Cystoisospora and Cyclospora are genera within the Coccidia subclass of protozoans Protozoans Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic. These single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites cause intestinal infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease in humans. Humans are the only host for these species, and they are both transmitted through the fecal–oral route. The symptoms of cystoisosporiasis and cyclosporiasis are watery diarrhea Watery diarrhea Rotavirus, abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen, and fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever. Severe cystoisosporiasis can occur in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals, particularly those with HIV HIV Anti-HIV Drugs/AIDS, and can lead to malabsorption Malabsorption General term for a group of malnutrition syndromes caused by failure of normal intestinal absorption of nutrients. Malabsorption and Maldigestion, weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery, and dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration. Both diseases are self-limited in immunocompetent individuals, though cyclosporiasis has a longer course. Diagnosis is made by identifying the oocysts in stool samples. Antimicrobial therapy, such as trimethoprim Trimethoprim The sulfonamides are a class of antimicrobial drugs inhibiting folic acid synthesize in pathogens. The prototypical drug in the class is sulfamethoxazole. Although not technically sulfonamides, trimethoprim, dapsone, and pyrimethamine are also important antimicrobial agents inhibiting folic acid synthesis. The agents are often combined with sulfonamides, resulting in a synergistic effect. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim– sulfamethoxazole Sulfamethoxazole A bacteriostatic antibacterial agent that interferes with folic acid synthesis in susceptible bacteria. Its broad spectrum of activity has been limited by the development of resistance. Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim, can be used (particularly in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Both organisms cause intestinal disease in humans.
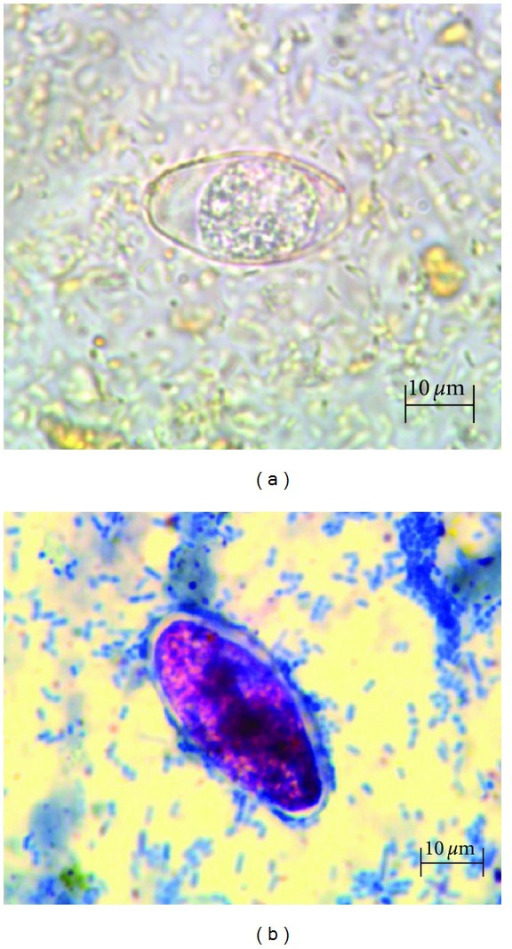
Microscopic images of Cystoisospora:
(a): Cystoisospora belli on saline mount
(b): Cystoisospora belli on modified acid-fast stain
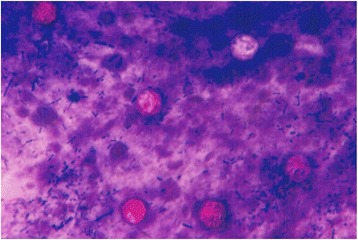
Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts from fecal smear stained by the acid-fast method
Image: “Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts” by Kaminsky RG et al. License: CC BY 4.0Cystoisospora:
Cyclospora:
Both species are found only in humans.
Cystoisospora (severe disease):
Cyclospora:
Both species are transmitted via the fecal–oral route (ingestion of contaminated food and water).
