2 homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids during cell division. Nondisjunction results in aneuploidy (a state of chromosomal imbalance).
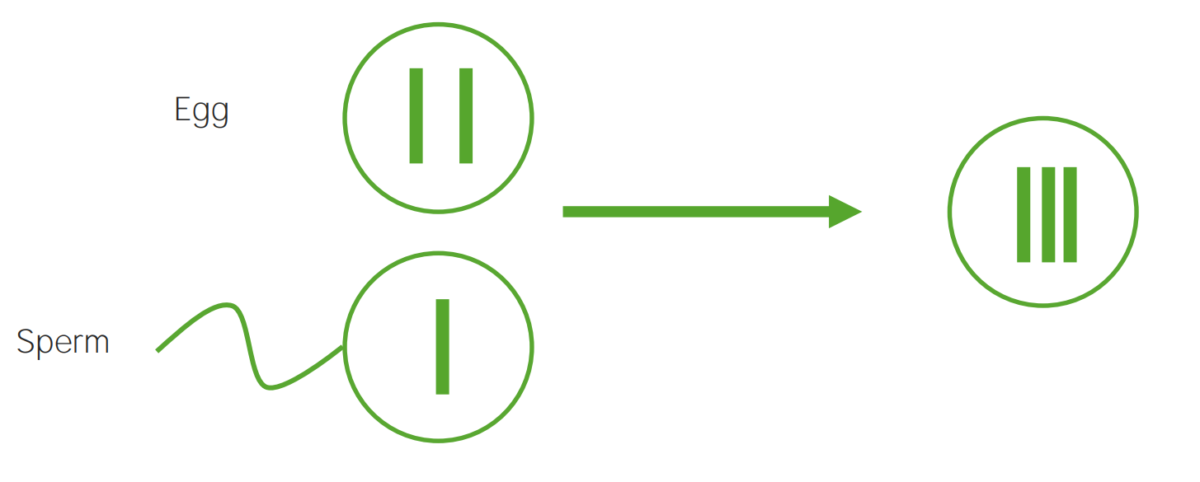
A diagram illustrating the etiological mechanism of nondisjunction in trisomy:
An egg carrying 2 copies of the same chromosome acquires another when fertilized, resulting in 3 copies.
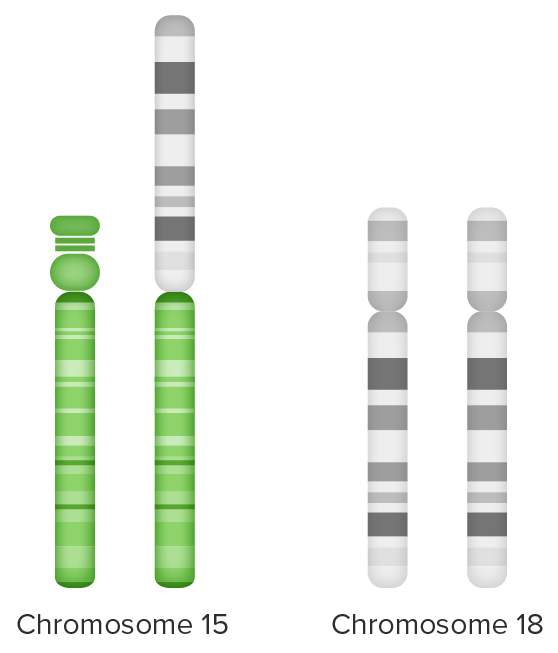
Unbalanced translocation:
Extra chromosome 18 material (long arm) attached to chromosome 15 (on the left) and
partial trisomy 18 from 2 sets of chromosome 18 + extra long arm chromosome 18 (on the right)
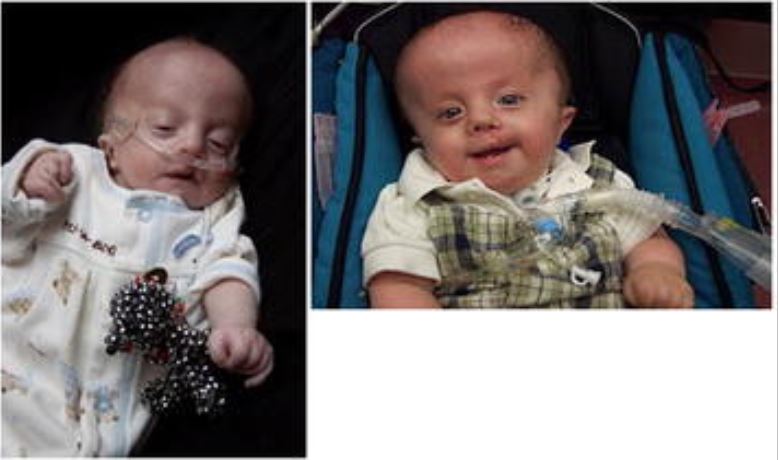
Boy with trisomy 18 in early infancy and at 1 year of age:
Note the characteristic hand feature of overriding fingers and tracheostomy in place.
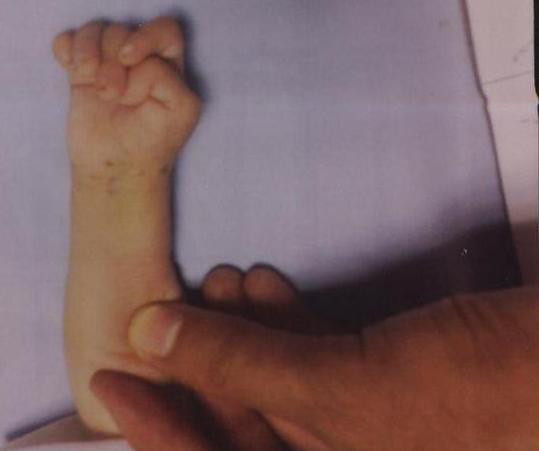
Infant with trisomy 18 and overlapping fingers
Image: “Congenital hydrocephalus in an Egyptian baby with trisomy 18: a case report” by Metwalley KA, Farghalley HS, Abd-Elsayed AA. License: CC BY 2.0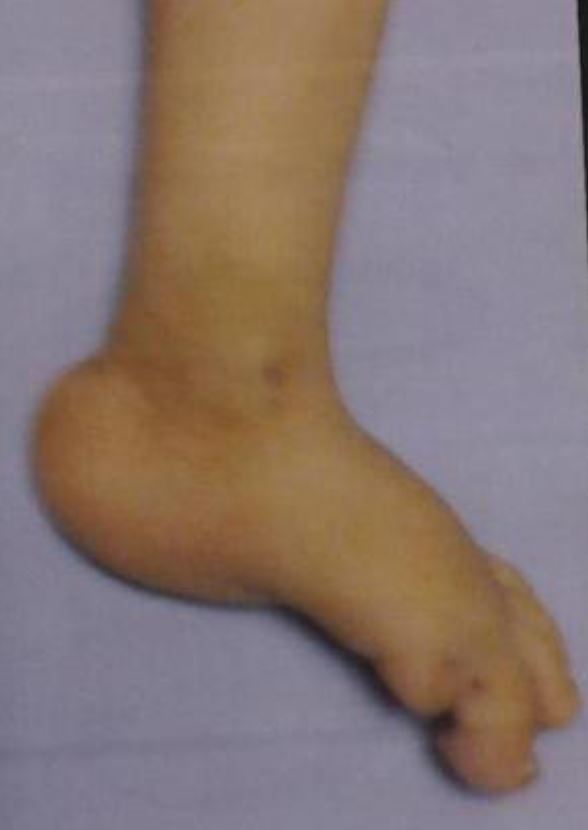
Infant with trisomy 18 and rocker-bottom feet (a common finding)
Image: “Congenital hydrocephalus in an Egyptian baby with trisomy 18: a case report” by Metwalley KA, Farghalley HS, Abd-Elsayed AA. License: CC BY 2.0| 1st trimester | 2nd trimester | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | PAPP-A | hCG | AFP AFP The first alpha-globulins to appear in mammalian sera during fetal development and the dominant serum proteins in early embryonic life. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases | Estriol Estriol A hydroxylated metabolite of estradiol or estrogen that has a hydroxyl group at C3, 16-alpha, and 17-beta position. Estriol is a major urinary estrogen. During pregnancy, a large amount of estriol is produced by the placenta. Isomers with inversion of the hydroxyl group or groups are called epiestriol. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins | hCG | Inhibin A Inhibin A Glycoproteins that inhibit pituitary follicle stimulating hormone secretion. Inhibins are secreted by the sertoli cells of the testes, the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles, the placenta, and other tissues. Inhibins and activins are modulators of follicle stimulating hormone secretions; both groups belong to the TGF-beta superfamily, as the transforming growth factor beta. Inhibins consist of a disulfide-linked heterodimer with a unique alpha linked to either a beta a or a beta B subunit to form inhibin a or inhibin b, respectively. Menstrual Cycle | |
| Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 13 | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | Unchanged | Unchanged | Unchanged | Unchanged |
| Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 18 | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | Unchanged |
| Trisomy 21 Trisomy 21 Down syndrome, or trisomy 21, is the most common chromosomal aberration and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental delay. Both boys and girls are affected and have characteristic craniofacial and musculoskeletal features, as well as multiple medical anomalies involving the cardiac, gastrointestinal, ocular, and auditory systems. Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) | ↑↑ | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
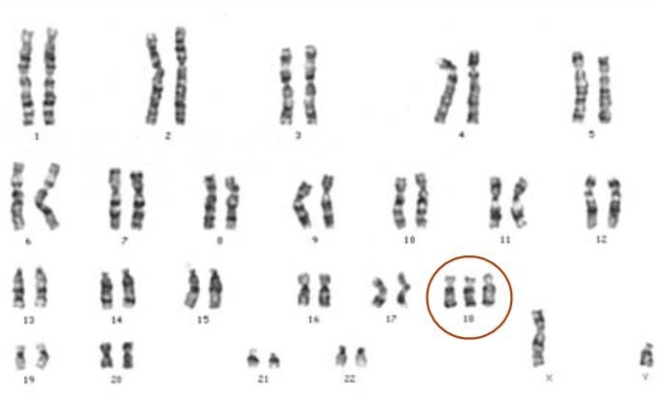
Karyotype of person affected with Edward Syndrome:
Three copies of chromosome 18 can be seen