Distal radius Radius The outer shorter of the two bones of the forearm, lying parallel to the ulna and partially revolving around it. Forearm: Anatomy fractures are one of the most common fractures encountered in practice and are often associated with falling onto an outstretched hand Hand The hand constitutes the distal part of the upper limb and provides the fine, precise movements needed in activities of daily living. It consists of 5 metacarpal bones and 14 phalanges, as well as numerous muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves. Hand: Anatomy. These fractures are most frequently seen in older individuals, especially women. In this population, these fractures are related to an increase in falls due to gait instability Gait Instability Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenberg Syndrome) with aging and associated osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis. In younger individuals, distal radius Radius The outer shorter of the two bones of the forearm, lying parallel to the ulna and partially revolving around it. Forearm: Anatomy fractures are usually related to high-energy trauma. Individuals often present with pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways and a dinner fork deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs of the distal forearm Forearm The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term "forearm" is used in anatomy to distinguish this area from the arm, a term that is commonly used to describe the entire upper limb. The forearm consists of 2 long bones (the radius and the ulna), the interosseous membrane, and multiple arteries, nerves, and muscles. Forearm: Anatomy. Diagnosis is clinical and confirmed with x-rays X-rays X-rays are high-energy particles of electromagnetic radiation used in the medical field for the generation of anatomical images. X-rays are projected through the body of a patient and onto a film, and this technique is called conventional or projectional radiography. X-rays of the wrist. Treatment can be operative or nonoperative depending on the age of the individual, articular involvement, and degree of displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms or angulation Angulation Buckle or Torus Fracture.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
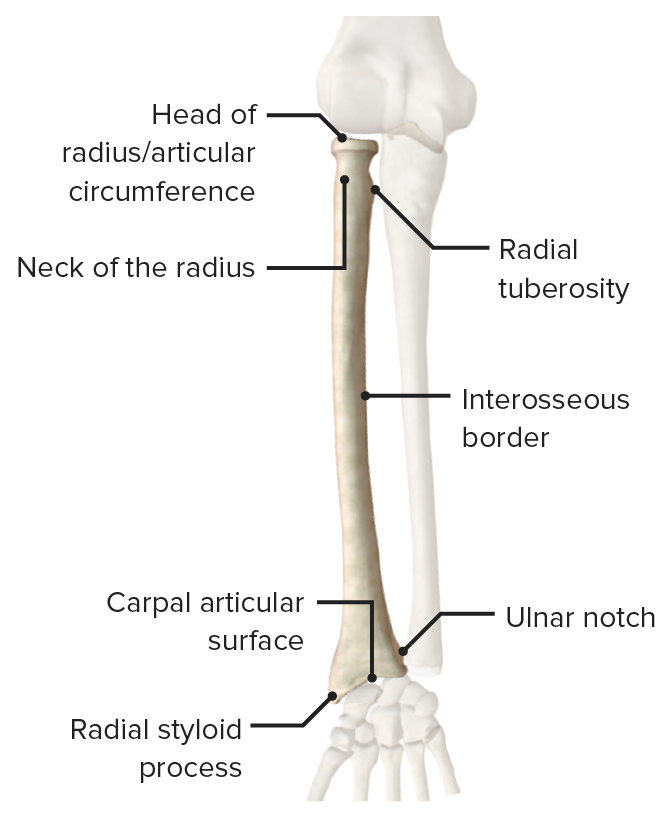
Anterior view of the radius featuring its bony landmarks and articular surfaces
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio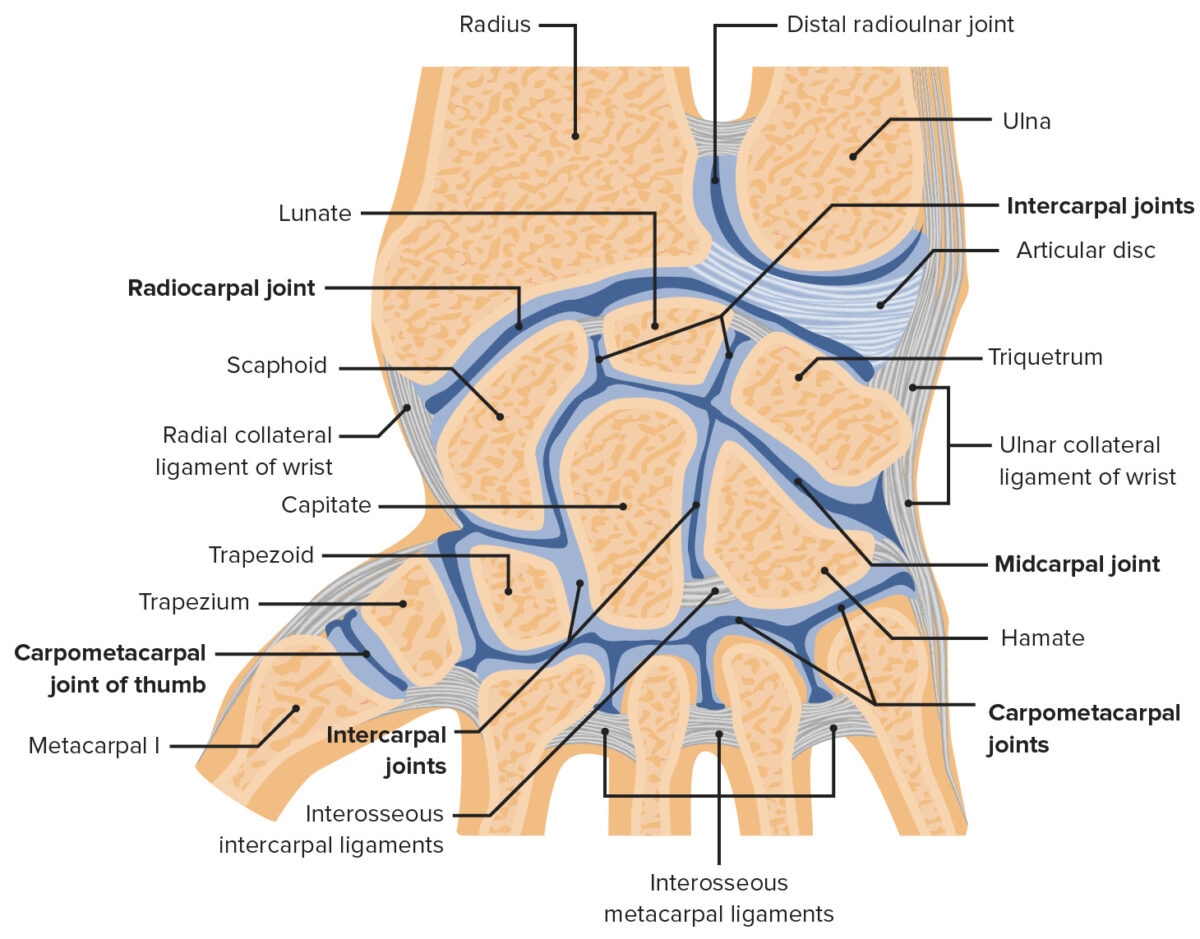
Wrist joint and its articulations with the radius and ulna:
The distal radius articulates with the scaphoid and lunate bones of the wrist at the radiocarpal joint. The distal radius also articulates with the ulna at the radioulnar joint.
Image by Lecturio.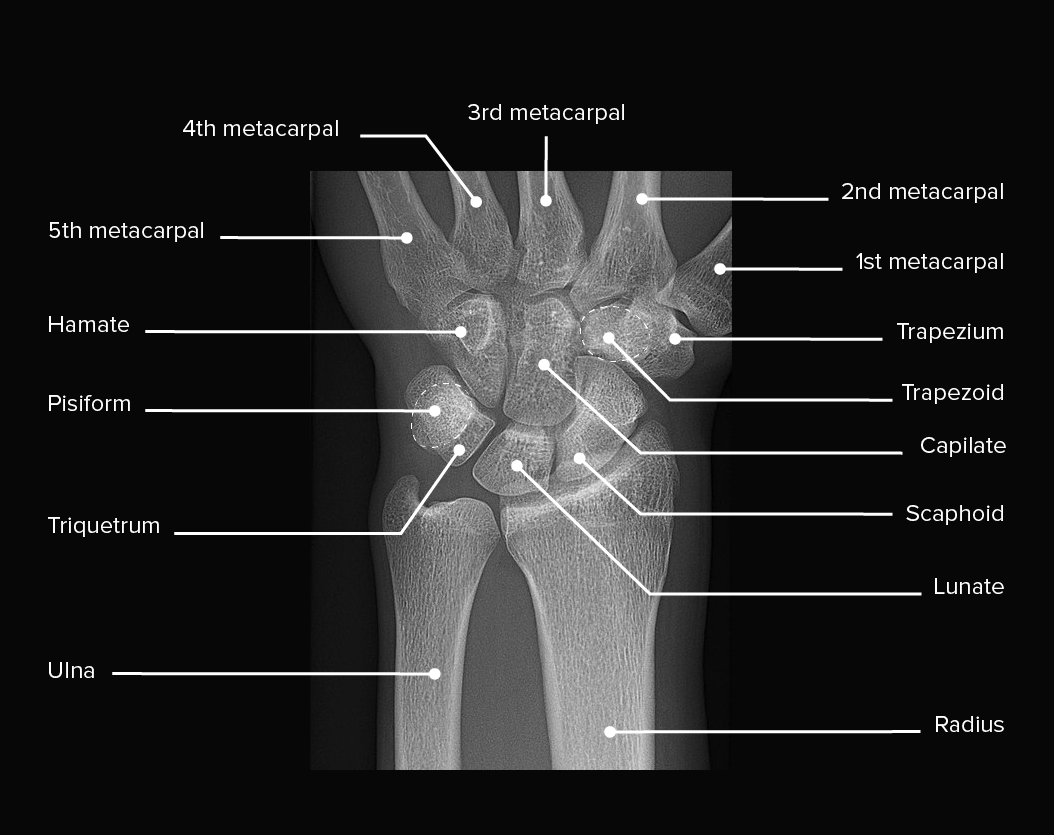
X-ray of a left wrist, showing normal anatomy and no injuries
Image: “X-ray of normal wrist” by Mikael Häggström, M.D. License: CC0 1.0, edited by Lecturio.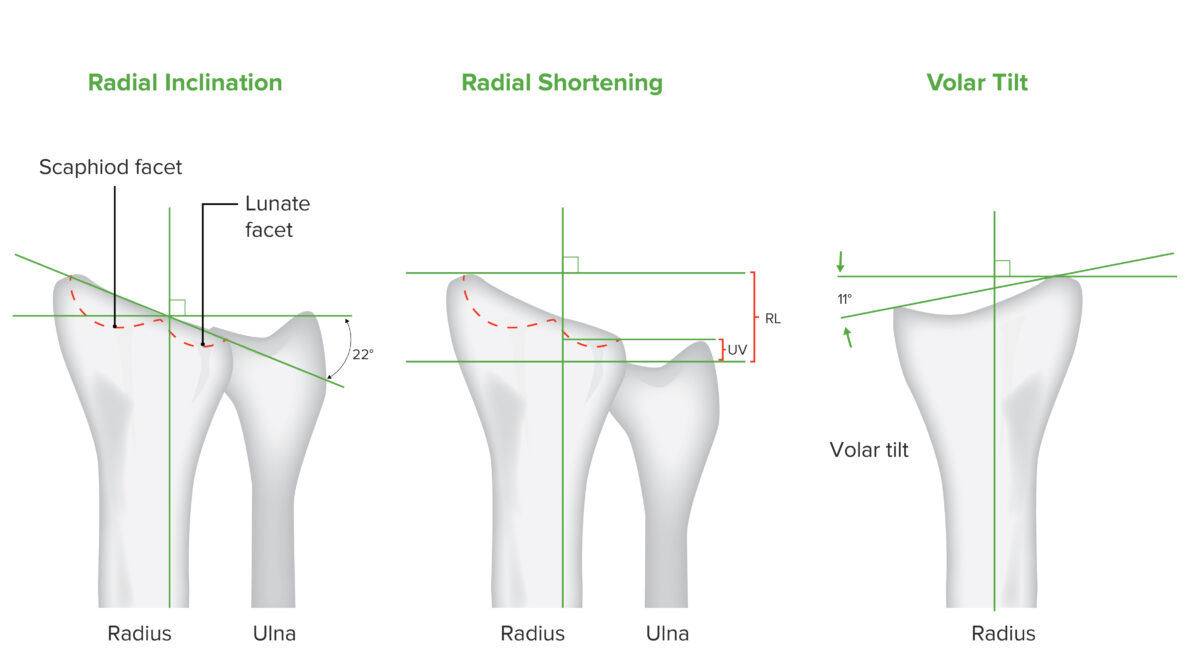
Movements of distal radius:
Inclination of the radius, shortening of the radius, and volar tilt are radiologically measured values used to evaluate the radial joint in the setting of a distal radius fracture.