Cystoisospora and Cyclospora undergo a similar life cycle:
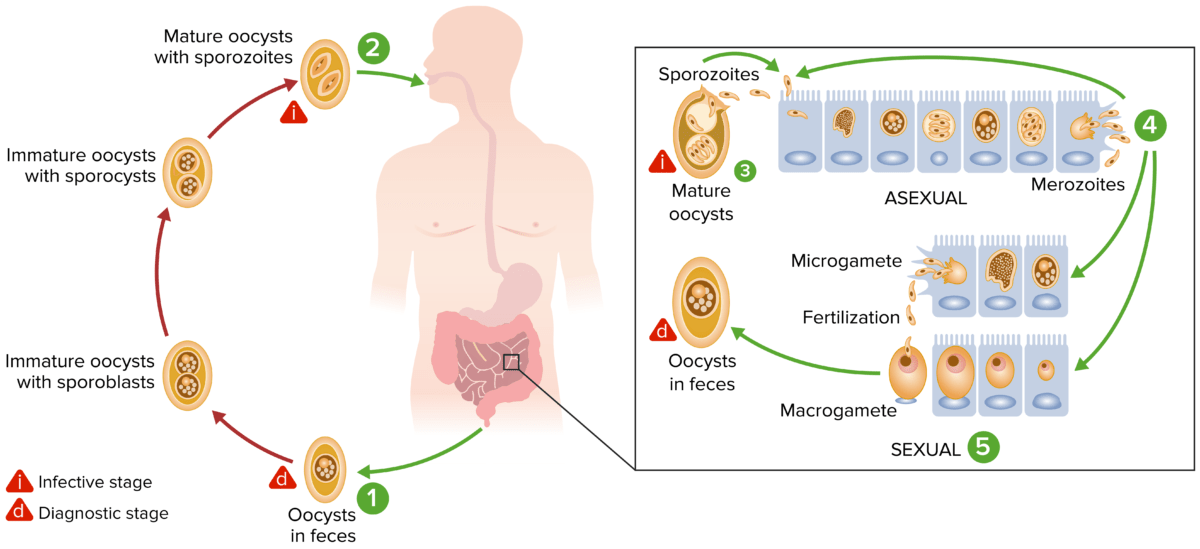
Cystoisospora belli life cycle. Ingestion of mature oocytes allows for the parasite to invade small intestine epithelial cells. There, it continues its life cycle and reproduces. Immature oocytes are excreted in the feces and mature in the environment, allowing for the cycle to continue.
Image by Lecturio.
A diagram of the life cycle of Cyclospora cayetanensis
Image by Lecturio.Cystoisosporiasis has an incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus period of 7–14 days. Presentation of the disease can vary depending on the individual’s immune status.
Cyclosporiasis has an incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus period of approximately 7 days.
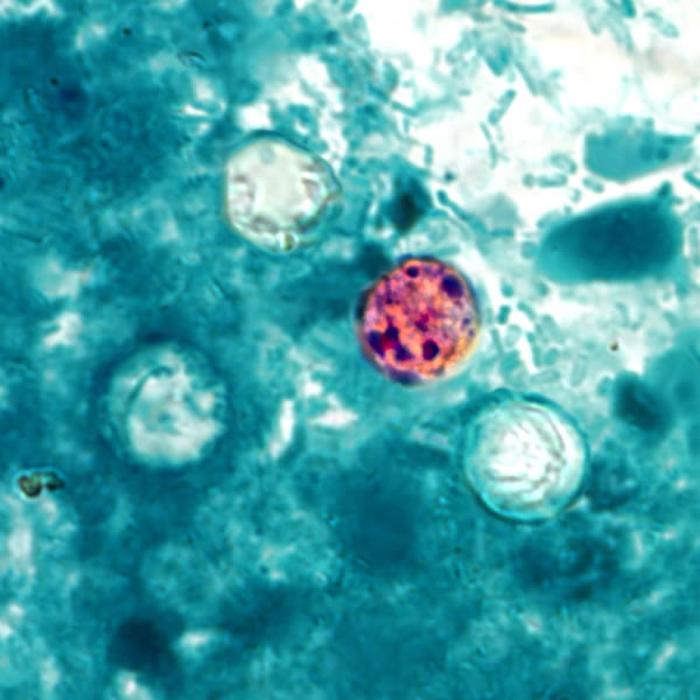
Photomicrograph of Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts in a stool sample found using a modified acid-fast stain
Image: “Cyclospora cayetanensis” by CDC. License: Public DomainAntimicrobials used for the treatment of cyclosporiasis include: