Connective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body, although the central nervous system parenchyma contains almost no classical connective tissue (limited mainly to meninges and perivascular structures). The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix Extracellular matrix A meshwork-like substance found within the extracellular space and in association with the basement membrane of the cell surface. It promotes cellular proliferation and provides a supporting structure to which cells or cell lysates in culture dishes adhere. Hypertrophic and Keloid Scars. The abundance, proportion, and composition of these components are key determinants of the type of connective tissue. There are many types of connective tissues such as blood, bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types, and cartilage Cartilage Cartilage is a type of connective tissue derived from embryonic mesenchyme that is responsible for structural support, resilience, and the smoothness of physical actions. Perichondrium (connective tissue membrane surrounding cartilage) compensates for the absence of vasculature in cartilage by providing nutrition and support. Cartilage: Histology, which constitute the specialized type.
Last updated: Dec 18, 2025
Connective tissue refers to a group of tissues of mesenchymal origin (rather than a single tissue type), whose main function is providing structural support to the organs of the body.
Connective tissue consists of 3 major elements: ground substance, fibers, and cells. The types and proportions of these elements determine the type of connective tissue.
Ground substance:
Fibers (2 types):
Cells:
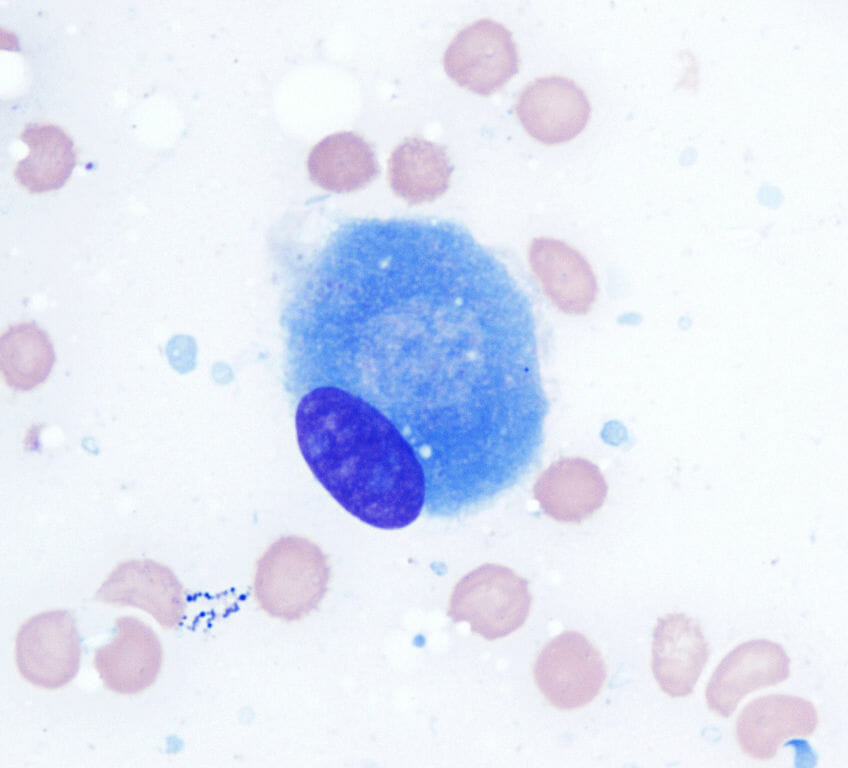
Microscopic view of an osteoblast (100x ; Wright Giemsa stain)
Image: “Osteoblast (Wright-Giemsa stain, 100x)” by Gabriel Caponetti. License: CC BY 3.0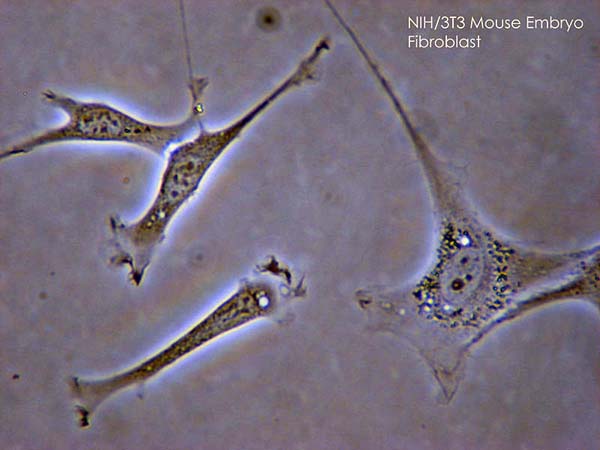
Fibroblasts (phase-contrast microscopy)
Image: “Fibroblast” by SubtleGuest. License: CC BY 2.5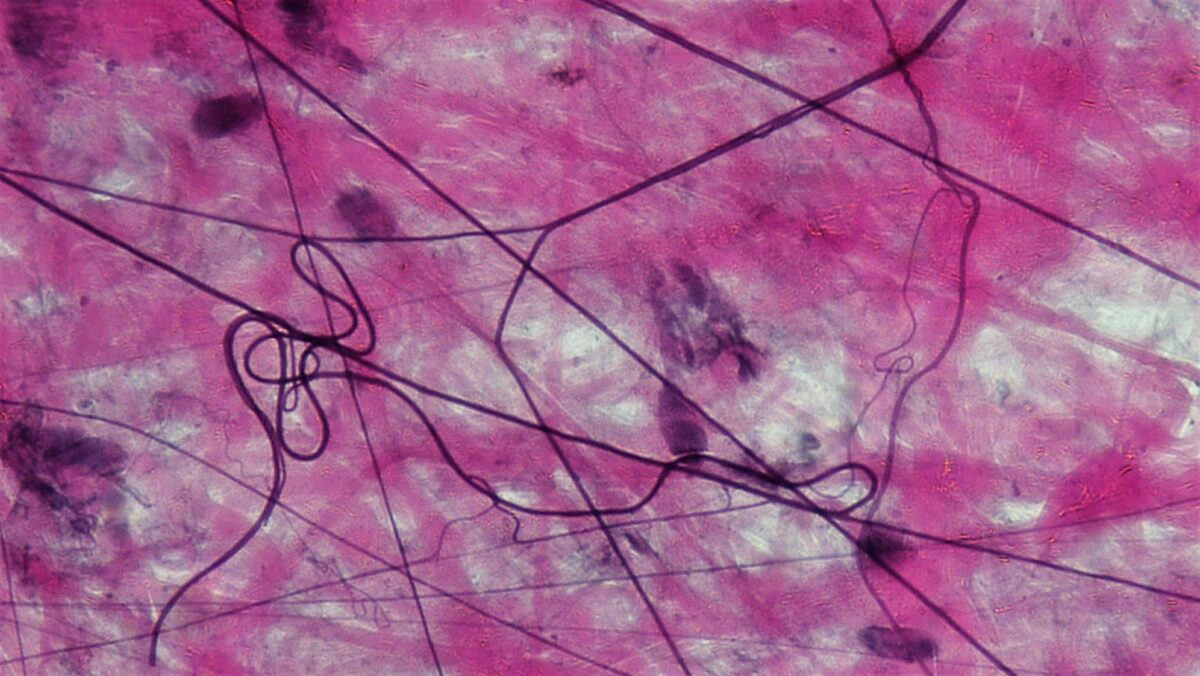
Areolar connective tissue
Image: “Connective Tissue Loose Aerolar (41743649782)” by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. License: CC0 1.0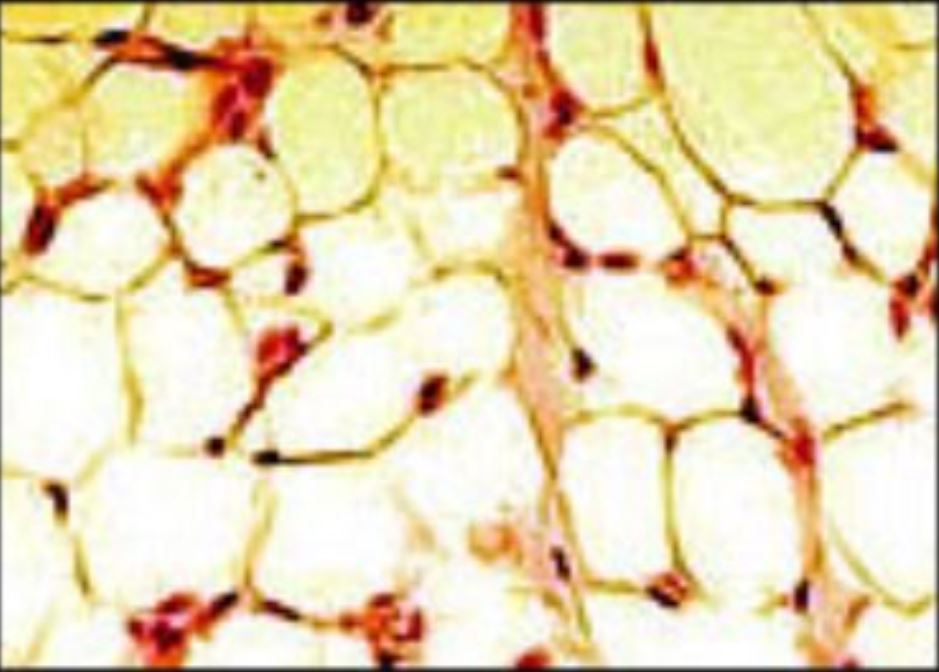