History:
Physical exam:
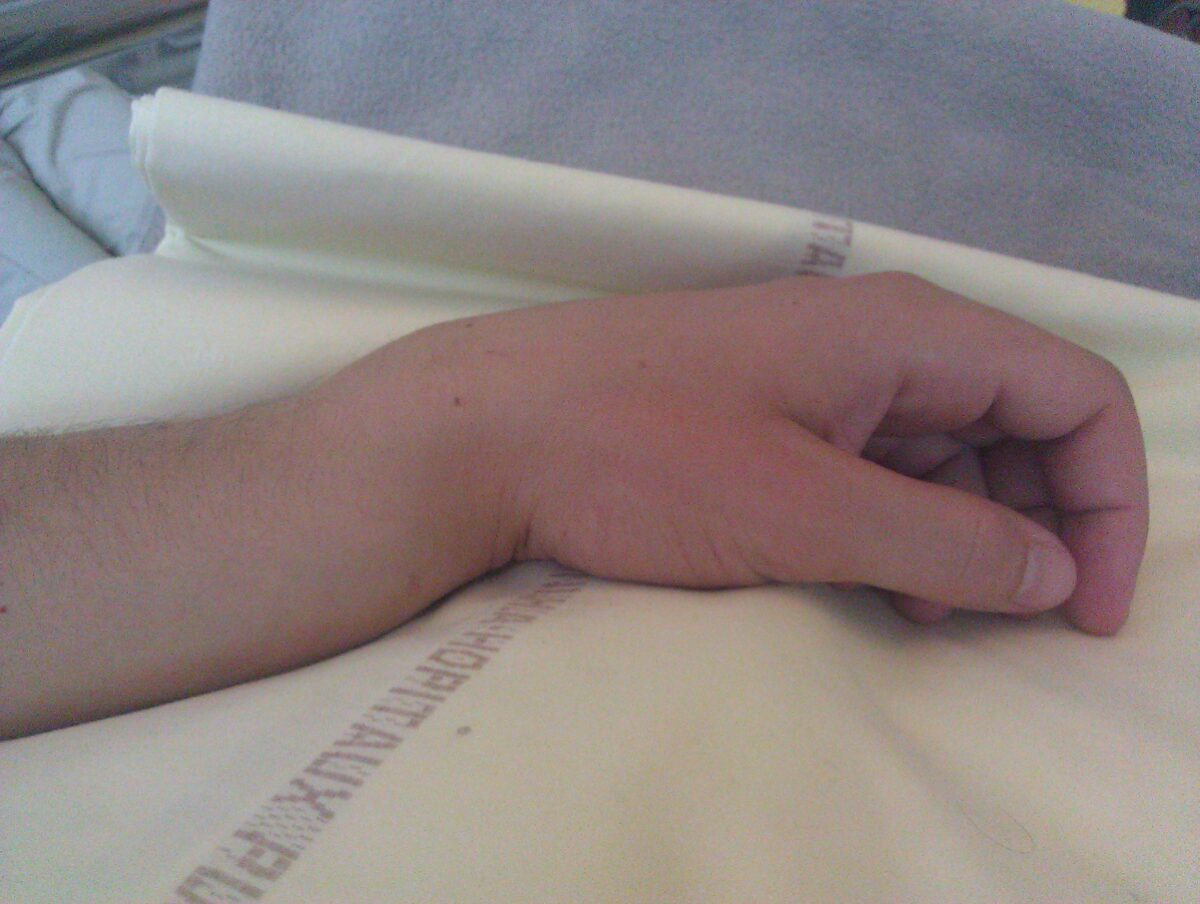
Colles fracture of the left hand:
Classic dinner fork deformity with posterior displacement clearly visible.
Diagnosis is clinical; however, imaging is needed for confirmation and evaluation of severity.
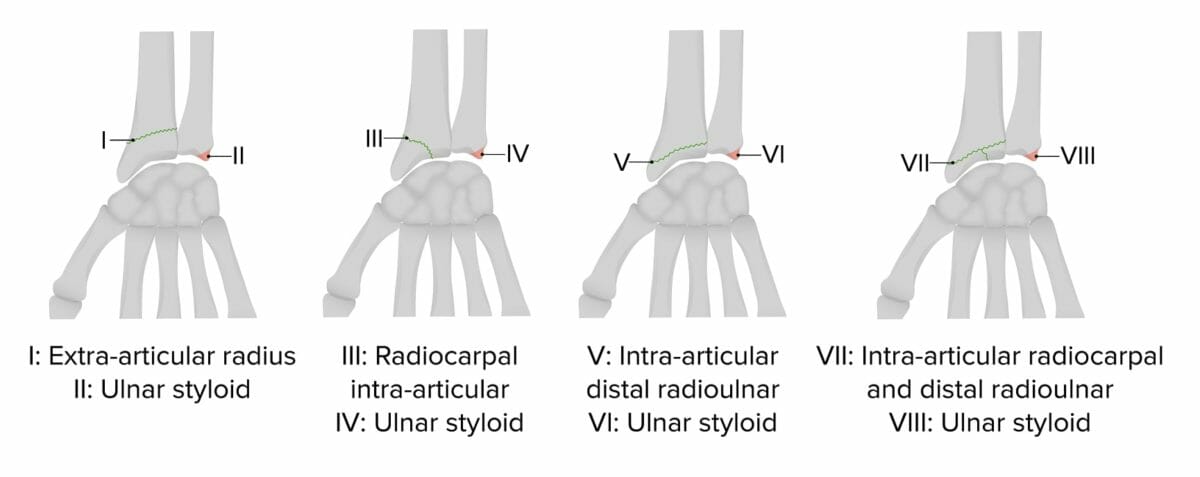
Frykman classification of distal radius fractures
Image by Lecturio.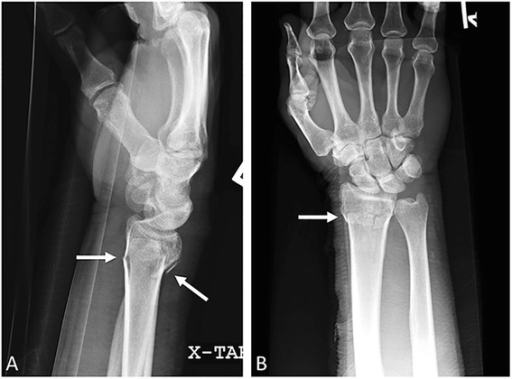
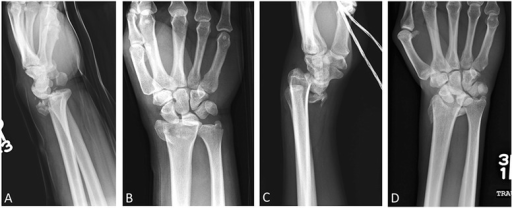
Colles fracture:
Lateral (a) and anteroposterior (b) wrist radiographs. Shown is a transverse distal radial metaphyseal fracture (arrows) with no intraarticular extension.
Barton and reverse Barton fractures:
Lateral (a) and anteroposterior (b) right wrist radiographs. Shown is a comminuted oblique intraarticular fracture with dorsal migration of the carpus, consistent with Barton fracture.
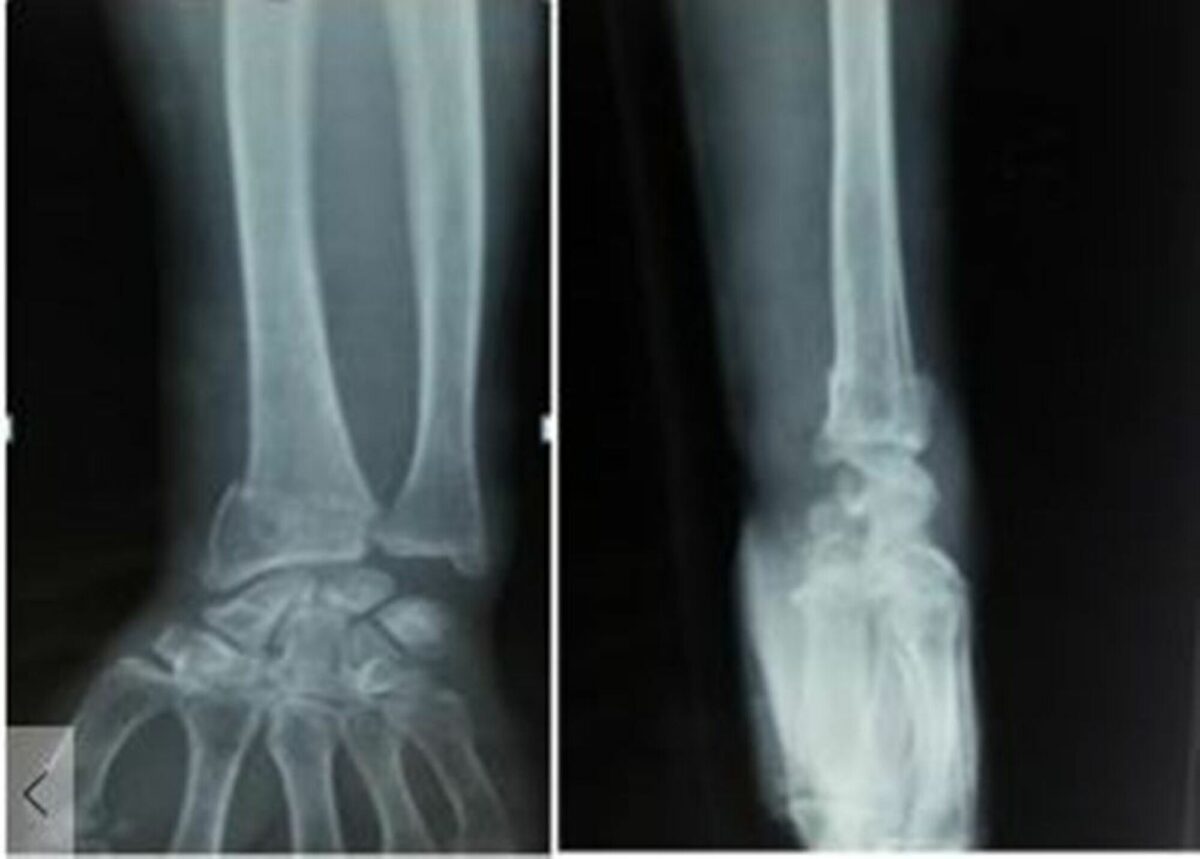
Radiographs (anteroposterior and lateral views) showing distal radius fracture
Image: “Radiographs anteroposterior and lateral view showing distal radius fracture” by Panthi S, et al. License: CC BY 3.0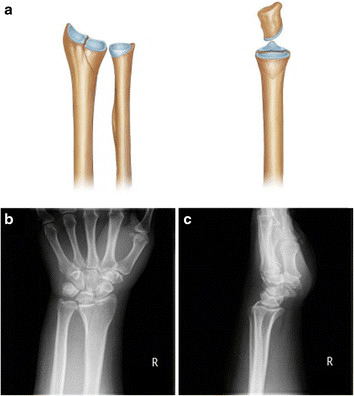
Die-punch fracture of the radius shows a vertical depression fracture:
a: The entire lunate fossa is vertically depressed (left, anterior view; right, lateral view).
