Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome is an intracellular protozoan and an important cause of infectious diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea. Infection is transmitted by the fecal–oral route and caused by ingestion of Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome oocysts; the most common source of outbreaks Outbreaks Sudden increase in the incidence of a disease. The concept includes epidemics and pandemics. Influenza Viruses/Influenza is contaminated water. Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome affects intestinal epithelial cells; infection presents as watery diarrhea Watery diarrhea Rotavirus, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, crampy abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen, and possibly fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever. The condition is typically self-limited (about 10‒14 days) in immunocompetent patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship, but it may be chronic and more severe in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship (possibly resulting in malabsorption Malabsorption General term for a group of malnutrition syndromes caused by failure of normal intestinal absorption of nutrients. Malabsorption and Maldigestion, dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration, and wasting). Cryptosporidiosis is one of the opportunistic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease that can occur in individuals with AIDS, resulting in AIDS cholangiopathy AIDS cholangiopathy AIDS-defining Conditions. Diagnosis involves microscopy, immunoassays Immunoassays Immunoassays are plate-based techniques that can detect and quantify many types of molecules through antibody-antigen reactions. An immunoassay typically involves an analyte, a targeted antibody, and labels. Classification of immunoassays is based on the type of label utilized, which includes enzymes (ELISA), light-emitting molecules/tracers (e.g., chemiluminescence and fluorescence immunoassays), and radioactive isotopes (radioimmunoassays). Immunoassays, or PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing of fecal samples. Management is primarily supportive, using the antiprotozoal Antiprotozoal Nitroimidazoles agent nitazoxanide in severe disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Transmission is by the fecal–oral route. Ingestion of Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome oocysts initiates infection. The different sources of transmission are:
Infection is initiated by the ingestion of fully sporulated and environment-resistant oocysts.
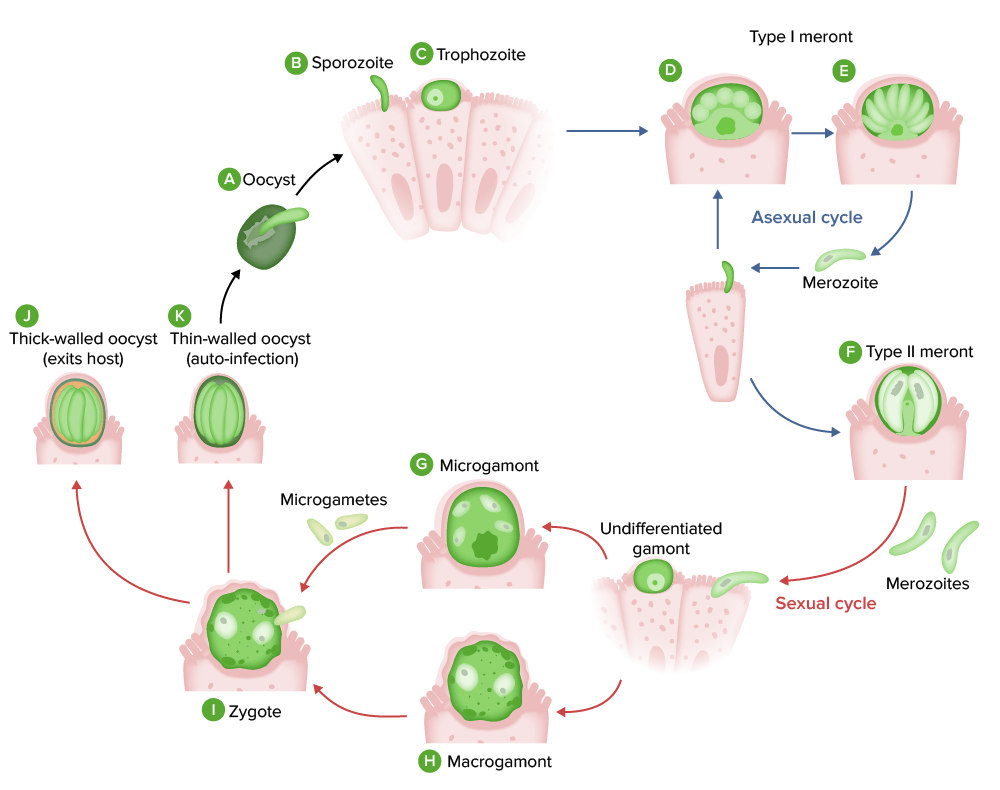
Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome causes secretory diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea associated with malabsorption Malabsorption General term for a group of malnutrition syndromes caused by failure of normal intestinal absorption of nutrients. Malabsorption and Maldigestion.
Symptomatic cryptosporidiosis presents with:
Cryptosporidiosis is associated with the following complications (more commonly in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship):
Stool tests do not regularly check for cryptosporidiosis unless there is a diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea outbreak. If suspected, specific testing for Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome should be requested when samples are sent to the laboratory.
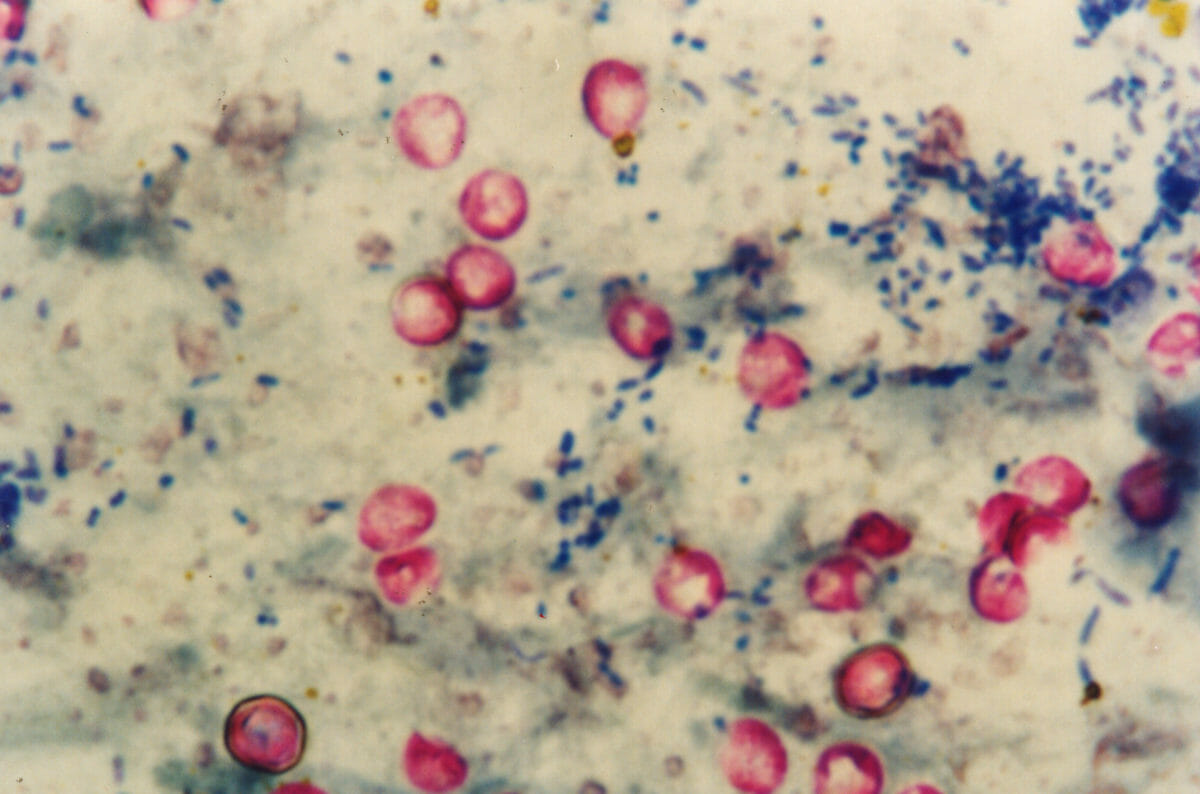
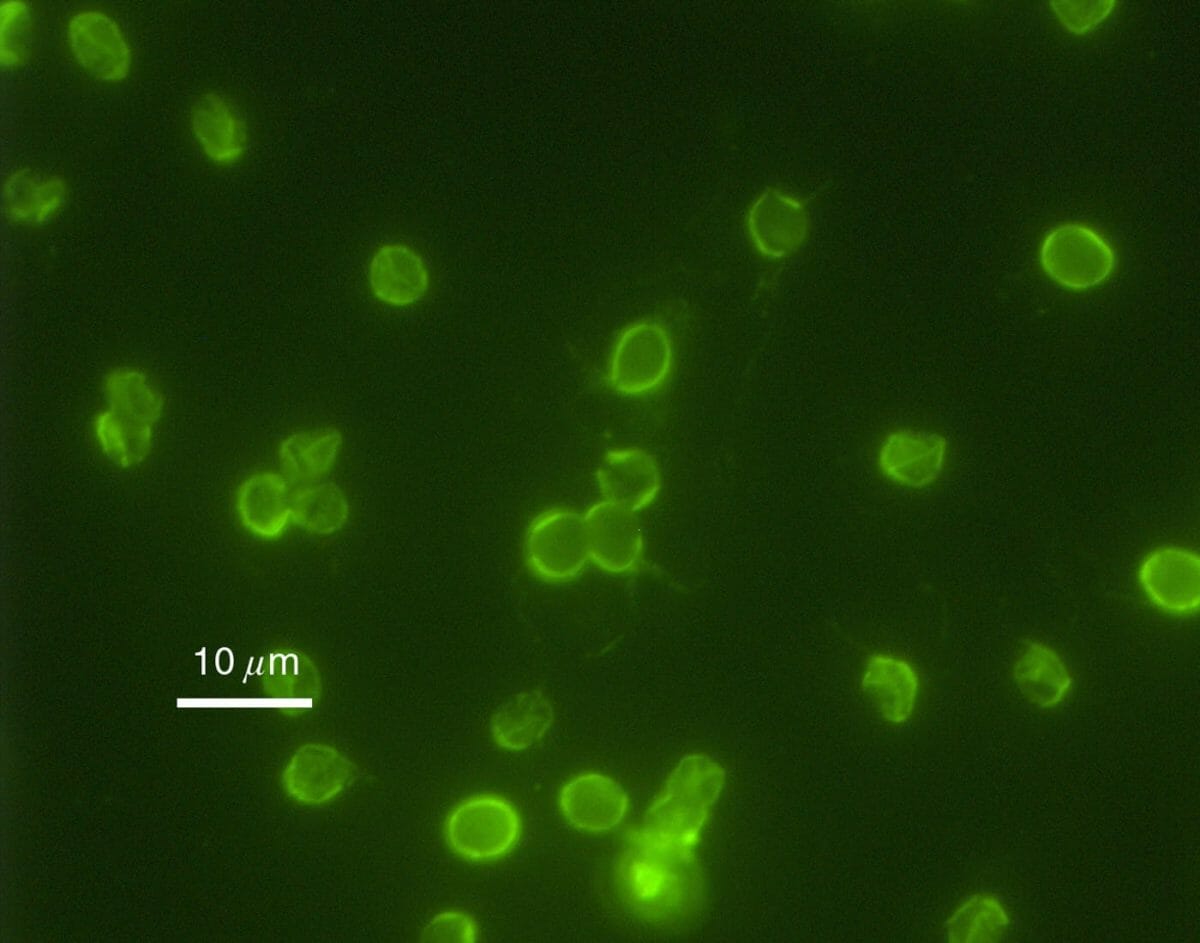

In cases with significant diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea:
Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic or have mild disease. Supportive treatment is the main approach.
Cryptosporidiosis is one of the opportunistic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease that can occur in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with HIV HIV Anti-HIV Drugs.