Diphyllobothriasis is an intestinal parasitic infection caused by several cestodes in the genera Dibothriocephalus and Adenocephalus, previously classified as Diphyllobothrium (also known as “ fish FISH A type of in situ hybridization in which target sequences are stained with fluorescent dye so their location and size can be determined using fluorescence microscopy. This staining is sufficiently distinct that the hybridization signal can be seen both in metaphase spreads and in interphase nuclei. Chromosome Testing tapeworms” or “broad tapeworms”). Diphyllobothriasis is acquired by ingesting infective larvae Larvae Wormlike or grublike stage, following the egg in the life cycle of insects, worms, and other metamorphosing animals. Ascaris/Ascariasis in undercooked or raw fish FISH A type of in situ hybridization in which target sequences are stained with fluorescent dye so their location and size can be determined using fluorescence microscopy. This staining is sufficiently distinct that the hybridization signal can be seen both in metaphase spreads and in interphase nuclei. Chromosome Testing (e.g., salmon, trout). The clinical presentation of diphyllobothriasis varies from asymptomatic, nonspecific symptoms to intestinal obstruction Intestinal obstruction Any impairment, arrest, or reversal of the normal flow of intestinal contents toward the anal canal. Ascaris/Ascariasis, and/or vitamin B12 deficiency. Diagnosis is established by the identification Identification Defense Mechanisms of eggs or proglottids Proglottids Taenia/Taeniasis in the stool. Management includes anthelmintic therapy Anthelmintic therapy Agents that kill parasitic worms. They are used therapeutically in the treatment of helminthiasis in man and animal. Toxocariasis (e.g., praziquantel Praziquantel An anthelmintic used in most schistosome and many cestode infestations. Anthelmintic Drugs) and, if needed, vitamin B12 supplementation.
Last updated: Jan 26, 2025
Diphyllobothriasis, or Dibothriocephalus infection, is caused by a parasitic infection from cestodes (tapeworms) in the genera Dibothriocephalus and Adenocephalus.
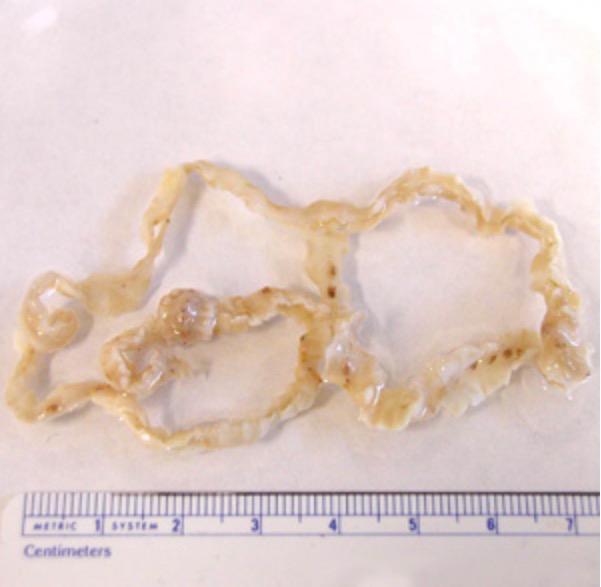
Adult Dibothriocephalus latus tapeworm
Image: “Dibothriocephalus latus with ruler” by CDC. License: CC BY 3.0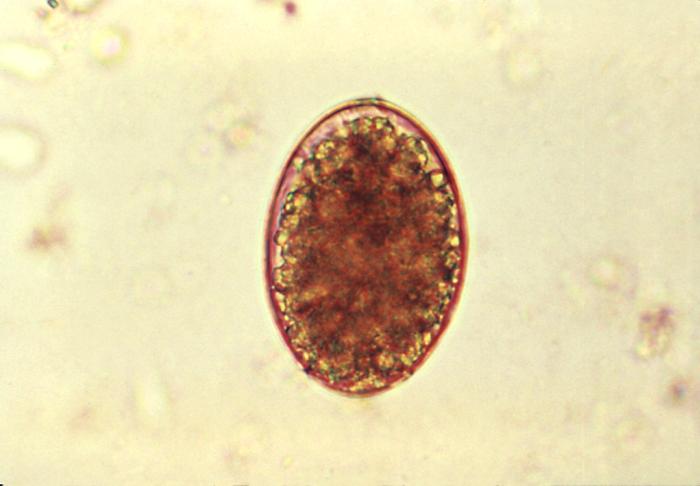
Photomicrograph of a Dibothriocephalus latus egg:
The eggs are ellipsoidal or oval.
