Carbohydrates store energy and are 1 of the 3 primary macronutrients (in addition to proteins and lipids). Carbohydrates are present in numerous foods, such as grains, fruits, legumes, and many vegetables. Polysaccharides, mostly in the form of starch, are the main dietary source of carbohydrates for humans. To be used as energy by humans, most carbohydrates must be digested (broken down) into monosaccharides that can be absorbed and then metabolized. The digestion of carbohydrates begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylases. The remaining starch is further broken down by pancreatic amylase and brush border enzymes in the intestines. The oxidation of 1 g of carbohydrate provides 4 kcal of energy.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
| Name | Definition | Examples in humans |
|---|---|---|
| Monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates | Molecules consisting of a single sugar group |
|
| Disaccharides Disaccharides Oligosaccharides containing two monosaccharide units linked by a glycosidic bond. Basics of Carbohydrates | A combination of 2 monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates |
|
| Oligosaccharides Oligosaccharides Carbohydrates consisting of between two (disaccharides) and ten monosaccharides connected by either an alpha- or beta-glycosidic link. They are found throughout nature in both the free and bound form. Basics of Carbohydrates | A combination of 3‒10 monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates | Usually attached to:
|
| Polysaccharides Polysaccharides Basics of Carbohydrates | A combination of > 10 monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates |
|
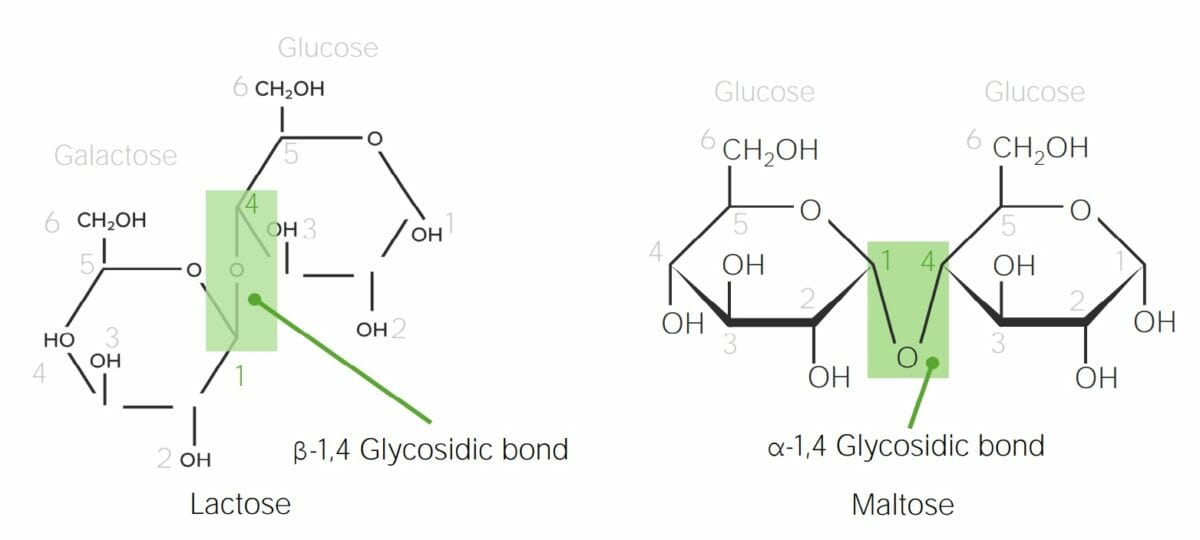
Chemical structure of lactose and maltose demonstrating α versus β glycosidic bonds:
In lactose, the anomeric carbon in galactose (C1) is in the β configuration (the hydroxyl group points up); therefore, when galactose bonds with the C4 in glucose, a β-1,4-glycosidic bond is formed. Maltose is made up of 2 glucose molecules. The anomeric carbon in glucose (C1) is the α configuration (the hydroxyl group points down); therefore, the bond in maltose is an α-1,4-glycosidic bond between 2 glucose molecules.
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates A class of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of cn(H2O)n. The largest class of organic compounds, including starch; glycogen; cellulose; polysaccharides; and simple monosaccharides. Basics of Carbohydrates are primarily digested by amylases and brush border enzymes Brush border enzymes Digestion and Absorption. Carbohydrates Carbohydrates A class of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of cn(H2O)n. The largest class of organic compounds, including starch; glycogen; cellulose; polysaccharides; and simple monosaccharides. Basics of Carbohydrates can only be absorbed as monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates, so these enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body’s constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes break large starch molecules all the way down into single monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates.
Note: Many dietary carbohydrates Carbohydrates A class of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of cn(H2O)n. The largest class of organic compounds, including starch; glycogen; cellulose; polysaccharides; and simple monosaccharides. Basics of Carbohydrates are in the form of starch, which is a mixture of amylose and amylopectin (both are made entirely of glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance molecules):
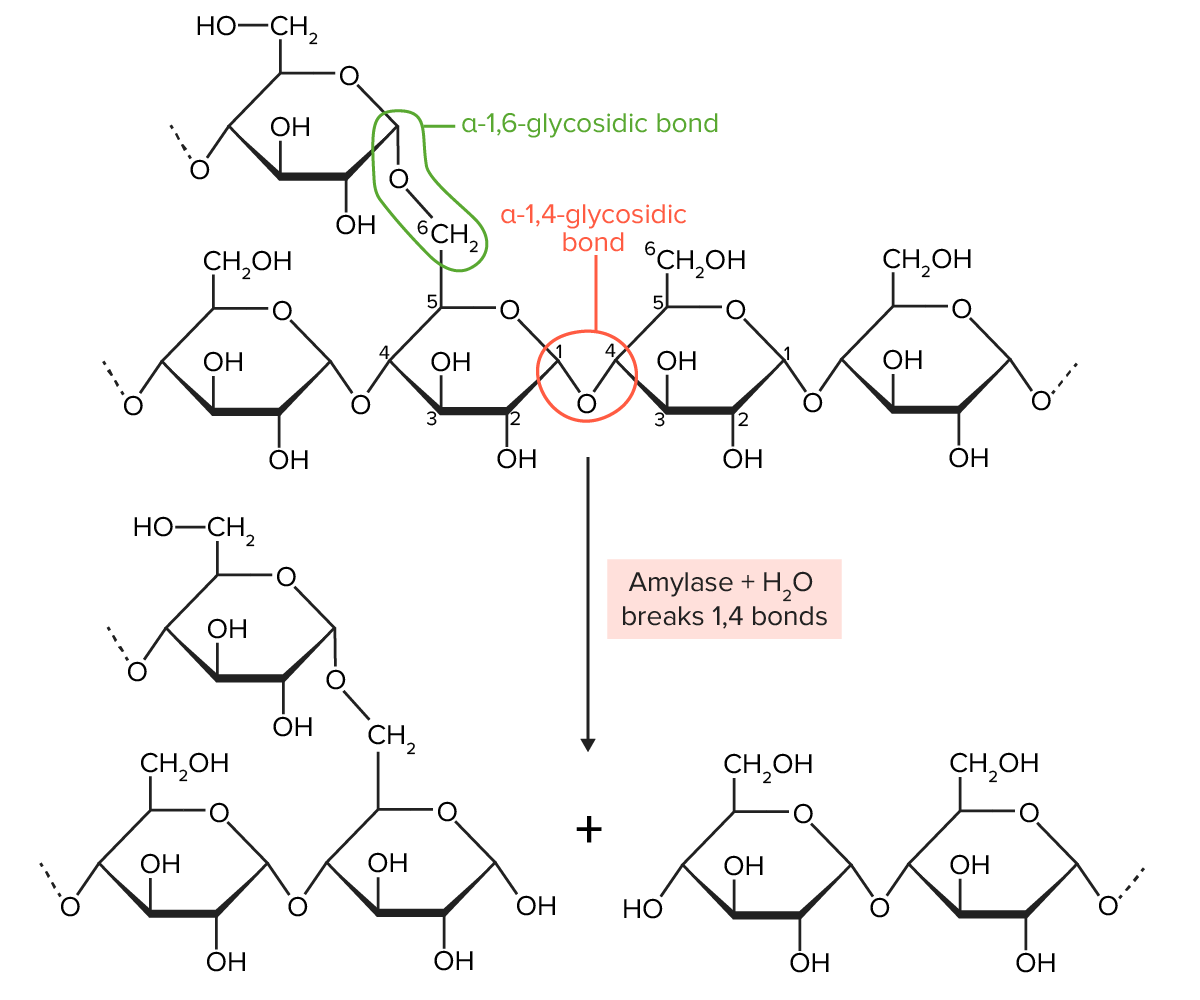
Amylopectin is partially digested by amylase. Amylopectin molecules are chains of glucose, joined together by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds (create a straight chain of glucose molecules) and α-1,6-glycosidic bonds (create a branch off the straight chain). Amylase breaks the α-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
Image by Lecturio.Brush border enzymes Brush border enzymes Digestion and Absorption are membrane-bound proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis on the luminal surface of enterocytes in the small intestine Small intestine The small intestine is the longest part of the GI tract, extending from the pyloric orifice of the stomach to the ileocecal junction. The small intestine is the major organ responsible for chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients. It is divided into 3 segments: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. Small Intestine: Anatomy. There are 4 major brush-border enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body’s constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion Digestion Digestion refers to the process of the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller particles, which can then be absorbed and utilized by the body. Digestion and Absorption.
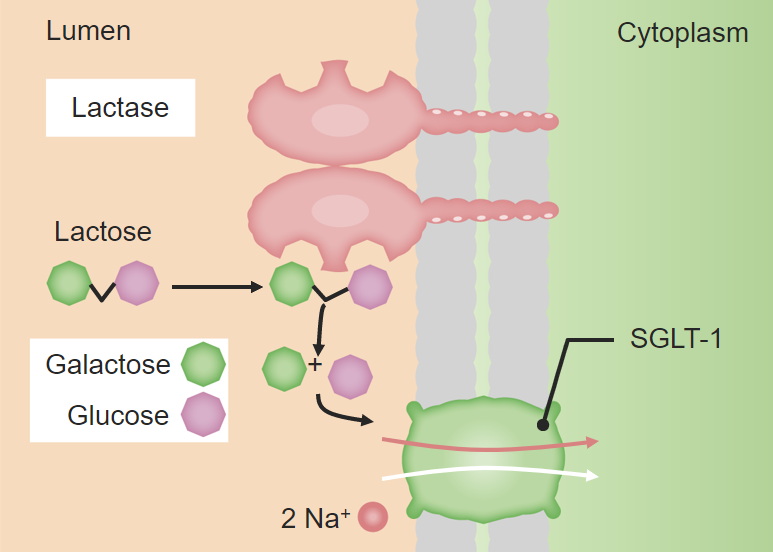
Brush border digestion:
Diagram of the disaccharide lactose being hydrolyzed into constituent monosaccharides (galactose and glucose) in order to be absorbed by the enterocytes. The brush border is used in the digestion of many other disaccharides.
SGLT1: sodium–glucose-linked transporter 1
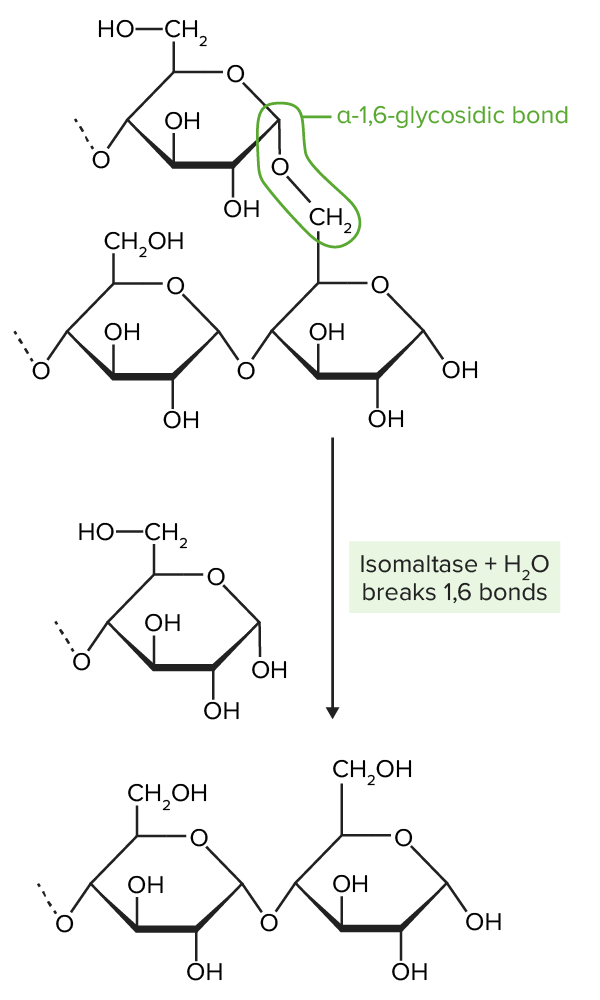
Isomaltase breaks the α-1,6-glycosidic bonds present in amylopectin. α-1,6-glycosidic bonds create branches off of “straight chains” of glucose by joining the 1st carbon on one chain (top ring structure) to the 6th carbon on another chain (bottom 2-ring structure). Isomaltase hydrolizes these bonds.
Image by Lecturio.After digestion Digestion Digestion refers to the process of the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller particles, which can then be absorbed and utilized by the body. Digestion and Absorption, carbohydrates Carbohydrates A class of organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of cn(H2O)n. The largest class of organic compounds, including starch; glycogen; cellulose; polysaccharides; and simple monosaccharides. Basics of Carbohydrates are absorbed and transported via the blood to the portal circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment. Transport may be either an active, facilitated, or passive mechanism.
Transporters have specific roles, and their functions may be active, facilitated, or passive.
