Craniosynostosis is the premature Premature Childbirth before 37 weeks of pregnancy (259 days from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period, or 245 days after fertilization). Necrotizing Enterocolitis fusion of 1 or more cranial sutures during the 1st year of life. Craniosynostosis is classified as simple or complex, and can be caused by environmental factors or genetic syndromes. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are typically asymptomatic and concern may arise from caregiver observations. Diagnosis is made clinically and by imaging of the head Imaging of the head Today, CT and MRI, especially the latter, are the preferred imaging methods for the study of the cranial vault and its contents. In conditions where emergent management is decided on the basis of presentation and imaging, CT has the advantage of rapid scan time and wider availability. Imaging of the Head and Brain. Treatment is surgical and prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas depends on classification and the presence of genetic syndromes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
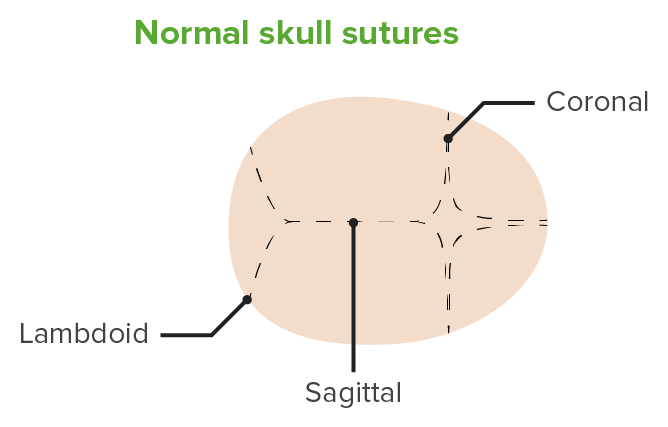
Normal cranial sutures
Image by Lecturio.Nonsyndromic:
Syndromic:
Aside from an abnormally shaped head, most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic. Careful exam should be performed to evaluate for signs of increased intracranial pressure Intracranial Pressure Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension including developmental delay.
| Type | Epidemiology | Deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs | Clinical presentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT) |
|
Unilateral:
|
Unilateral:
|
| Lambdoid |
|
|
Unilateral:
|
| Metopic |
|
|
|
| Multiple |
|
|
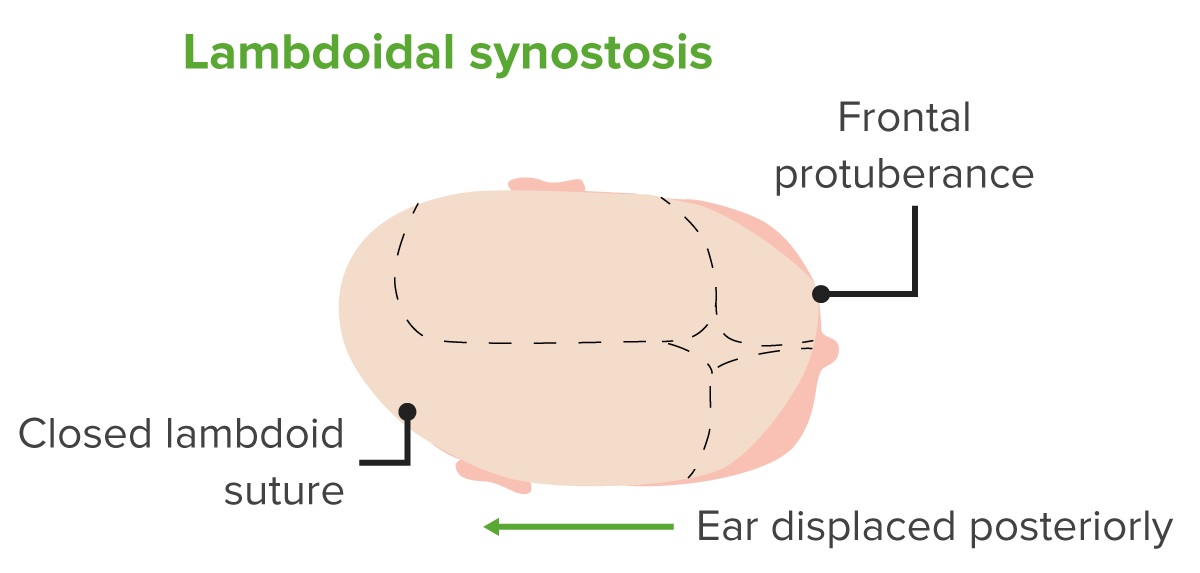
Diagram of a head with lambdoidal craniosynostosis.
Notice the fusion of the lambdoid suture, the anterior and posterior protuberances, and the posterior displacement of the ear.
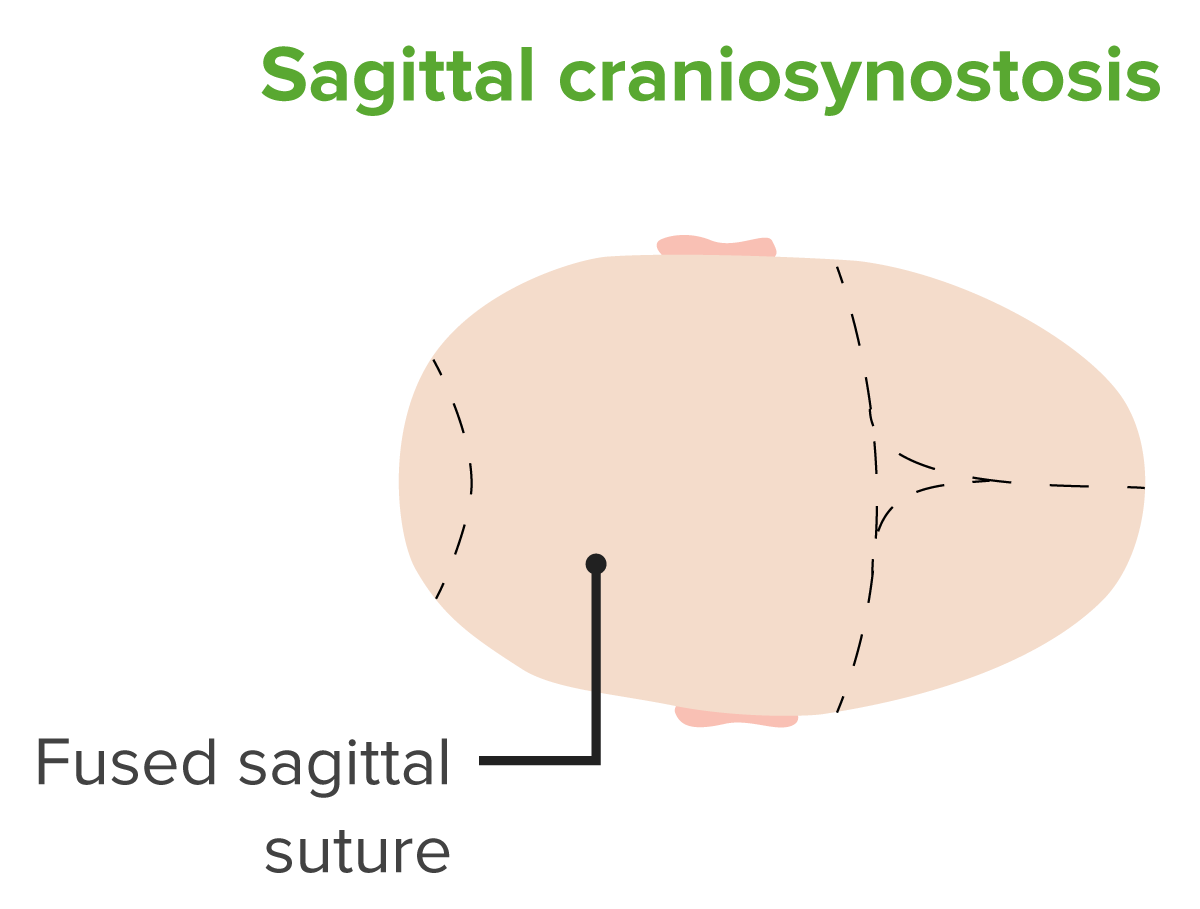
Diagram of a head with sagittal craniosynostosis.
Notice the fusion of the sagittal suture.
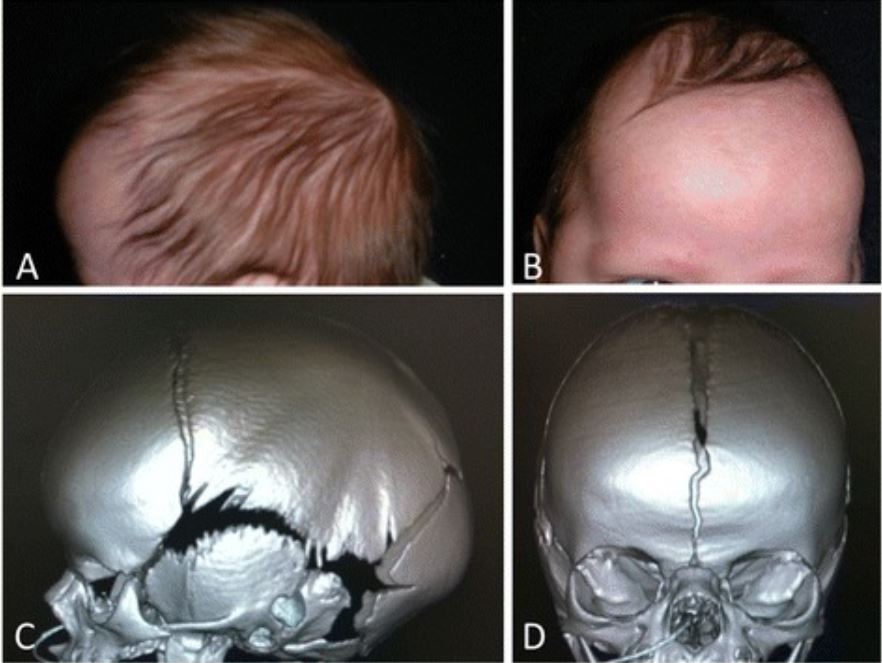
Scaphocephaly from sagittal craniosynostosis.
Phenotypic photographs (A, B) and computed tomography (CT) imaging (C, D) showing preoperative scaphocephaly from sagittal craniosynostosis.
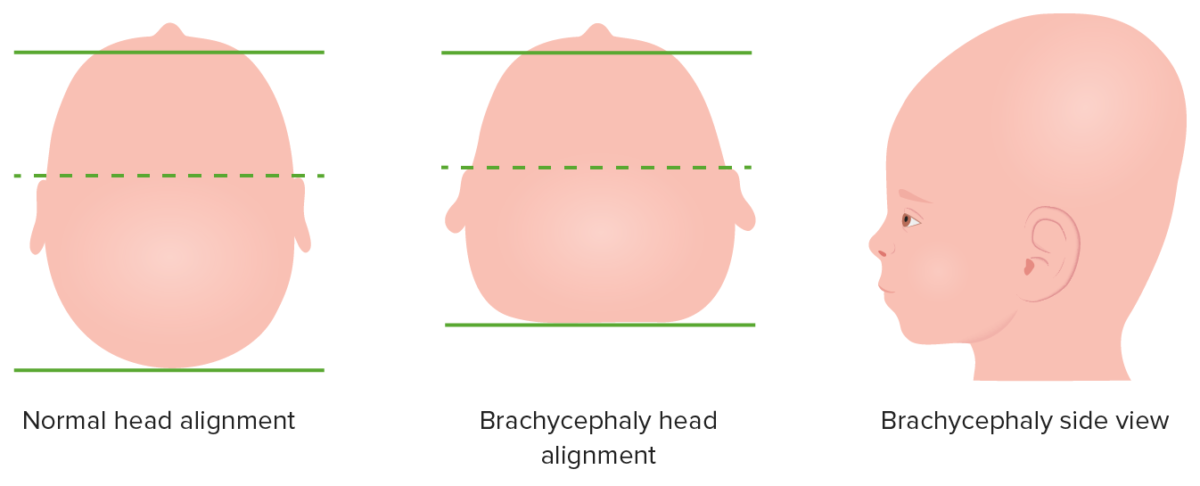
Depiction of brachycephalic malformation due to bilateral coronal suture fusion of an infant’s head, top-down and side view
Image by Lecturio.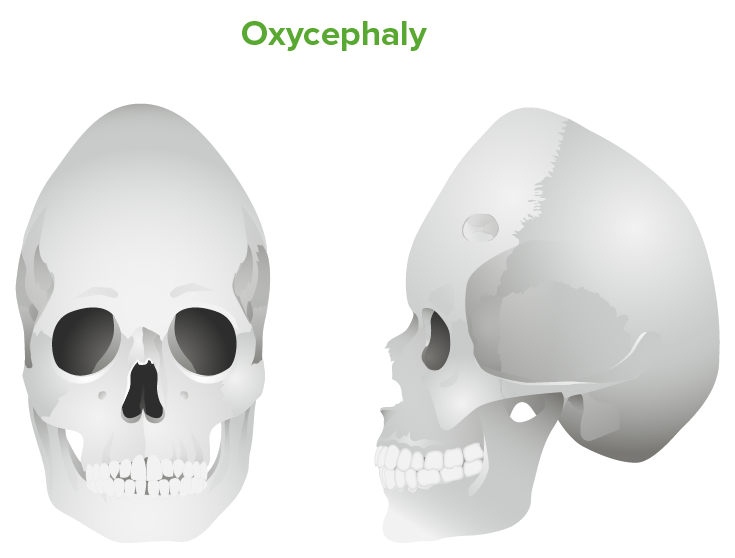
