Tinea infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are a group of diseases caused by fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology infecting keratinized tissue (hair, nails, and skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions). These infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are termed dermatomycoses and are caused by the dermatophyte fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology. There are approximately 40 dermatophyte fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology that are part of 3 genera, including Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, and Microsporum. These infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease can affect any part of the body but occur most often in warm, moist regions like the groin Groin The external junctural region between the lower part of the abdomen and the thigh. Male Genitourinary Examination and the feet. The diagnosis is clinical with characteristic skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions findings, but it can be confirmed with microscopy of skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions scrapings. The treatment depends on the site and magnitude of infection but typically begins with topical antifungals like the -azole drugs and terbinafine Terbinafine In addition to the 3 other major classes of antifungal agents (azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins), several other clinically important antifungal agents are used, including flucytosine, griseofulvin, and terbinafine. Terbinafine acts within the stratum corneum of the skin and are used to treat dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails. Flucytosine, Griseofulvin, and Terbinafine, and it may progress to oral versions of these medications if topical treatment fails.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Tinea infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are classified and named by the body region affected.
Signs and symptoms are similar between the tinea infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, with some minor differences depending on the body region affected. Lesions tend to be well-demarcated, annular Annular Dermatologic Examination, peripheral plaques with a rim of scale Scale Dermatologic Examination. They may also have associated erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion and/or maceration.
| Name | Body region | Etiology | Epidemiology and risk factors | Clinical features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinea pedis (“athlete’s foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Foot: Anatomy”) | Feet, interdigital spaces of toes |
|
|
|
| Tinea corporis (“ringworm”) | Trunk and extremities (excluding hands and feet) |
|
|
|
| Tinea cruris (“jock itch”) | Groin Groin The external junctural region between the lower part of the abdomen and the thigh. Male Genitourinary Examination, inguinal folds |
|
|
|
| Tinea unguium (onychomycosis) | Fingernails or toenails | T. rubrum |
|
|
| Tinea capitis | Hair follicles and scalp |
|
|
|
| Majocchi granuloma (fungal folliculitis) | Hair follicles on the body | T. rubrum |
|
|
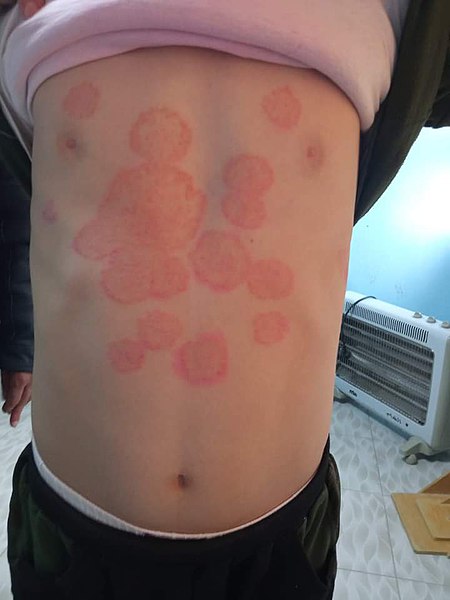
Tinea corporis, “ringworm” on a child:
Infection is most commonly due to Trichophyton rubrum, which presents with pruritic, erythematous, circular plaques with peripheral scales and central clearing.
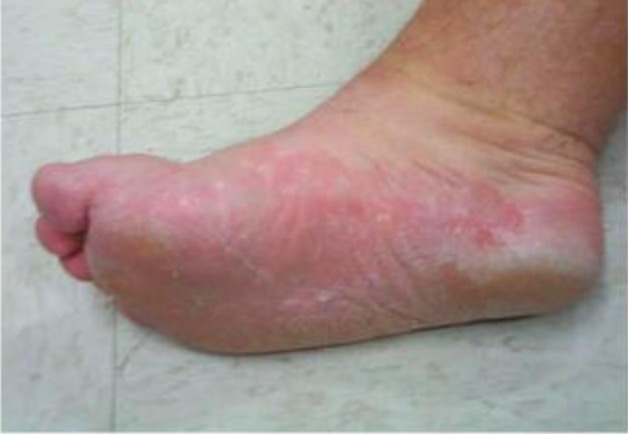
Tinea pedis:
Infection is most commonly due to Trichophyton rubrum. The hyperkeratotic form presents with scaling in a “moccasin” distribution.
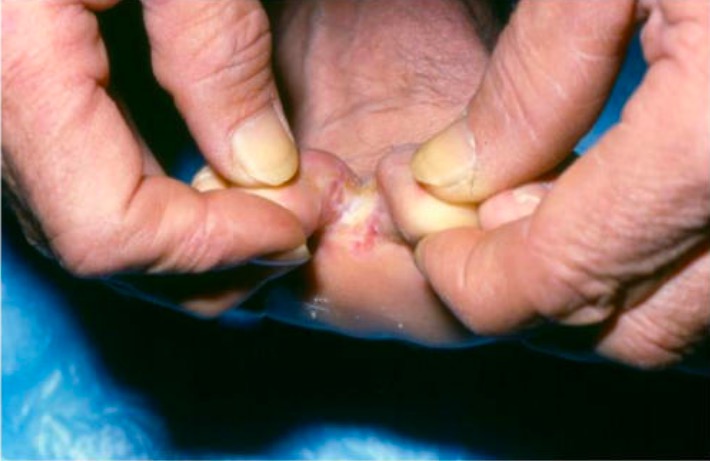
Tinea pedis:
Infection is most commonly due to Trichophyton rubrum. The interdigital form presents with pruritic, scaly macerations in the interdigital webs of the toes.
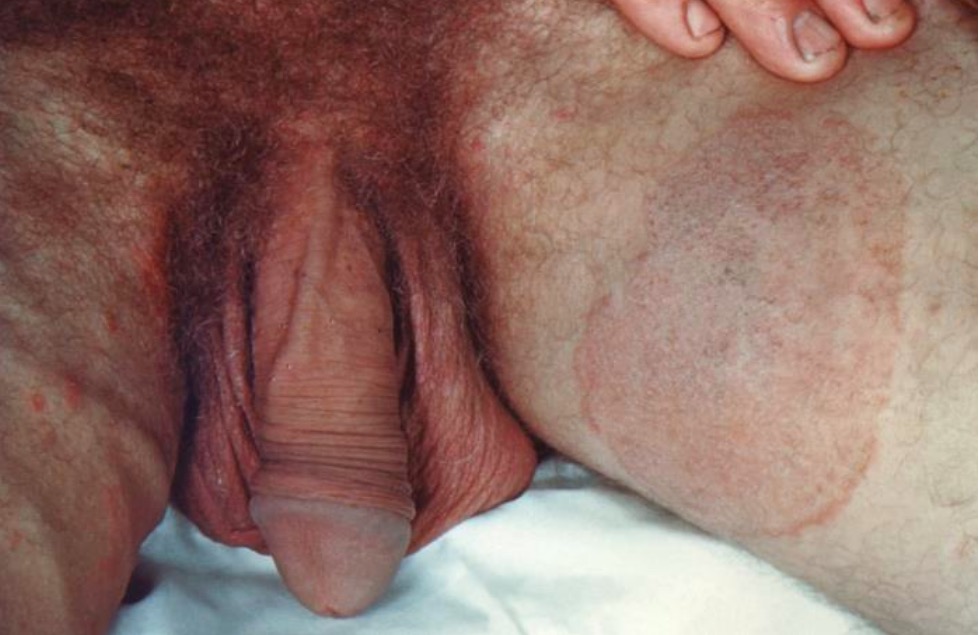
Tinea cruris, “jock itch”:
This infection is most commonly caused by Epidermophyton floccosum and presents with pruritic, erythematous plaque-like lesions in the groin that spare the scrotum.
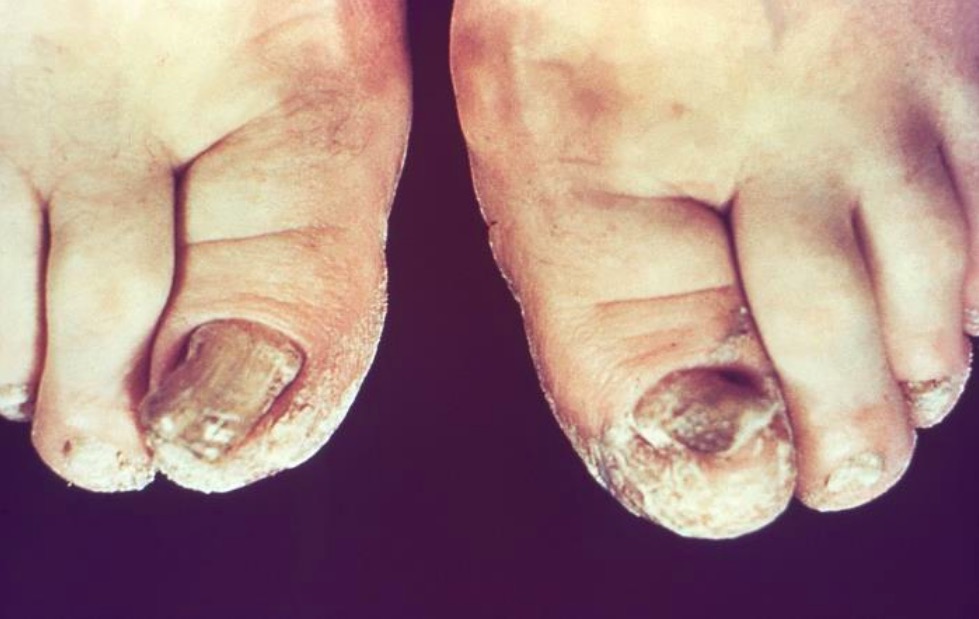
Tinea unguium (dermatophyte onychomycosis):
This infection is commonly caused by Trichophyton rubrum and presents with discoloration, thickening, and dystrophy of the toenails, often with subungual debris.
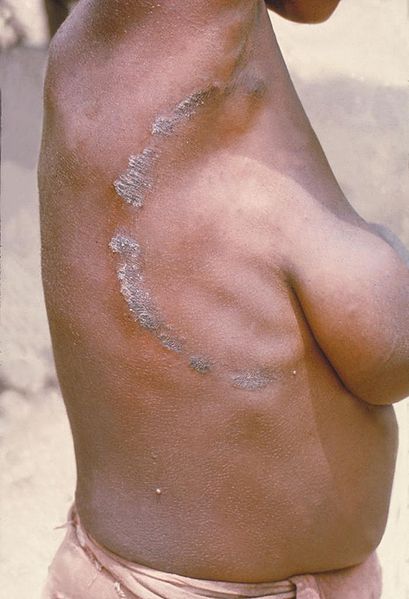
Tinea corporis, “ringworm” on an adult:
Infection is most commonly due to Trichophyton rubrum and presents with pruritic, erythematous, circular plaques with peripheral scales and central clearing.
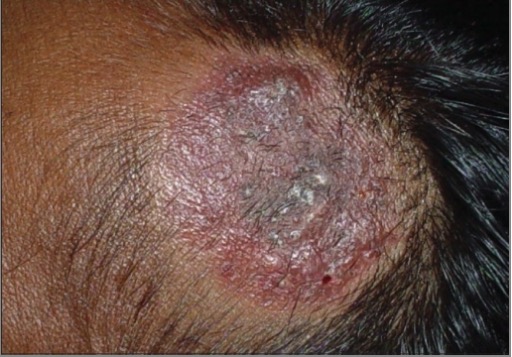
Kerion
Image: “ Trichomycoses” by Department of Dermatology, Madras Medical College (Retd.), Chennai – 600 003, India. License: CC BY 2.0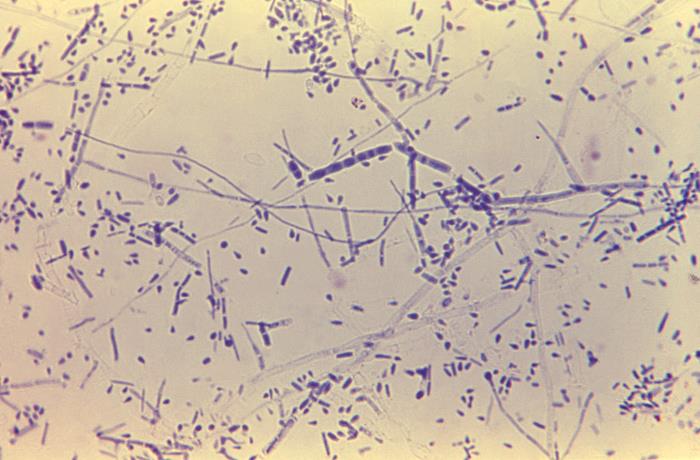
Trichophyton rubrum: This 475× magnification of T. rubrum shows centrally grouped, elongated macroconidia with septations. There are also many microconidia in the shape of teardrops.
Image: “Trichophyton rubrum” by CDC/Dr. Lucille K. Georg. License: Public Domain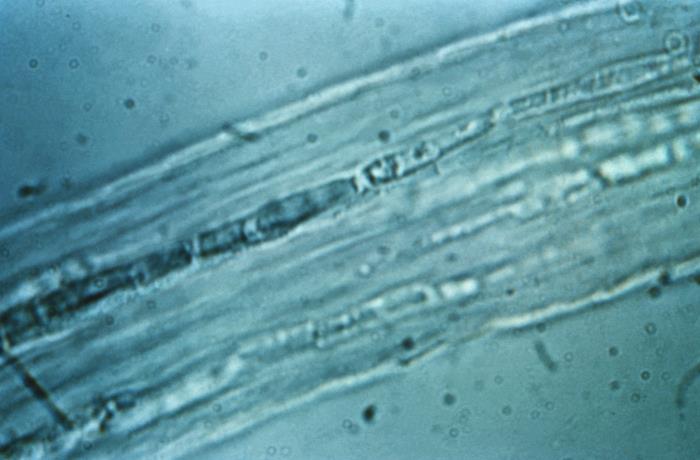
Endothrix infection: Microsporum visible within a hair follicle shaft
Image: “Microsporum” by CDC/Dr. Lucille K. Georg. License: Public DomainAll variants of tinea are treated with antifungals.