Passive glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption represents a minority of absorptive capabilities. Most absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption occurs in the 1st part of the small intestine Small intestine The small intestine is the longest part of the GI tract, extending from the pyloric orifice of the stomach to the ileocecal junction. The small intestine is the major organ responsible for chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients. It is divided into 3 segments: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. Small Intestine: Anatomy ( duodenum Duodenum The shortest and widest portion of the small intestine adjacent to the pylorus of the stomach. It is named for having the length equal to about the width of 12 fingers. Small Intestine: Anatomy, jejunum Jejunum The middle portion of the small intestine, between duodenum and ileum. It represents about 2/5 of the remaining portion of the small intestine below duodenum. Small Intestine: Anatomy).
Order of events in monosaccharide absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption:
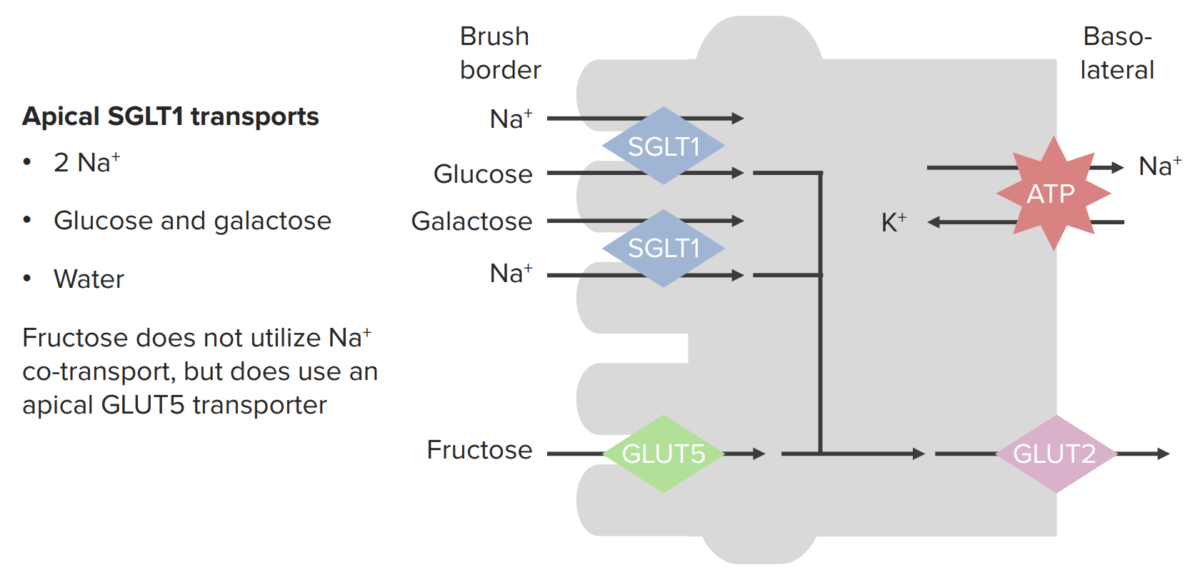
Absorption of monosaccharides across enterocytes
SGLT1: sodium–glucose-linked transporter
GLUT5: glucose transporter 5
GLUT2: glucose transporter 2
Once in the blood, monosaccharides Monosaccharides Single chain carbohydrates that are the most basic units of carbohydrates. They are typically colorless crystalline substances with a sweet taste and have the same general formula CNH2NON. Basics of Carbohydrates are transported to cells throughout the body and absorbed into peripheral cells by a number of different transporters. Several important glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance transporters include:
| Transporter | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| GLUT1 | Most human cells: RBC, CNS, cornea Cornea The transparent anterior portion of the fibrous coat of the eye consisting of five layers: stratified squamous corneal epithelium; bowman membrane; corneal stroma; descemet membrane; and mesenchymal corneal endothelium. It serves as the first refracting medium of the eye. Eye: Anatomy, placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity, fetal tissue |
|
| GLUT2 GLUT2 A glucose transport facilitator that is expressed primarily in pancreatic beta cells; liver; and kidneys. It may function as a glucose sensor to regulate insulin release and glucose homeostasis. Digestion and Absorption |
|
|
| GLUT3 |
|
|
| GLUT4 |
|
|
| GLUT5 GLUT5 A hexose transporter that mediates fructose transport in skeletal muscle and adipocytes and is responsible for luminal uptake of dietary fructose in the small intestine. Digestion and Absorption |
|
Transports fructose |
| SGLT1 | Apical membrane of enterocytes in small intestines | Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption of glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance and galactose Galactose An aldohexose that occurs naturally in the d-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins. Deficiency of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase causes an error in galactose metabolism called galactosemia, resulting in elevations of galactose in the blood. Lactose Intolerance from the gut lumen into enterocytes |
| SGLT2 | Proximal convoluted tubule Proximal convoluted tubule The renal tubule portion that extends from the bowman capsule in the kidney cortex into the kidney medulla. The proximal tubule consists of a convoluted proximal segment in the cortex, and a distal straight segment descending into the medulla where it forms the u-shaped loop of henle. Osmotic Diuretics |
|