Adipose tissue
Image: “Illu connective tissues 1” by National Cancer Institute. License: Public Domain, cropped by Lecturio.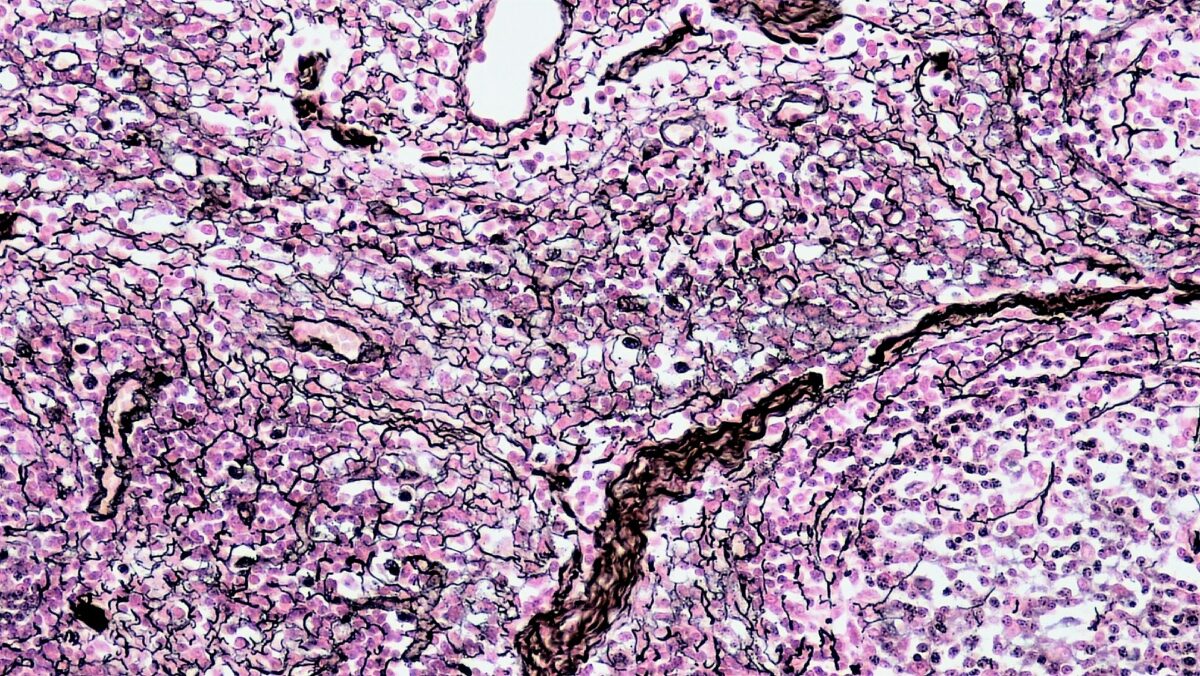
Reticular connective tissue
Image: “Connective Tissue Reticular (40885193805)” by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. License: CC0 1.0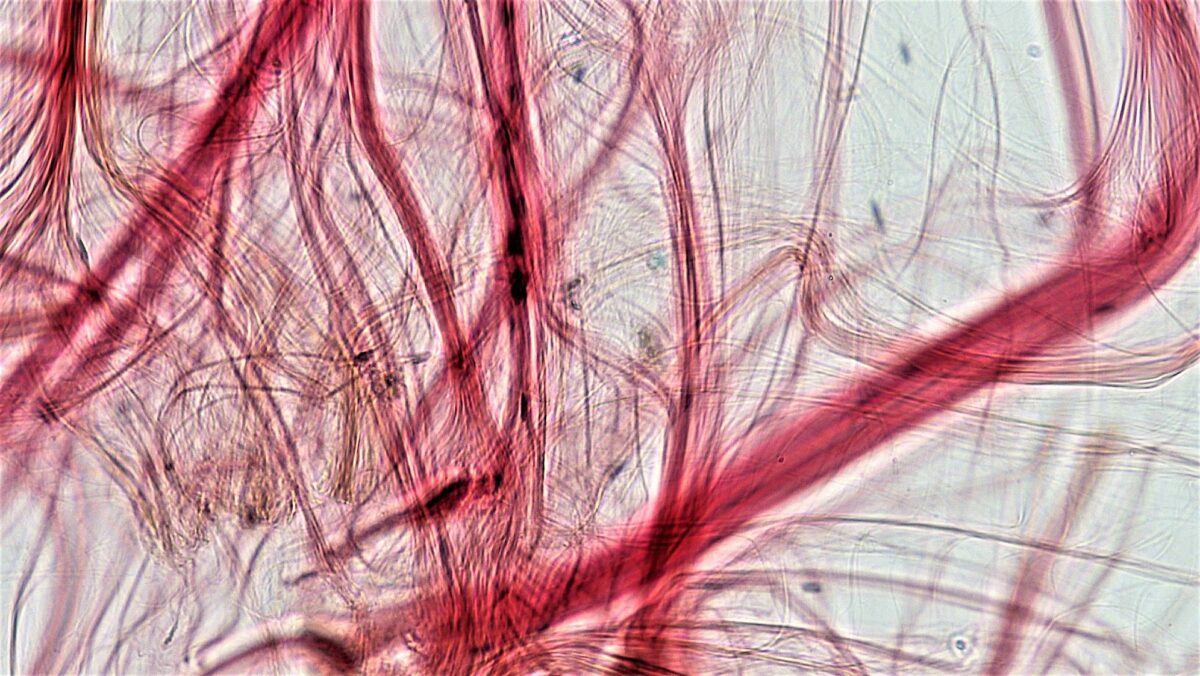
Tendon (dense regular connective tissue)
Image: “Connective Tissue Tendon (26987380607)” by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. License: CC0 1.0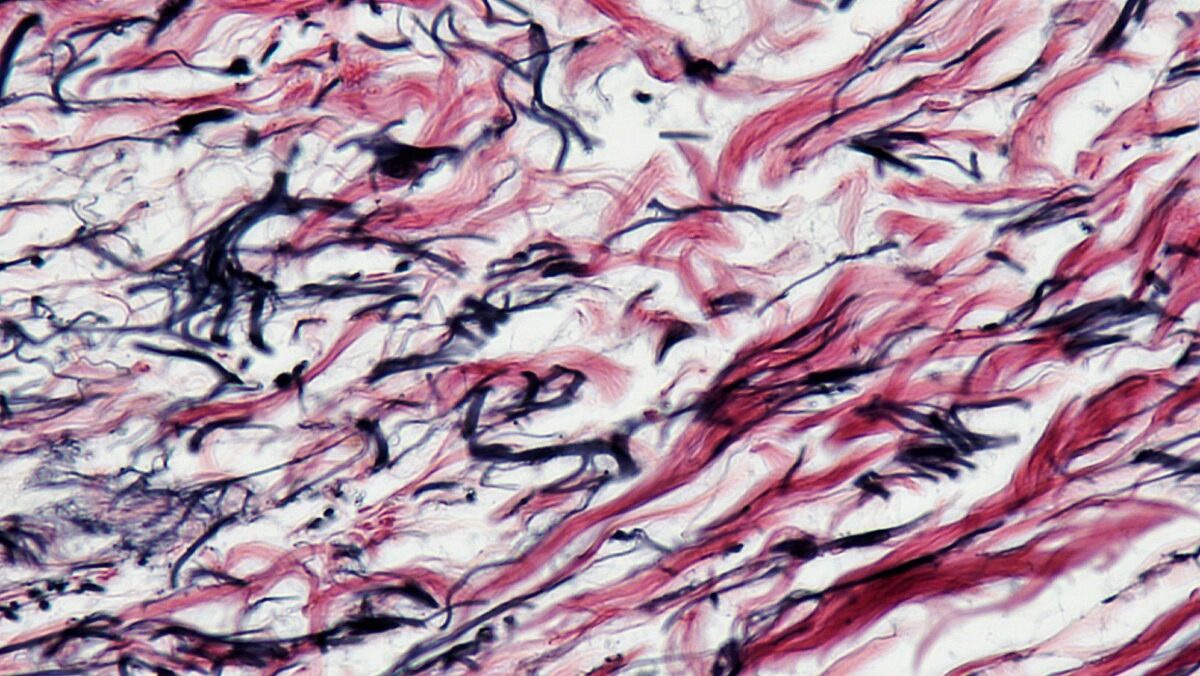
Elastic connective tissue
Image: “Connective Tissue Human Elastic Tissue (41813163882)” by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. License: CC0 1.0