Oxycephaly: tall cranium due to inadequately treated bilateral coronal suture fusion
Image by Lecturio.Diagnosis relies on clinical observation, but imaging may be used to further characterize anatomy for classification or surgery
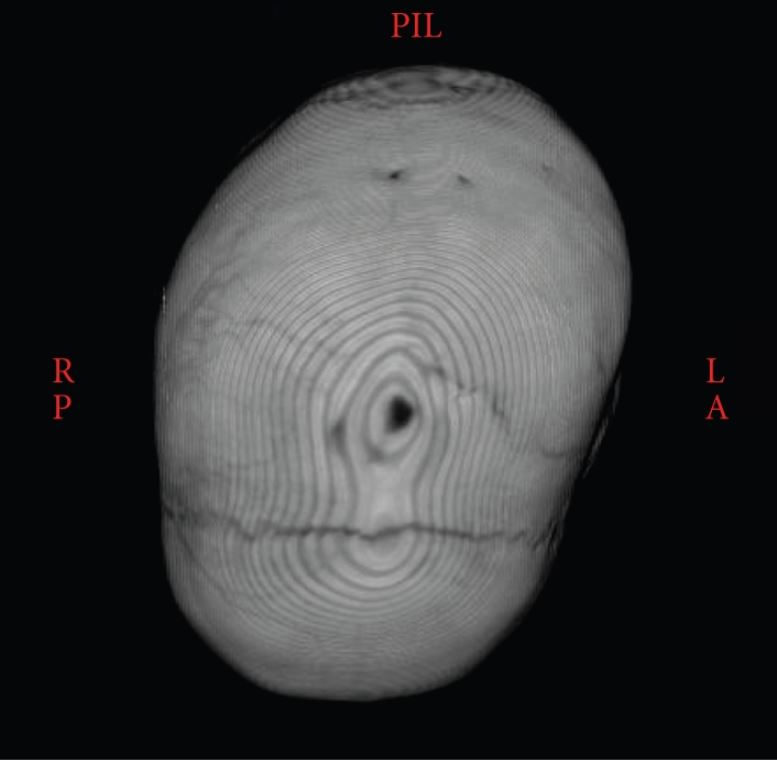
3D CT showing the synostotic sagittal suture with a posteriorly twisted skull
Image: “Atypical craniosynostosis with torticollis and neurological symptoms” by Koljonen V, Leikola J, Valanne L, Hukki J. License: CC BY 3.0