Definitive hosts:
Intermediate hosts:
Diphyllobothriasis is transmitted through the consumption of raw or undercooked fish FISH A type of in situ hybridization in which target sequences are stained with fluorescent dye so their location and size can be determined using fluorescence microscopy. This staining is sufficiently distinct that the hybridization signal can be seen both in metaphase spreads and in interphase nuclei. Chromosome Testing.
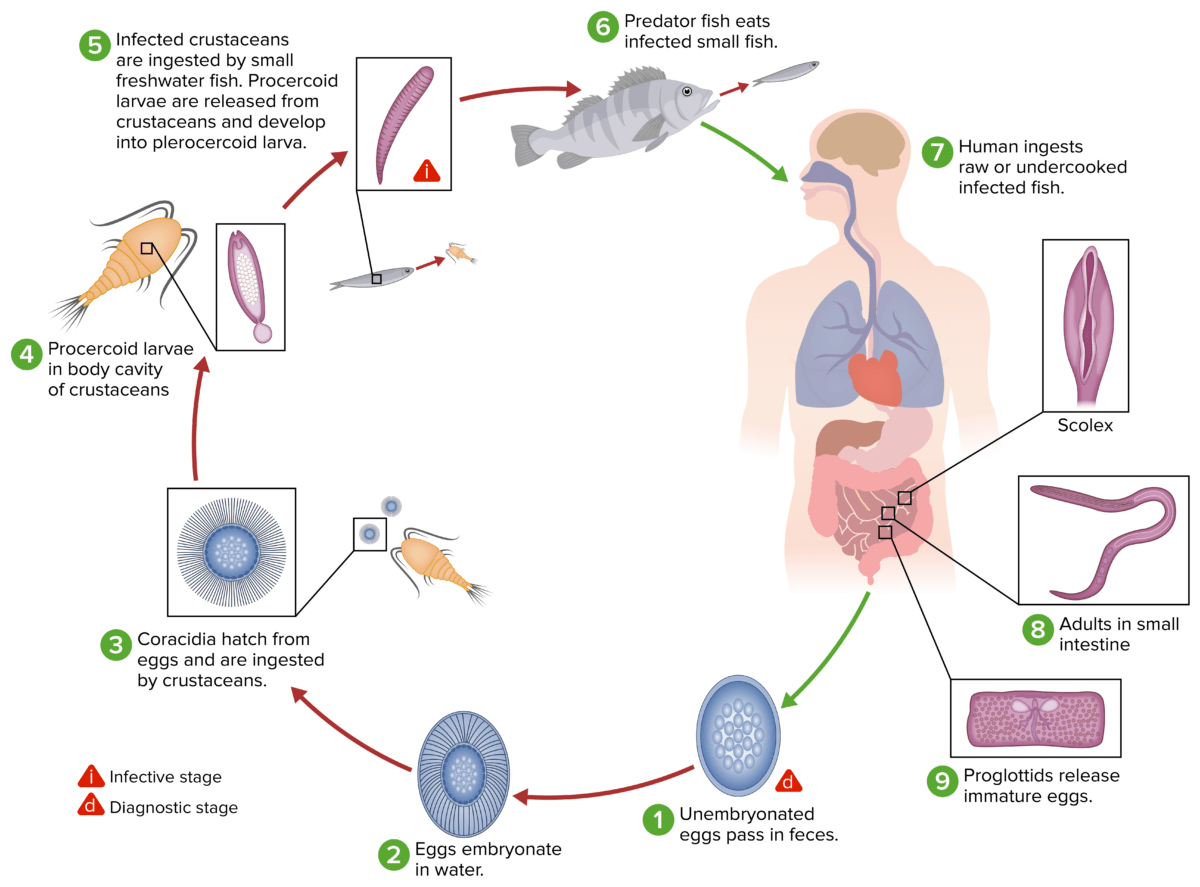
The life cycle of species of Dibothriocephalus, the causal agents of the disease diphyllobothriasis
The following may be caused by heavy infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease or aberrant migration of the tapeworms:
| Organism | Dibothriocephalus latus | Taenia Taenia Taenia belong to the Cestoda class of helminths. Humans are infected with these tapeworms by eating undercooked beef (T. saginata) or pork (T. solium and T. asiatica). Taeniasis is often asymptomatic, but the ingestion of larvae can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea, and constipation or diarrhea. Taenia/Taeniasis saginata | Echinococcus Echinococcus Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus tapeworms. Infection most often occurs from the ingestion of Echinococcus eggs in food or water contaminated with dog feces. Signs and symptoms are caused by hydatid cyst development in visceral organs and depend on the species. Echinococcus/Echinococcosis granulosus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics |
|
|
|
| Transmission | Eating raw, infected fish FISH A type of in situ hybridization in which target sequences are stained with fluorescent dye so their location and size can be determined using fluorescence microscopy. This staining is sufficiently distinct that the hybridization signal can be seen both in metaphase spreads and in interphase nuclei. Chromosome Testing | Eating raw, infected beef | Fecal to oral (ingestion of contaminated food or water) |
| Disease | Diphyllobothriasis | Taeniasis Taeniasis Taenia belong to the Cestoda class of helminths. Humans are infected with these tapeworms by eating undercooked beef (T. saginata) or pork (T. solium and T. asiatica). Taeniasis is often asymptomatic, but the ingestion of larvae can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea, and constipation or diarrhea. Taenia/Taeniasis | Cystic echinococcosis Cystic Echinococcosis Echinococcus/Echinococcosis |
| Clinical |
|
|
Depends on location and size of hydatid cysts Cysts Any fluid-filled closed cavity or sac that is lined by an epithelium. Cysts can be of normal, abnormal, non-neoplastic, or neoplastic tissues. Fibrocystic Change |
| Diagnosis | Eggs or proglottids Proglottids Taenia/Taeniasis in stool | Eggs or proglottids Proglottids Taenia/Taeniasis in stool |
|
| Management |
|
|
|
| Prevention |
|
Cook beef thoroughly. |
|
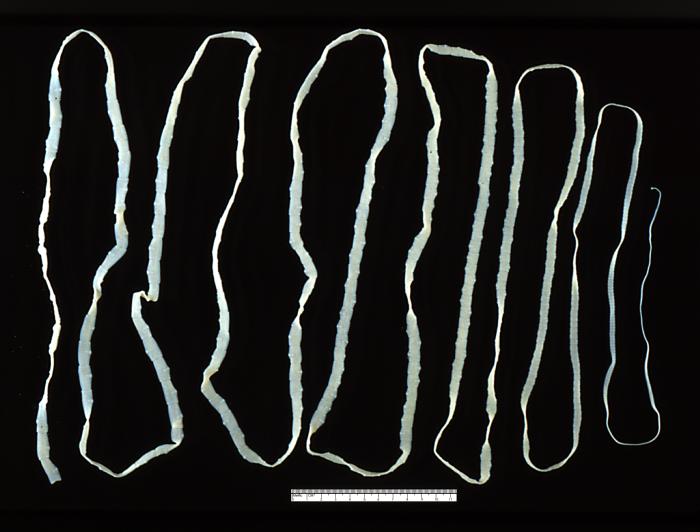
Adult Taenia saginata tapeworm measuring approximately 4 meters in length
Image: “ 5260” by CDC. License: Public Domain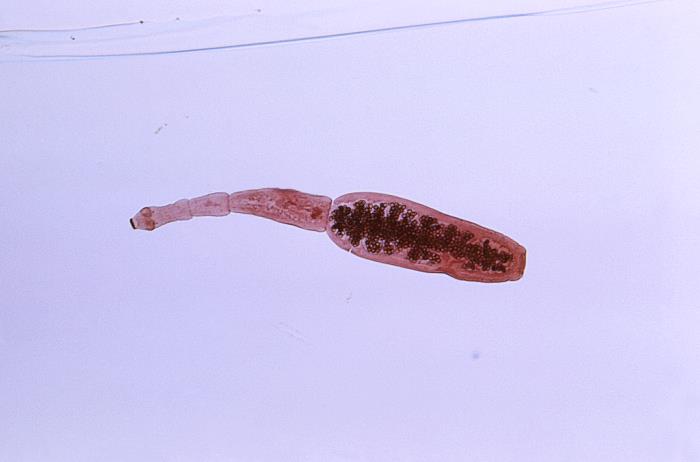
Photomicrograph showing the morphology of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus:
Note the head on the left and the scolex with hook-rimmed rostellum.