Cor pulmonale is right ventricular (RV) dysfunction caused by lung disease that results in pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery The short wide vessel arising from the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle and conveying unaerated blood to the lungs. Lungs: Anatomy hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension. The most common cause of cor pulmonale is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis. Dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea is the usual presenting symptom. Clinical findings include signs of right-sided heart failure Right-Sided Heart Failure Ebstein’s Anomaly and hypoxemia Hypoxemia Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome. While right cardiac catheterization Cardiac Catheterization Procedures in which placement of cardiac catheters is performed for therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Cardiac Surgery is the gold standard test, most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are diagnosed clinically and through the use of noninvasive testing. Echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA) shows RV enlargement and elevated pulmonary arterial systolic pressure. Management is first focused on the underlying disease. Oxygen therapy improves disease progression, while diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication reduce RV filling pressure. Lung transplantation Lung transplantation The transference of either one or both of the lungs from one human or animal to another. Organ Transplantation is an option for those refractory to therapy.
Last updated: Feb 25, 2025
| Primary lung disease | Diseases causing chronic hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage | Primary pulmonary vascular disease |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
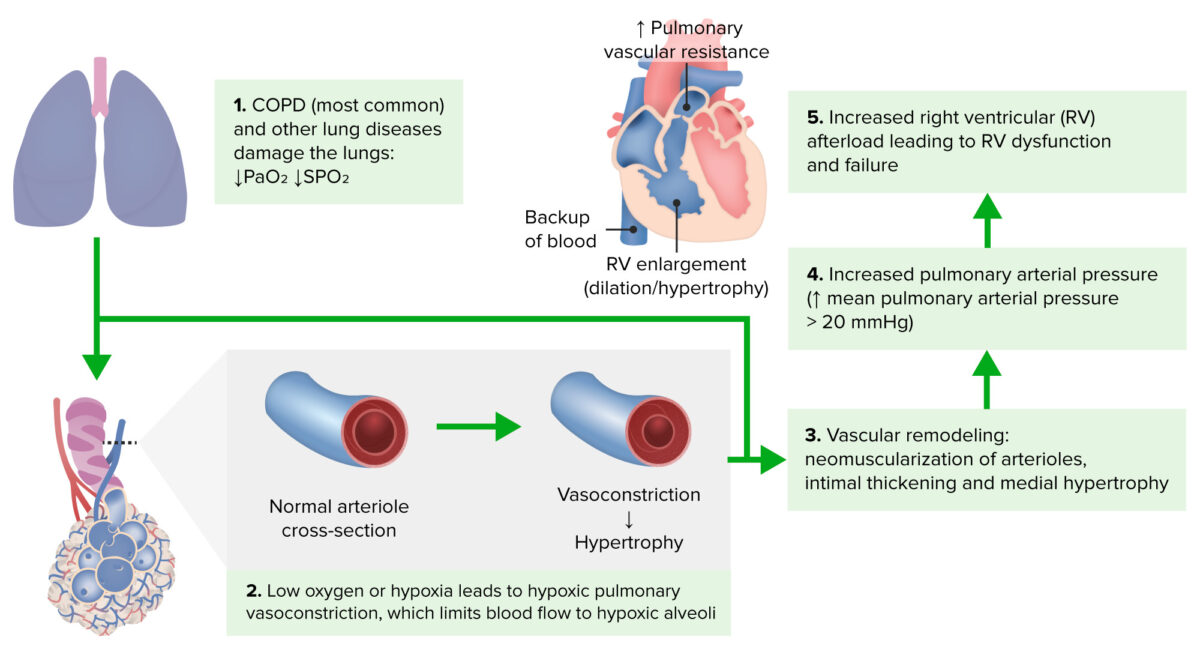
Pathophysiology of cor pulmonale
Image by Lecturio.Inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination
Chest auscultation
Right heart catheterization
Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography) echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA)
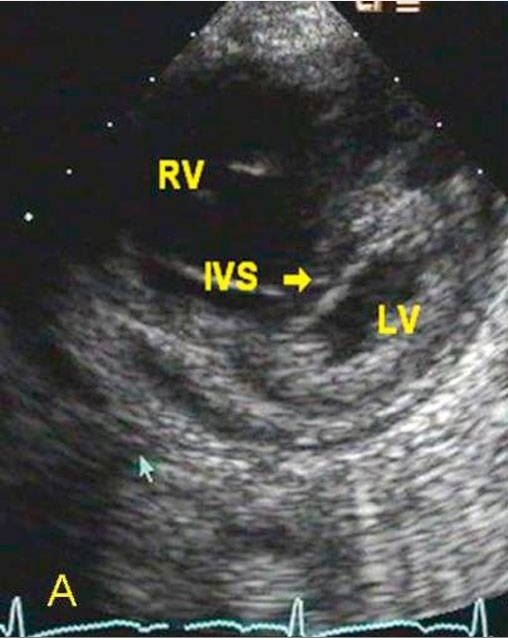
Parasternal short-axis 2D echocardiographic image from a patient with cor pulmonale showing severe RV dilation and evidence of RV hypertension with marked interventricular septal (IVS) flattening in systole
Image: “Parasternal short axis 2D echocardiographic images” by Acharya S, Mahajan SN, Shukla S, Diwan SK, Banode P, Kothari N. License: CC BY 3.0, edited by Lecturio.Laboratory studies
Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
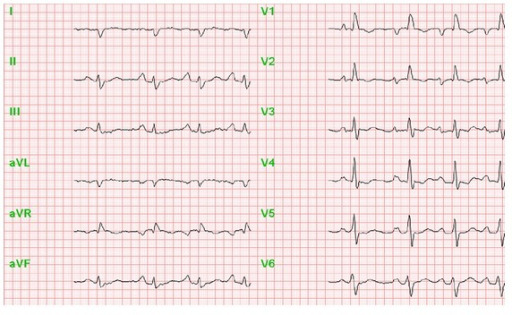
Note the increased P wave amplitude in leads II, III, and aVF, suggestive of right atrial enlargement.
Image: “Perioperative anesthesiological management of patients with pulmonary hypertension” by Gille J, Seyfarth HJ, Gerlach S, Malcharek M, Czeslick E, Sablotzki A. License: CC BY 3.0Chest X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary function test Pulmonary function test Pulmonary function tests are a group of diagnostic procedures yielding useful, quantifiable information about the rate of the flow of air through the individual’s airways, lung capacity, and the efficiency of gas exchange in relation to time. The most commonly utilized tests include spirometry (before and after bronchodilator use), lung volumes, and quantitation of diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (CO). The tests can be influenced by the individual’s effort/fatigue, disease state, or anatomical malformation. Pulmonary Function Tests
Chest computed tomography Chest Computed Tomography Hemothorax (CT) scan
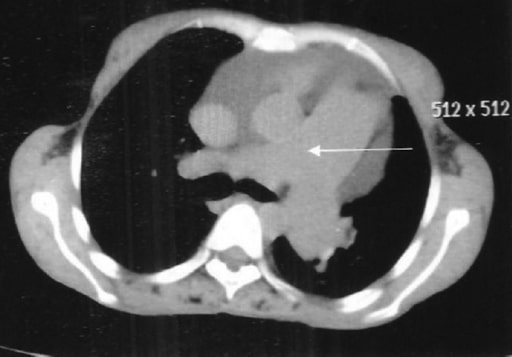
High-resolution CT thorax showing dilated pulmonary artery (arrow)
Image: “Rheumatoid interstitial lung disease presenting as cor pulmonale.” by Acharya S, Mahajan SN, Shukla S, Diwan SK, Banode P, Kothari N. License: CC BY 2.0Ventilation-perfusion scan
Cardiac magnetic resonance Cardiac magnetic resonance Aortic Regurgitation imaging (MRI)
Management is first focused on the underlying cause of cor pulmonale.