b and c: Anteroposterior (left) and lateral (right) radiographs
Management, whether nonsurgical or surgical, is based on the type of fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures (based on articular involvement and displacement Displacement The process by which an emotional or behavioral response that is appropriate for one situation appears in another situation for which it is inappropriate. Defense Mechanisms) and the age and activity level of the individual.
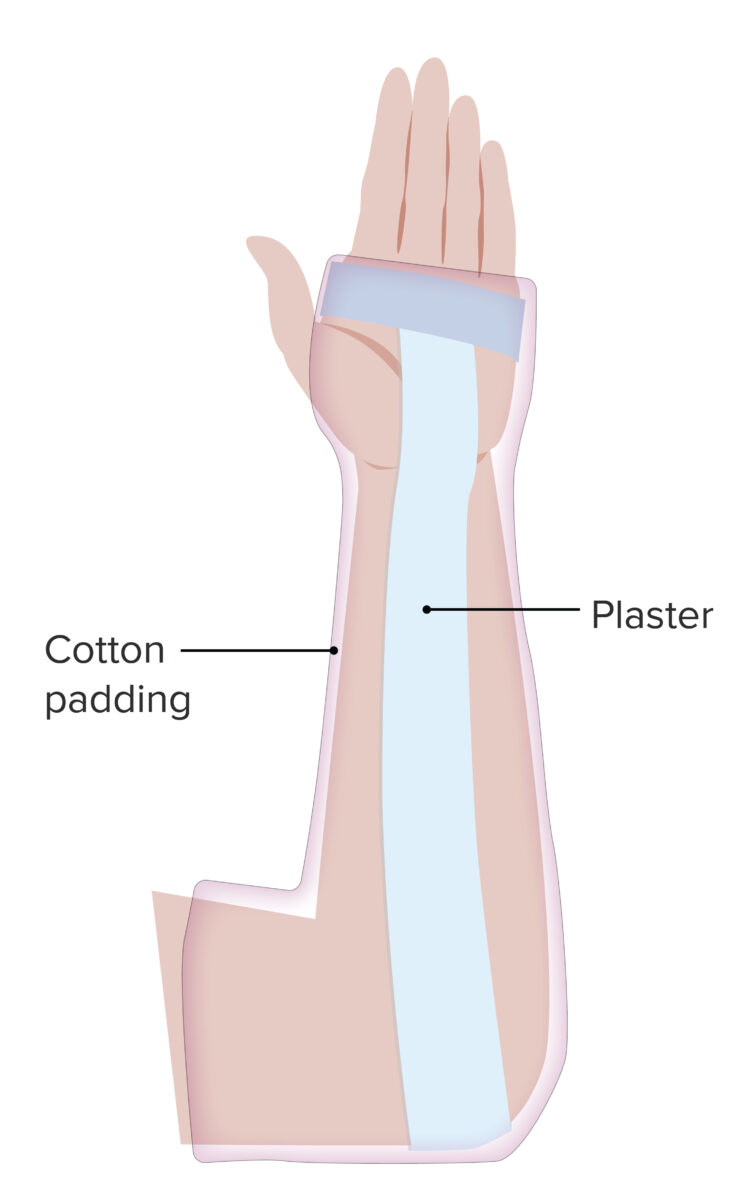
Forearm sugar tong splint:
A simple splint, the sugar tong splint is indicated in distal radius and ulnar fractures that are not displaced. The splint impedes pronation/supination and immobilizes the elbow joint.
Surgical management is indicated in the presence of: