Dog and cat bites can cause superficial and deep tissue destruction, as well as serious wound infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Dog bites occur more frequently in men and children and often cause crushing Crushing Blunt Chest Trauma or tearing trauma. Cat bites are more frequent in adult women and result in puncture wounds. Because puncture wounds allow inoculation of bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology into the deep tissues, cat bites are more frequently associated with infection. The diagnosis is clinical, and cultures should be obtained if the wound appears infected. Management requires fastidious Fastidious Bordetella wound care and antibiotics for high-risk or infected wounds.
Last updated: Apr 26, 2025
International data are lacking, but statistics in the United States include:
| Dog bites | Cat bites |
|---|---|
| Approximately 90% of all animal bites | Approximately 10% of all animal bites |
| Men > women | Women > men |
| Children > adults | Adults > children |
| Less often result from provocation | More often result from provocation |
In addition to the risk of contracting the rabies Rabies Acute viral CNS infection affecting mammals, including humans. It is caused by rabies virus and usually spread by contamination with virus-laden saliva of bites inflicted by rabid animals. Important animal vectors include the dog, cat, bat, fox, raccoon, skunk, and wolf. Rabies Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology from an animal bite, wound infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease can be caused by the following organisms:
| Dog bites | Cat bites | Both |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Patient-related factors:
Bite-related factors:
| Dog bites | Cat bites | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Children: head, face,
neck
Neck
The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body.
Peritonsillar Abscess Adults: hands, arms |
Extremities |
| Wound type | Crushing Crushing Blunt Chest Trauma and tearing | Puncture |
| Consequences | Deeper structures are often damaged (tendons, bones, and blood vessels). | Inoculates bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology into the deep tissues |
| Risk of deep infection | Less likely | More likely (and requires shorter time to manifest) |
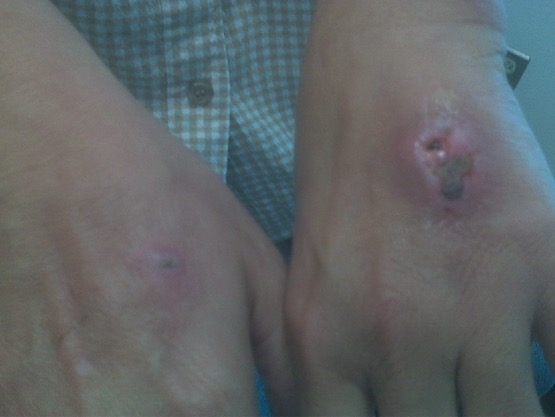
Bilateral, ulcerative, nodular wounds on the dorsum of a patient’s hands after sustaining dog bites
Image: “Ulcerative, nodular wounds” by Warren Alpert Brown University School of Medicine, 1125 North Main Street, Providence, RI 02906, USA. License: CC BY 4.0The diagnosis of a cat or dog bite is clinical, but the following may be utilized in select cases:
Wounds at low risk for infection do not require antibiotic prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins. Antibiotic prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins is indicated for:
High-risk wounds:
High-risk conditions:
Like dog and cat bites, human bites can carry a significant risk for infection.
Infection after a human bite is often polymicrobial. Common organisms include: