Decompression sickness (DCS), known informally as “the bends,” is a condition caused by compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma and decompression of gases contained in the body during descent and rapid ascent while diving. Clinical presentation of DCS may be nonspecific and variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, with a time of onset that can vary from immediately to 12 hours after surfacing. Diagnosis is made clinically. Management is early supportive therapy and hyperbaric recompression treatment carried out in a specialized facility.
Last updated: Apr 4, 2025
Decompression sickness (DCS) comprises varied symptoms caused by gas bubbles that come out of solution in the body after ascending from a deep dive.
Based on severity of symptoms and location of gas bubbles:
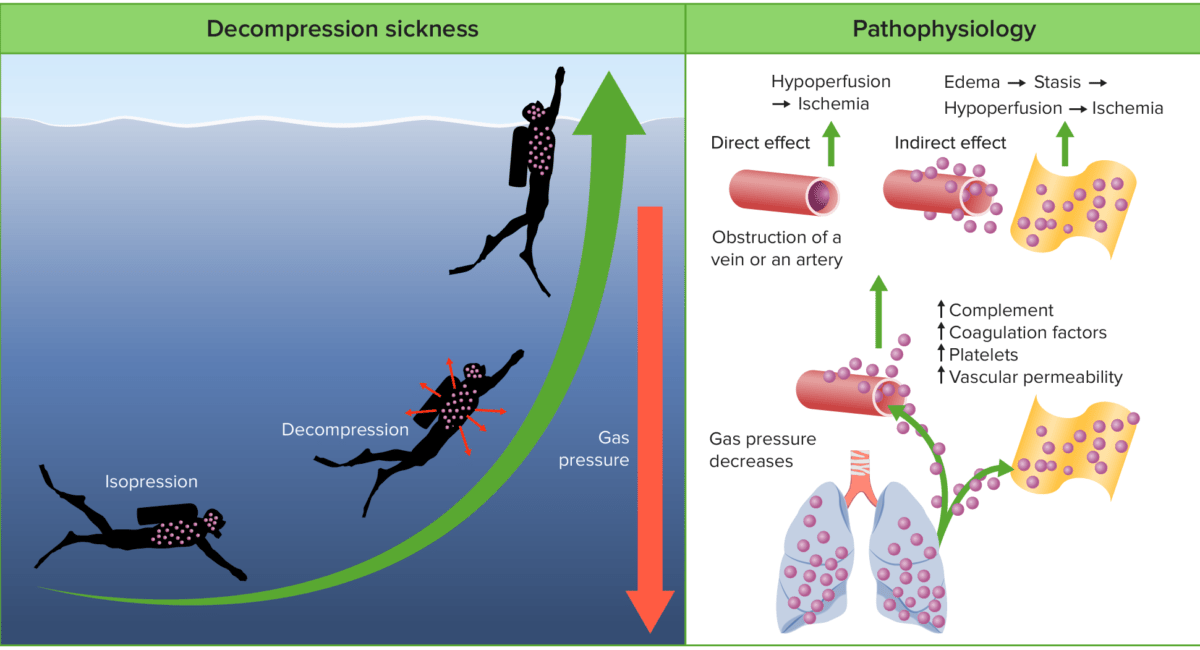
Pathophysiology of decompression sickness:
During descent, the increased pressure results in gases dissolving into the body’s tissues and blood. During decompression, the tissues become supersaturated with these gases, resulting in the formation of free gas. These bubbles of gas can be filtered in the pulmonary capillaries in small quantities. However, in large quantities, the gases can cause direct vascular obstruction, the activation of platelets and coagulation cascades, capillary leakage, and inflammatory responses.
| Neurologic: cerebral |
|
|---|---|
| Neurologic: spinal |
|
| Neurologic: vestibulocochlear |
|
| Neurologic: peripheral | Patchy nondermatomal sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology disturbance |
| Musculoskeletal | Joint pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways (“the bends”) |
| Ocular |
|
| Pulmonary | |
| Cardiovascular |
|
| Cutaneous |
|
| Lymphatic | Soft tissue Soft Tissue Soft Tissue Abscess edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema |
| Constitutional | Fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia and malaise Malaise Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus |
Diagnosis is based on:
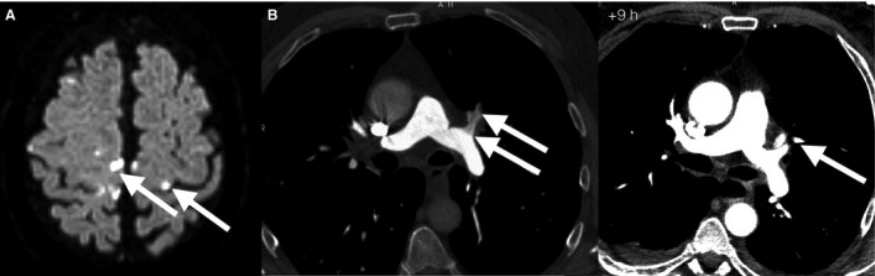
A 61‐year‐old experienced male diver presenting with a diagnosis of DCS:
(A) MRI of the head showing multiple cerebral thromboembolisms.
(B) CT scan of the chest 6 hours after the first symptoms showing multiple pulmonary thromboembolisms of the segmental arteries.
Follow‐up CT scans of the chest 9 hours later: no pulmonary thromboembolism of the same segmental arteries.
The main goal of therapy is to dissolve bubbles and recompress gas in body fluids.
The following conditions greatly increase the likelihood of developing decompression sickness: