Congenital infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are acquired in utero or during passage through the birth canal Birth canal Pelvis: Anatomy at birth and can be associated with significant morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status and mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status for the infant. The TORCH infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are a group of congenital infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease grouped due to their similar presentation. The acronym TORCH arises from the names of the infectious agents that cause the diseases included in this group: toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host's immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis, other agents ( syphilis Syphilis Syphilis is a bacterial infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum pallidum (T. p. pallidum), which is usually spread through sexual contact. Syphilis has 4 clinical stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Syphilis, varicella zoster virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology (VZV), parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or "slapped cheek syndrome." Parvovirus B19, and HIV HIV Anti-HIV Drugs), rubella Rubella An acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. The virus enters the respiratory tract via airborne droplet and spreads to the lymphatic system. Rubella Virus, CMV, and herpes simplex.
Last updated: Oct 14, 2022
A group of specific congenital infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease acquired either in utero or during delivery:
Prenatal screening Screening Preoperative Care is important in identification Identification Defense Mechanisms.
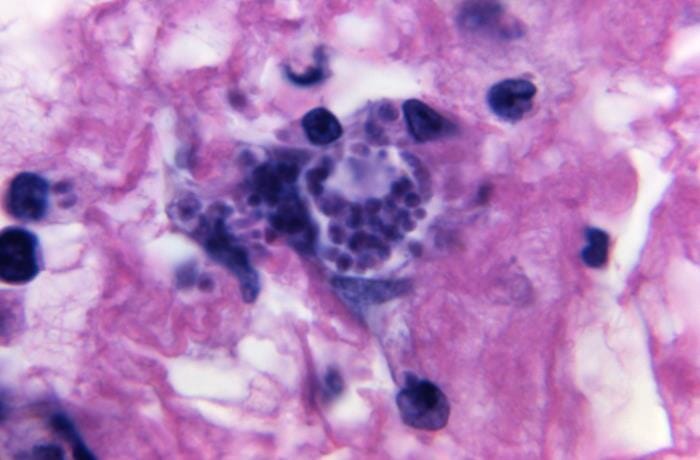
Toxoplasma gondii: Under a high magnification of 1,125x, this photomicrograph of a tissue sample reveals a close view of a darkly stained Toxoplasma gondii tissue cyst, which contains numbers of spherical bradyzoites.
Image: “21122” by CDC/Dr. Green. License: Public Domain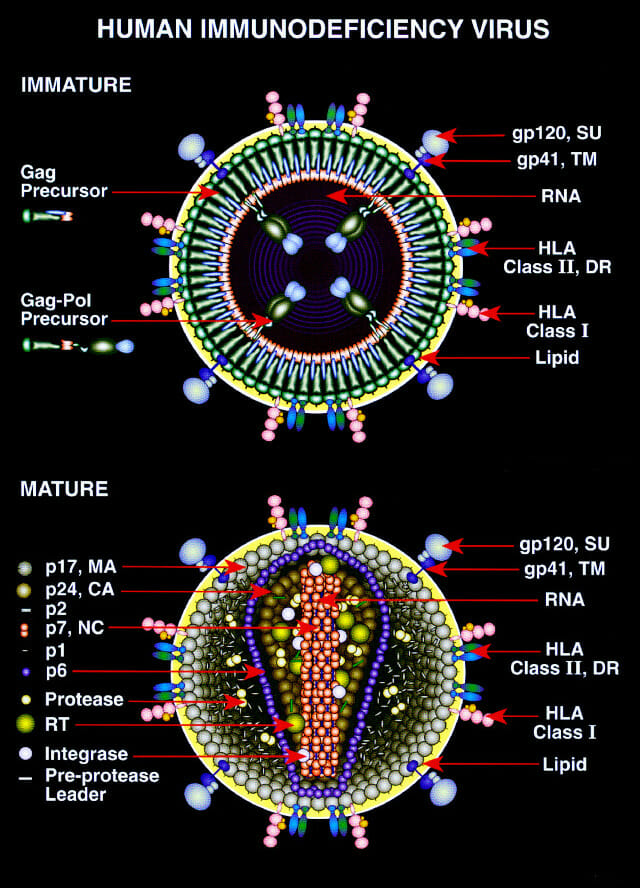
Diagram of the immature and mature forms of HIV
Image: “Diagram of the immature and mature forms of HIV” by Drs. Louis E. Henderson and Larry Arthur. License: Public Domain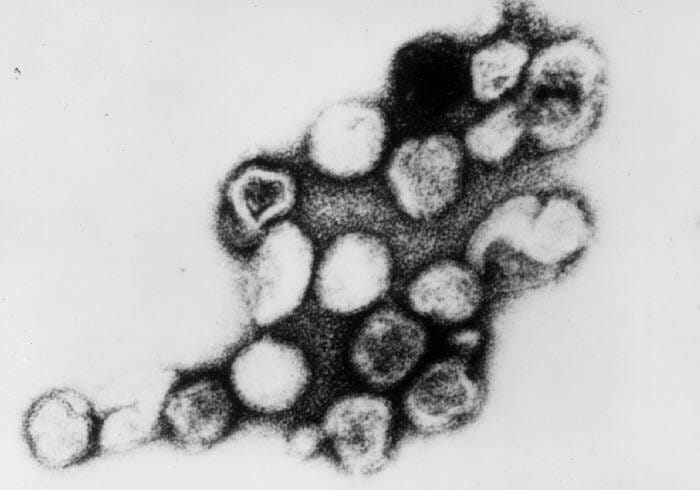
Transmission electron micrograph of rubella virus
Image: “Rubella virus” by CDC/Dr. Erskine Palmer. License: Public DomainThe triad of congenital toxoplasmosis Congenital toxoplasmosis Prenatal protozoal infection with toxoplasma gondii which is associated with injury to the developing fetal nervous system. The severity of this condition is related to the stage of pregnancy during which the infection occurs; first trimester infections are associated with a greater degree of neurologic dysfunction. Clinical features include hydrocephalus; microcephaly; deafness; cerebral calcifications; seizures; and psychomotor retardation. Signs of a systemic infection may also be present at birth, including fever, rash, and hepatosplenomegaly. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis in infants include:
The early manifestations of congenital syphilis Congenital syphilis Syphilis acquired in utero and manifested by any of several characteristic tooth (Hutchinson’s teeth) or bone malformations and by active mucocutaneous syphilis at birth or shortly thereafter. Ocular and neurologic changes may also occur. Syphilis may affect several systems:
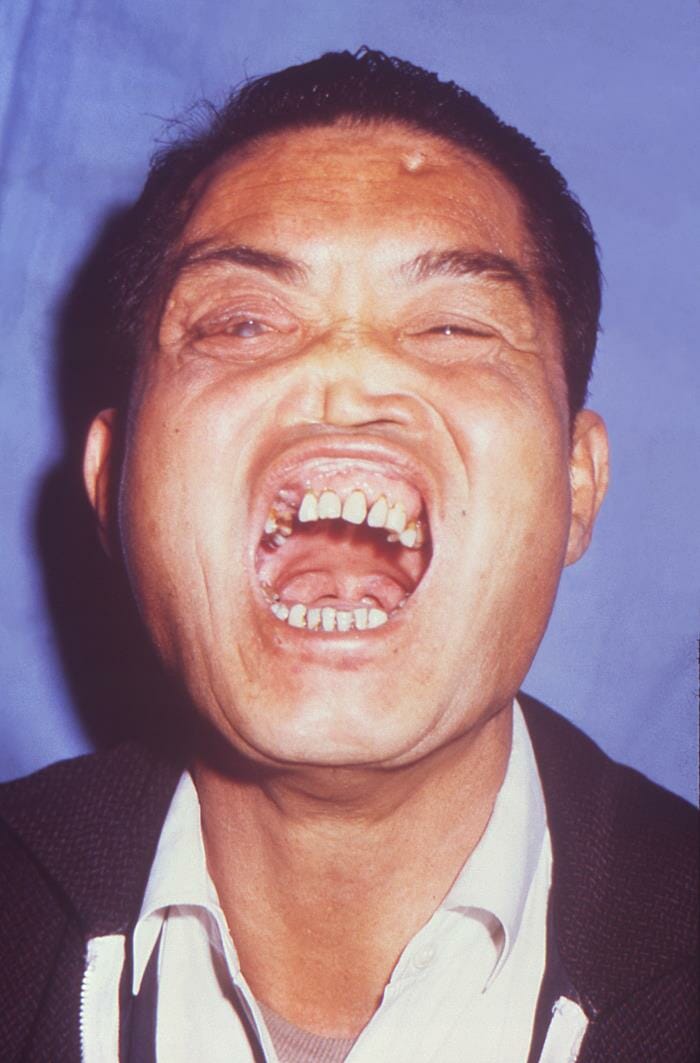
Stigmata of congenital syphilis, including frontal bossing, mulberry molars, Hutchinson teeth, saddle nose, and a cataract in the right eye.
Image: “16463” by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC/ Brian Hill. License: Public Domain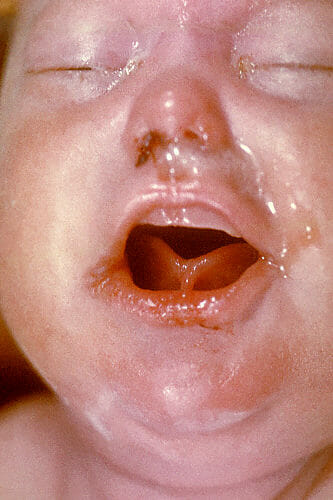
A newborn displays snuffles, indicating congenital syphilis.
Image: “2246” by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC/ Dr. Norman Cole. License: Public DomainThe most common presentation of congenital varicella syndrome includes:
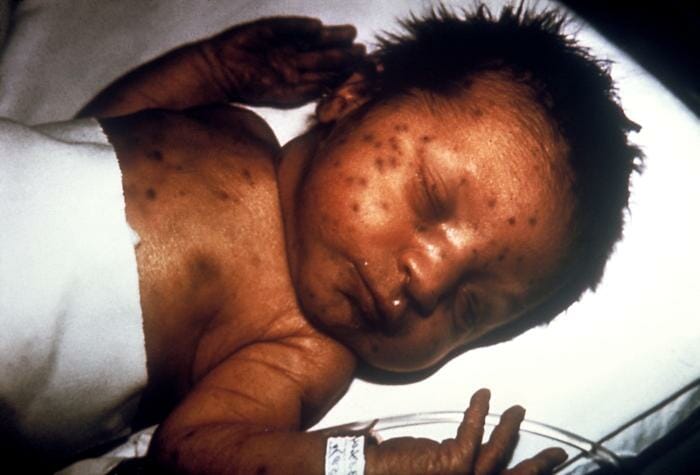
An infant with congenital rubella syndrome showing the blueberry muffin rash
Image: “ 713” by CDC/ Dr. Andre J. Lebrun. License: Public Domain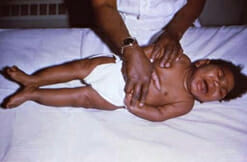
An infant with congenital cytomegalovirus infection exhibits microcephaly and lower limb spasticity
Symptoms usually start within the 1st day of life but can be delayed up to 1 week after birth.
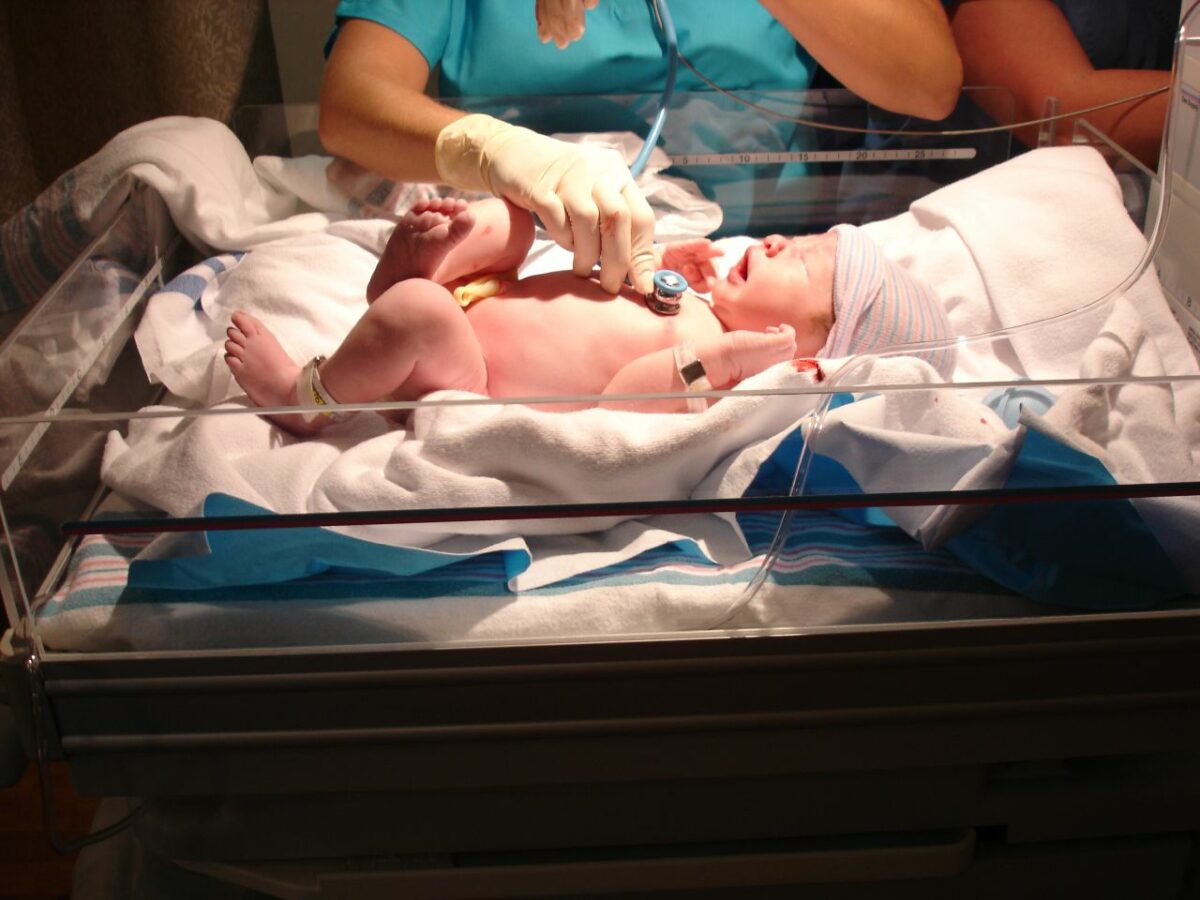
Normal baby on examination:
The respiratory rate is 30–60/min; periodic breathing patterns are noted in term and late-preterm babies. The skin is normally pink (indicating adequate oxygenation), both upper and lower extremities have a flexor tone, and the baby arouses on stimulation.
Treatment depends on severity: