The molecule DNA is the repository of heritable genetic information. In humans, DNA is contained in 23 chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics pairs within the nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles. The molecule provides the basic template for replication of genetic information, RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure transcription Transcription Transcription of genetic information is the first step in gene expression. Transcription is the process by which DNA is used as a template to make mRNA. This process is divided into 3 stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Stages of Transcription, and protein biosynthesis Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of peptides and proteins on ribosomes, directed by messenger RNA, via transfer RNA that is charged with standard proteinogenic amino acids. Virology to promote cellular function and survival.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The hereditary material DNA is a double-stranded nucleotide polymer:
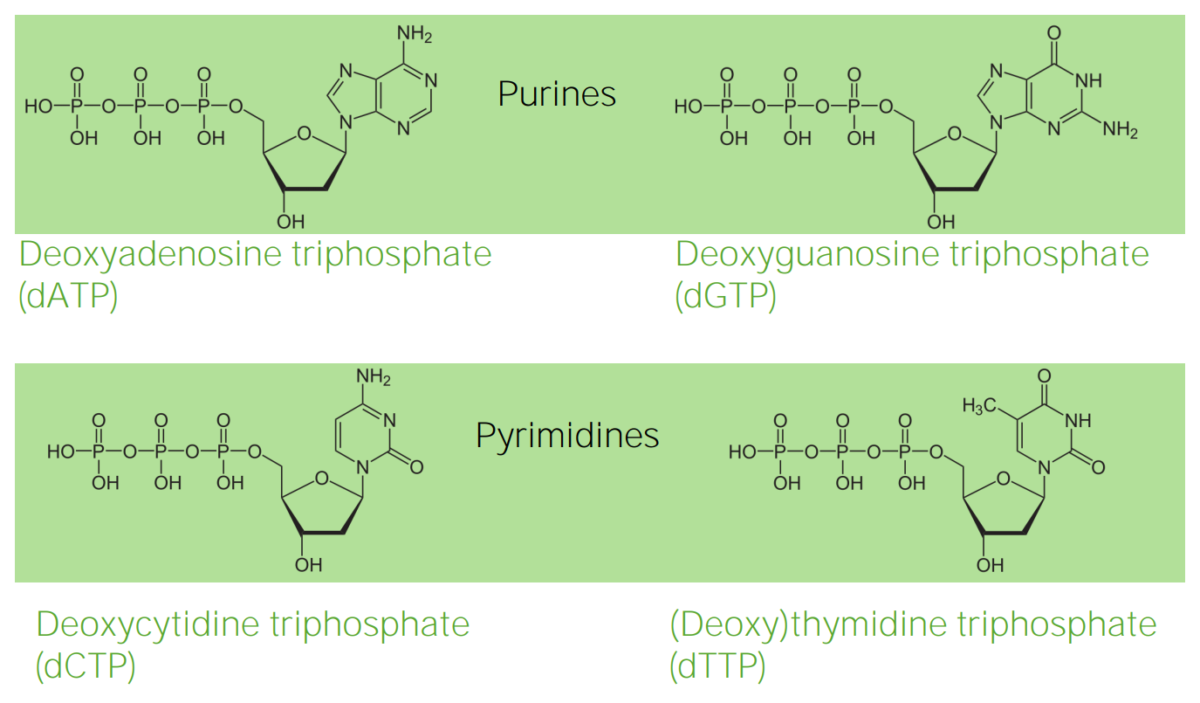
Structure of deoxyribonucleotides
Image by Lecturio.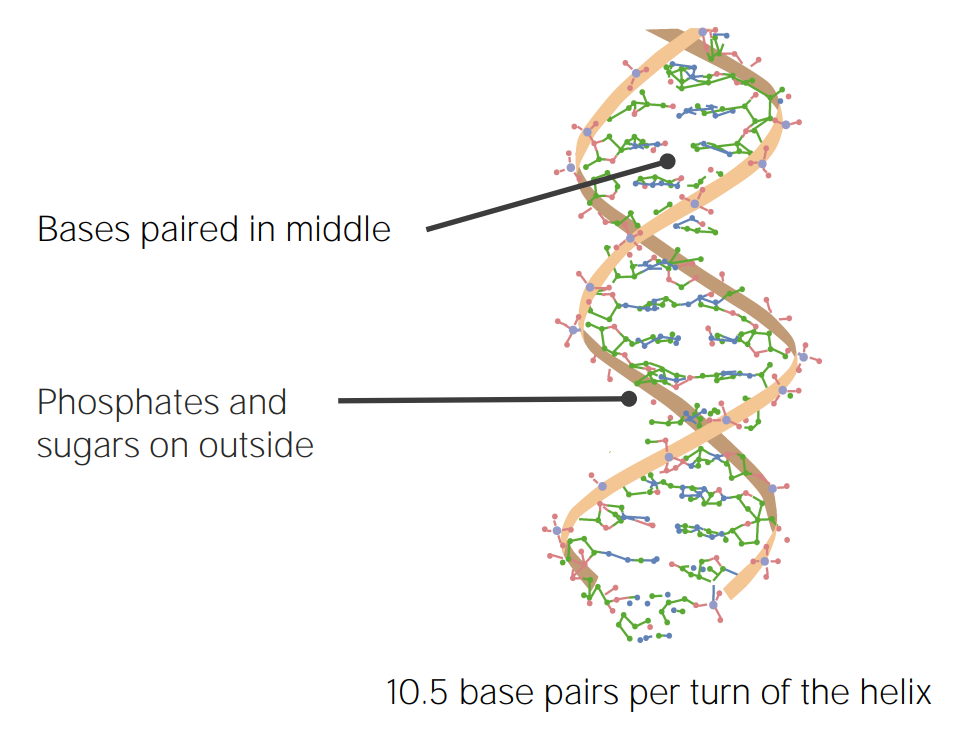
Structure of DNA as described by Watson and Crick
Image by Lecturio.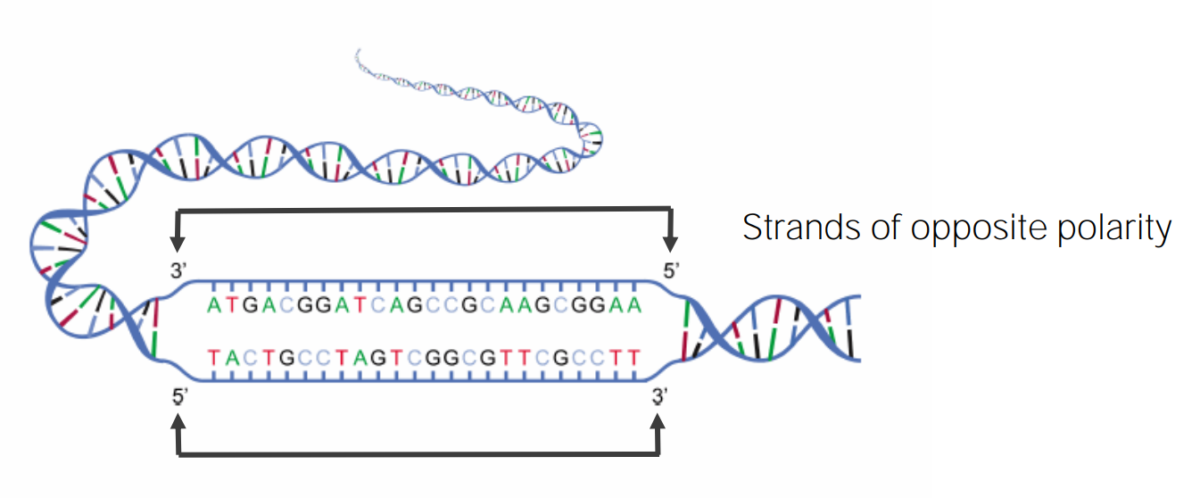
Diagram of the DNA double helix showing the antiparallel (polar) nature of each complementary strand
Image by Lecturio.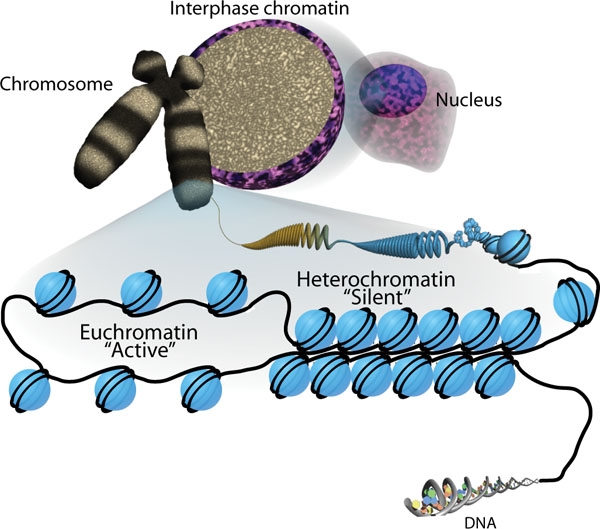
Packaging of DNA and the 2 states of chromatin:
Euchromatin (active) where DNA is being replicated or transcribed; and heterochromatin (silent), where DNA is not being replicated or transcribed.