Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus tapeworms. Infection most often occurs from the ingestion of Echinococcus eggs in food or water contaminated with dog feces. Signs and symptoms are caused by hydatid cyst development in visceral organs and depend on the species. E. granulosus causes cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change echinococcosis, which can involve any organ. The most notable presentations involve the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy or lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy, resulting in RUQ abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen, hepatomegaly, cough, or dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. E. multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis, which typically involves the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy. Serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus and imaging may be used for the diagnosis, the latter of which can show characteristic findings of hydatid cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change. Management depends on the size and complexity of the cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change but can involve observation, anthelmintic therapy Anthelmintic therapy Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of helminthiasis in man and animal. Toxocariasis, percutaneous drainage, or surgery.
Last updated: Jan 26, 2025
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus tapeworms. Features include:
Eggs:
Adults:
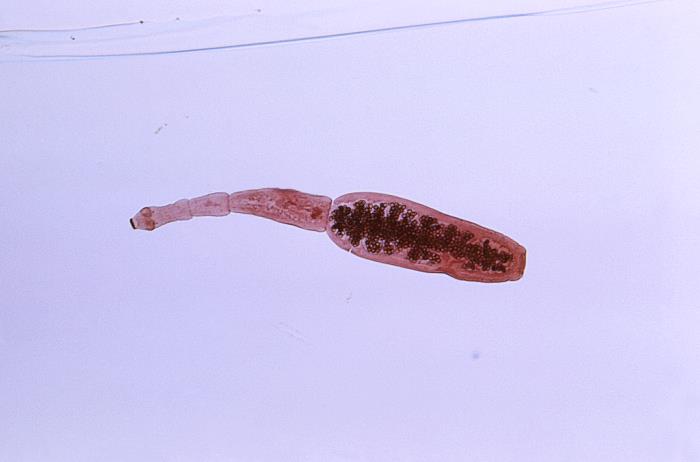
This photomicrograph shows the morphology exhibited by the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus:
Note the head on the left and the scolex with hook-rimmed rostellum.
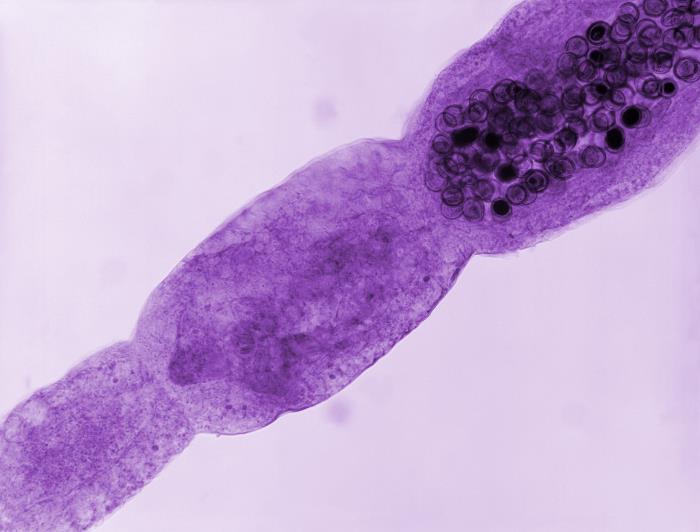
Photomicrograph of an Echinococcus multilocularis tapeworm:
Note the terminal proglottid filled with darkly stained ova.
E. granulosus:
E. multilocularis:
E. vogeli and E. oligarthrus:
E. granulosus:
E. multilocularis:
Transmission occurs through ingestion of eggs, usually from food or water contaminated with animal feces.
E. granulosus:
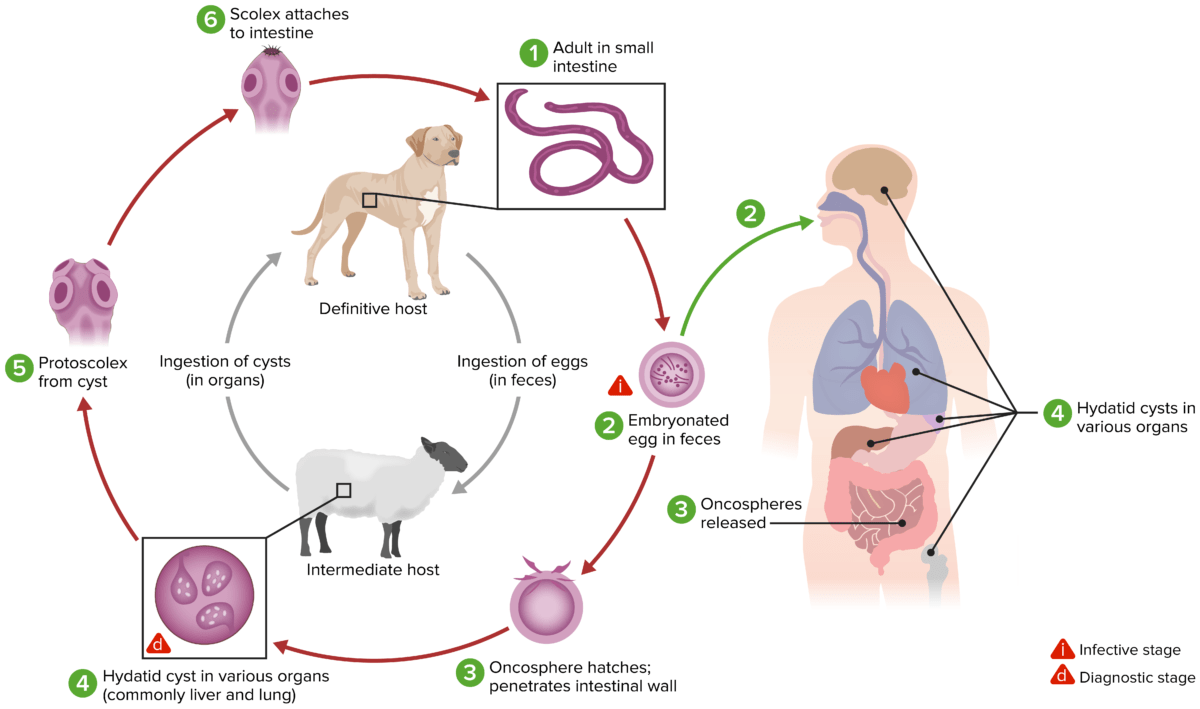
The life cycle for Echinococcus granulosus
Image by Lecturio.E. multilocularis:
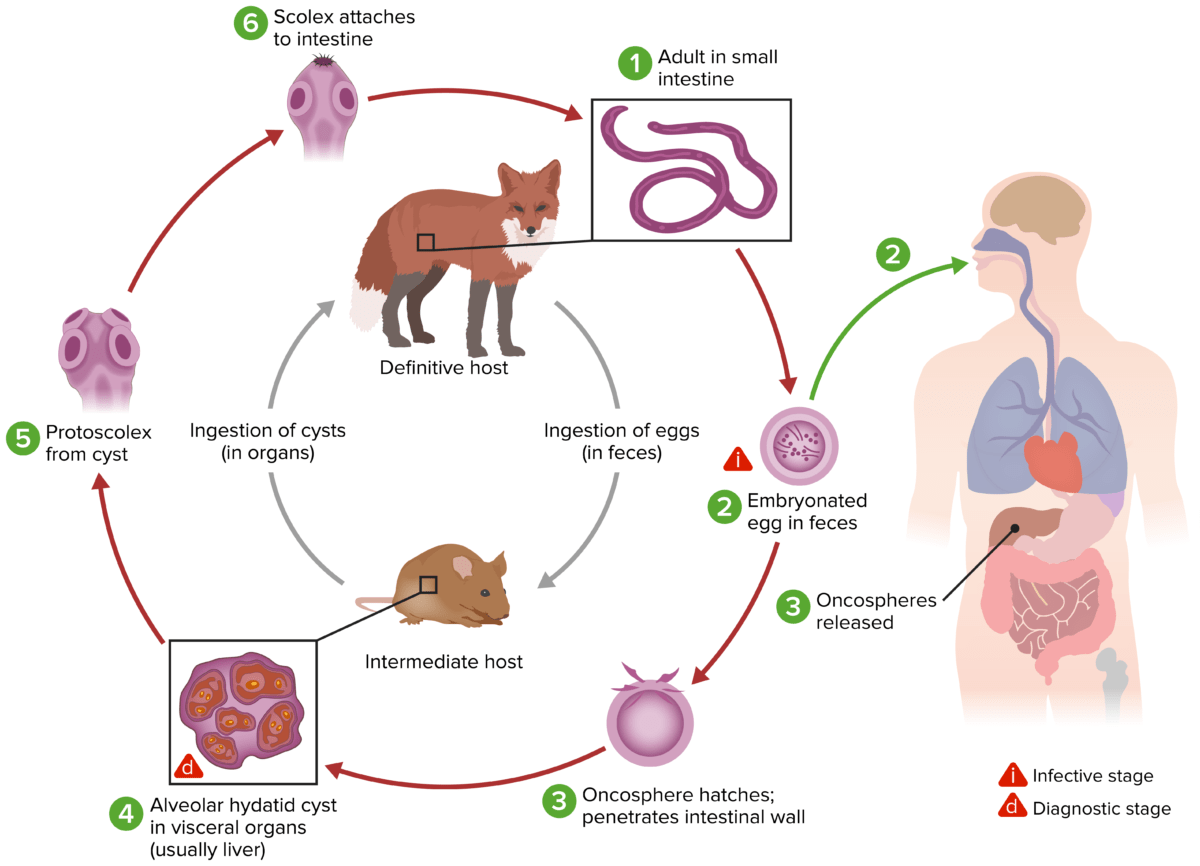
The life cycle for Echinococcus multilocularis
Image by Lecturio.Both cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change and alveolar echinococcosis are characterized by asymptomatic incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus periods (months to years).
Symptoms depend on:
Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy (75% of cases):
Lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy (5%–15% of cases):
Central nervous system Central nervous system The main information-processing organs of the nervous system, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and meninges. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification:
Other organ systems:
Imaging of hydatid cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change is the mainstay of diagnosis.
Ultrasonography:
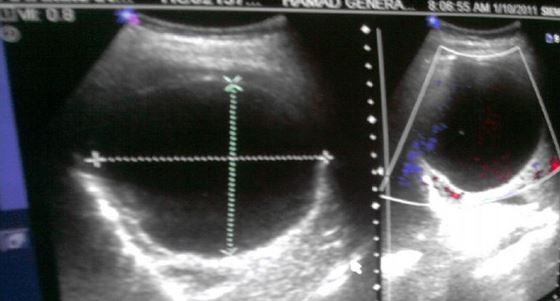
Abdominal ultrasound showing a well-defined hydatid cyst in the right lobe of the liver due to cystic echinococcosis
Image: “An imported case of echinococcosis in a pregnant lady” by Al-Ani A et al. License: CC BY 3.0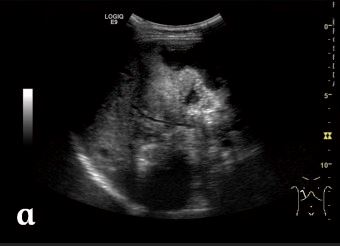
Abdominal ultrasound showing an irregular, heterogeneous mass lesion in the liver due to alveolar echinococcosis:
There are no clear boundaries. Hyperechoic foci due to calcification can be seen.
CT:
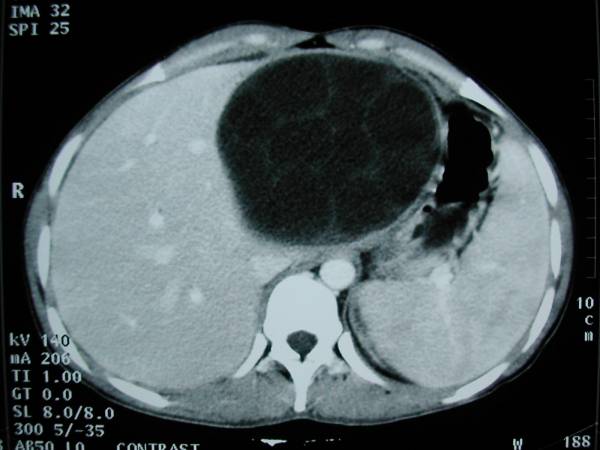
CT image showing a large, multilocular hydatid cyst in the liver due to cystic echinococcosis
Image: “Hydatid cyst of the left liver with typical multivesicular image” by Majbar AM et al. License: CC BY 2.0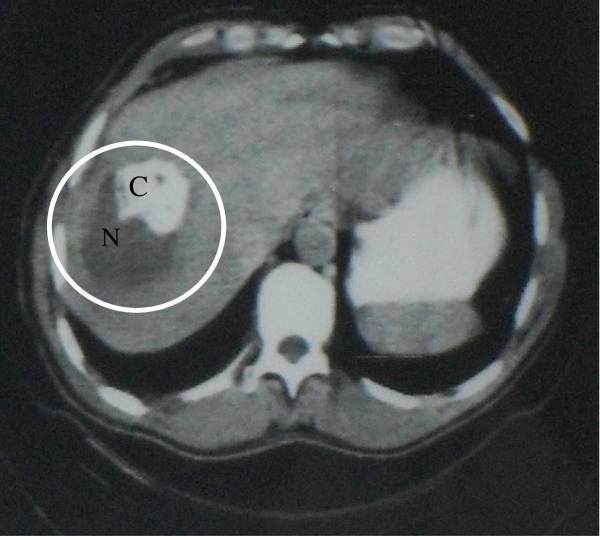
CT image showing a heterogeneous cyst with necrosis (N) and calcification (C):
This necrosis and calcification is caused by alveolar echinococcosis.
MRI:
Serologic tests are used for diagnosing echinococcosis and for monitoring after treatment.
There are 4 management strategies: observation, medical therapy, percutaneous drainage, and surgery.
Observation is appropriate:
Medical therapy:
Percutaneous drainage:
Surgery:
| Organism | Dibothriocephalus latus | Taenia Taenia Taenia belong to the Cestoda class of helminths. Humans are infected with these tapeworms by eating undercooked beef (T. saginata) or pork (T. solium and T. asiatica). Taeniasis is often asymptomatic, but the ingestion of larvae can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea, and constipation or diarrhea. Taenia/Taeniasis saginata | Echinococcus granulosus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics |
|
|
|
| Transmission | Eating raw infected fish FISH A type of in situ hybridization in which target sequences are stained with fluorescent dye so their location and size can be determined using fluorescence microscopy. This staining is sufficiently distinct that the hybridization signal can be seen both in metaphase spreads and in interphase nuclei. Chromosome Testing | Eating raw infected beef | Fecal–oral (ingestion of contaminated food or water) |
| Disease | Diphyllobothriasis Diphyllobothriasis Diphyllobothriasis represents an intestinal parasitic infection caused by the cestode Diphyllobothrium. Diphyllobothriasis is acquired by ingestion of late larvae in undercooked or raw fish. The clinical presentation of diphyllobothriasis varies from asymptomatic, nonspecific symptoms to intestinal obstruction, and/or vitamin B12 deficiency. Dibothriocephalus/Diphyllobothriasis | Taeniasis Taeniasis Taenia belong to the Cestoda class of helminths. Humans are infected with these tapeworms by eating undercooked beef (T. saginata) or pork (T. solium and T. asiatica). Taeniasis is often asymptomatic, but the ingestion of larvae can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea, and constipation or diarrhea. Taenia/Taeniasis | Cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change echinococcosis |
| Clinical |
|
|
Depends on location and size of hydatid cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change |
| Diagnosis | Eggs or proglottids Proglottids Taenia/Taeniasis in stool | Eggs or proglottids Proglottids Taenia/Taeniasis in stool |
|
| Management |
|
|
|
| Prevention |
|
Beef should be cooked thoroughly. |
|
Adult Diphyllobothrium latum tapeworm
Image: “Dibothriocephalus latus with ruler” by CDC. License: CC BY 3.0
Adult Taenia saginata tapeworm measuring approximately 4 m
Image: “ 5260” by CDC. License: Public Domain