Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (DPGN) is a histopathologic classification of glomerulonephritis (GN) characterized by an increased cellular proliferation affecting > 50% of the glomeruli. Mesangial, endothelial, and epithelial cells are notably increased. The most common causes are lupus nephritis class IV and IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions nephropathy. Individuals may present with symptoms related to the renal disease, such as fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children, hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, and edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema. Other manifestations related to the underlying disease can be present. Diagnosis is made by laboratory tests, renal imaging Renal imaging The renal system is composed of 2 kidneys, 2 ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. Varying conditions such as infections, cysts, solid masses, ischemia, and mechanical obstruction can affect the renal system. Evaluation of diseases rely on imaging methods such as radiography, ultrasonography, CT, and MRI. Some of these are also used to guide tissue sampling (e.g., renal biopsy). Imaging of the Urinary System, and renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis. Microscopic findings show hypercellularity of mesangial and endothelial cells, with capillary loop thickening. Early aggressive therapy is indicated and is based on the specific etiology.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (DPGN), a histopathologic classification of glomerulonephritis (GN) commonly associated with autoimmune diseases Autoimmune diseases Disorders that are characterized by the production of antibodies that react with host tissues or immune effector cells that are autoreactive to endogenous peptides. Selective IgA Deficiency, is characterized by an increased cellular proliferation affecting > 50% of the glomeruli.
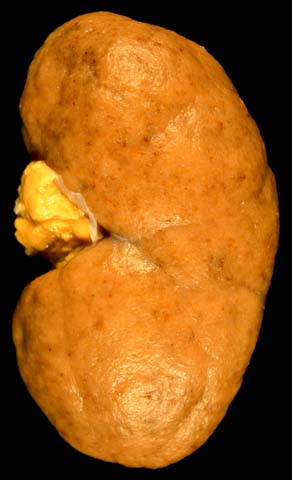
“Flea-bitten” appearance of the cortical surface of a kidney in diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis.
Image: “Diffuse Proliferative Lupus Nephritis class IV” by Ed Uthman. License: Public DomainPresentations vary considerably, with most symptoms occurring because of the decrease in GFR GFR The volume of water filtered out of plasma through glomerular capillary walls into Bowman’s capsules per unit of time. It is considered to be equivalent to inulin clearance. Kidney Function Tests caused by DPGN.

Hematuria:
Urine is dark or tea-colored
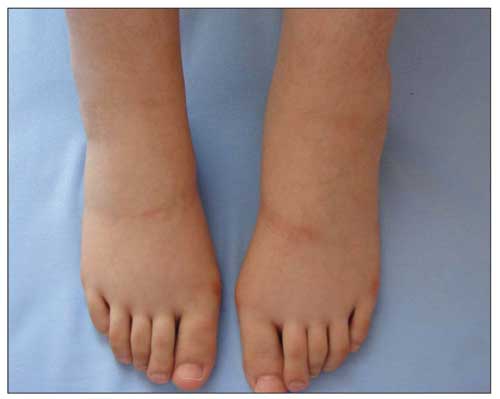
Lower-extremity edema
Image: “Lower extremity oedema 4 days after the initiation of insulin therapy” by Baş VN. License: CC BY 2.5Because DPGN is caused by another condition, the symptoms of the underlying cause are often present, such as in:
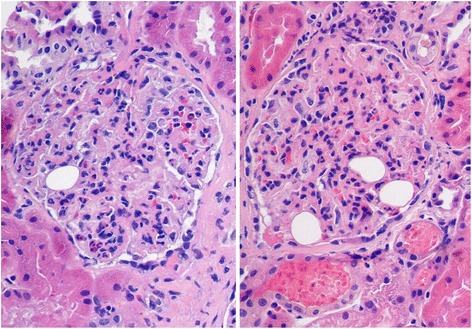
Histology for diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis with leukocytic infiltration
Image: “Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis with leukocytic infiltration” by Cannata-Ortiz P. License: CC BY 4.0To reduce progression of renal disease, management will vary depending on the underlying condition. Options are as follows: