Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation (CAH) consists of a group of autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance disorders that cause a deficiency of an enzyme needed in cortisol Cortisol Glucocorticoids, aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia, and androgen synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). The most common subform of CAH is 21-hydroxylase deficiency, followed by 11β-hydroxylase deficiency. Clinical manifestations depend on the specific enzyme affected. Notably, CAH is the most common cause of ambiguous genitalia Ambiguous Genitalia Primary Amenorrhea in genotypic female individuals. All forms of CAH cause low levels of cortisol Cortisol Glucocorticoids, high levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone Adrenocorticotropic hormone An anterior pituitary hormone that stimulates the adrenal cortex and its production of corticosteroids. Acth is a 39-amino acid polypeptide of which the n-terminal 24-amino acid segment is identical in all species and contains the adrenocorticotropic activity. Upon further tissue-specific processing, acth can yield alpha-msh and corticotropin-like intermediate lobe peptide (clip). Adrenal Hormones (ACTH), and adrenal hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation. Laboratory studies help confirm the diagnosis. Lifelong glucocorticoid replacement is needed, and surgical correction of ambiguous genitalia Ambiguous Genitalia Primary Amenorrhea is often performed.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation comprises a spectrum of disorders in which different gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics mutations cause different enzyme deficiencies affecting steroid biogenesis, which is carried out by the adrenal glands Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands are a pair of retroperitoneal endocrine glands located above the kidneys. The outer parenchyma is called the adrenal cortex and has 3 distinct zones, each with its own secretory products. Beneath the cortex lies the adrenal medulla, which secretes catecholamines involved in the fight-or-flight response. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy.
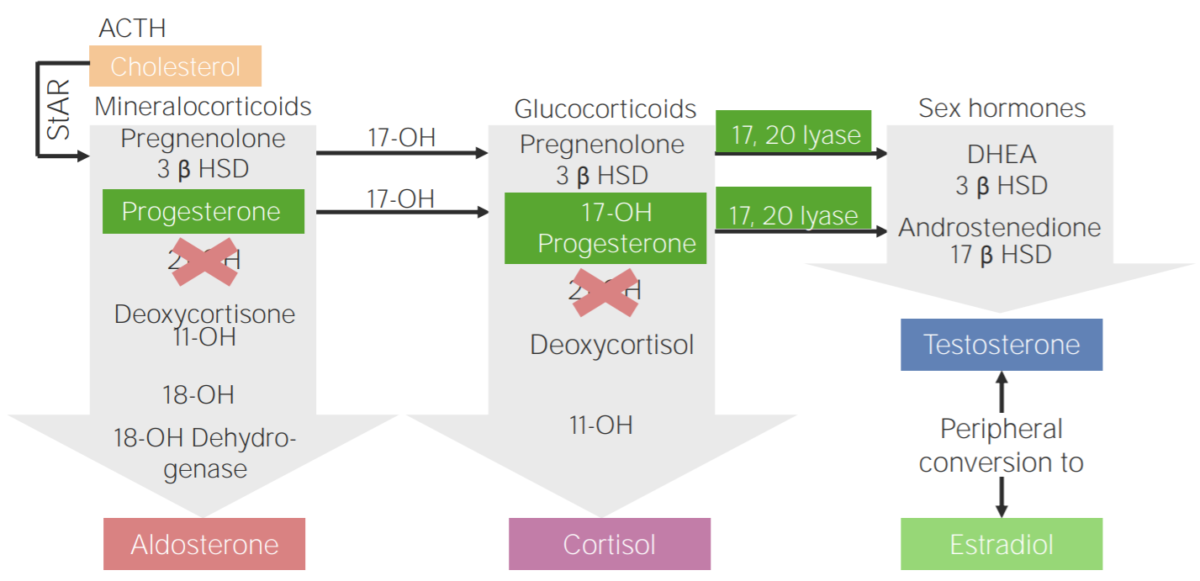
21-hydroxylase deficiency:
Diagram of the pathophysiology of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
3β HSD: 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
11-OH: 11β-hydroxylase
17-OH: 17α-hydroxylase
17-OH progesterone: 17-hydroxyprogesterone
17β HSD: 17β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase
18-OH: 18-hydroxylase
21-OH: 21-hydroxylase
ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone
DHEA: dehydroepiandrosterone
StAR: steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
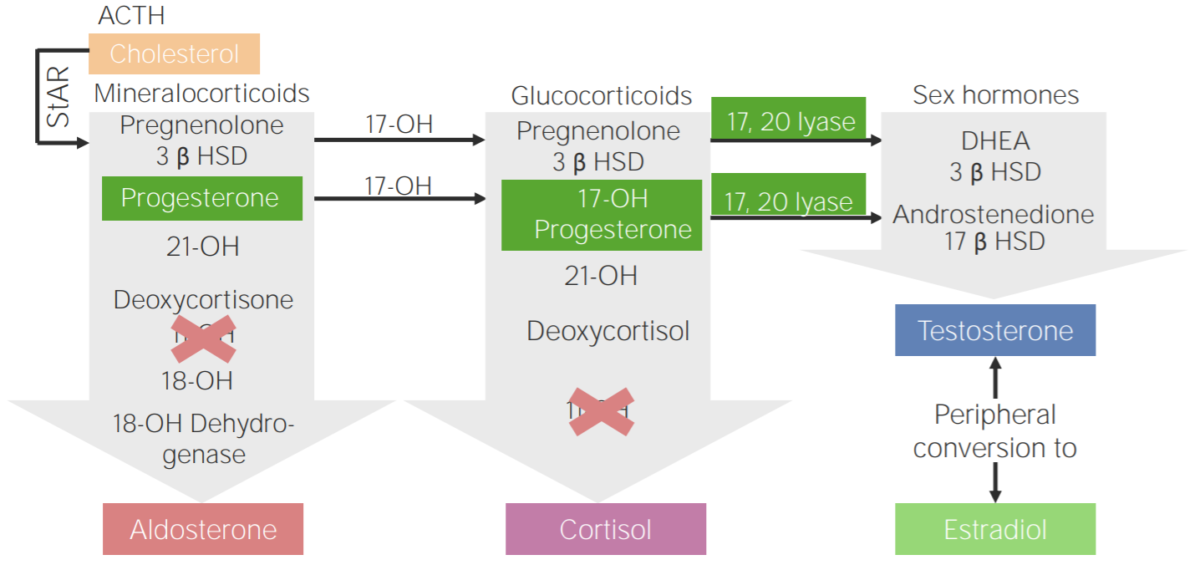
11β-hydroxylase deficiency:
Diagram of the pathophysiology of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 11β-hydroxylase deficiency
3β HSD: 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
11-OH: 11β-hydroxylase
17-OH: 17α-hydroxylase
17-OH progesterone: 17-hydroxyprogesterone
17β HSD: 17β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase
18-OH: 18-hydroxylase
21-OH: 21-hydroxylase
ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone
DHEA: dehydroepiandrosterone
StAR: steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
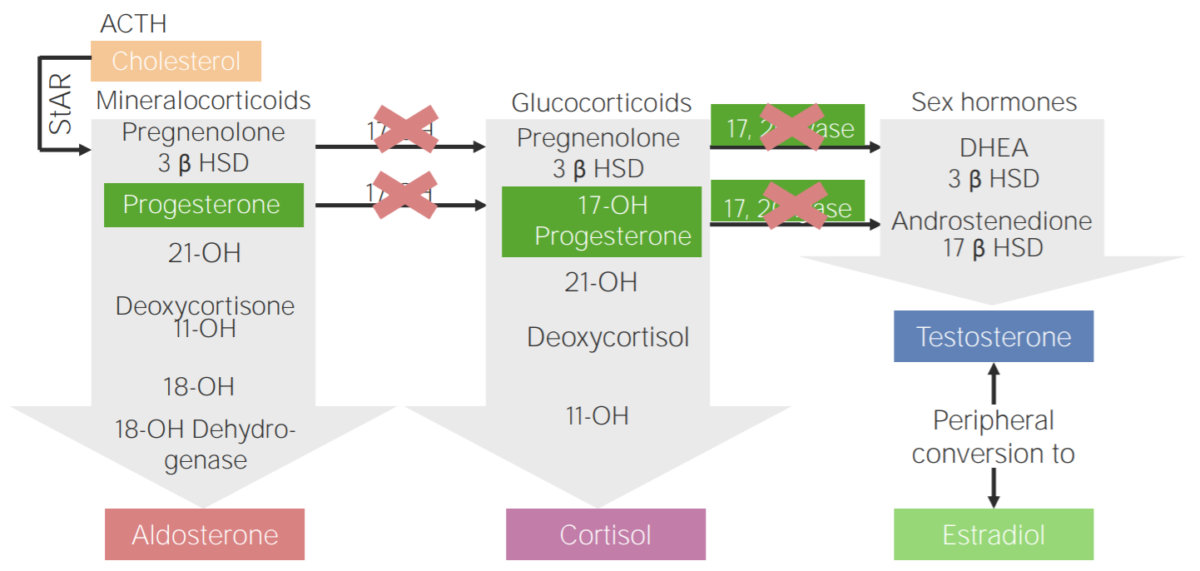
17α-hydroxylase deficiency:
Diagram of the pathophysiology of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency
3β HSD: 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
11-OH: 11β-hydroxylase
17-OH: 17α-hydroxylase
17-OH progesterone: 17-hydroxyprogesterone
17β HSD: 17β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase
18-OH: 18-hydroxylase
21-OH: 21-hydroxylase
ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone
DHEA: dehydroepiandrosterone
StAR: steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
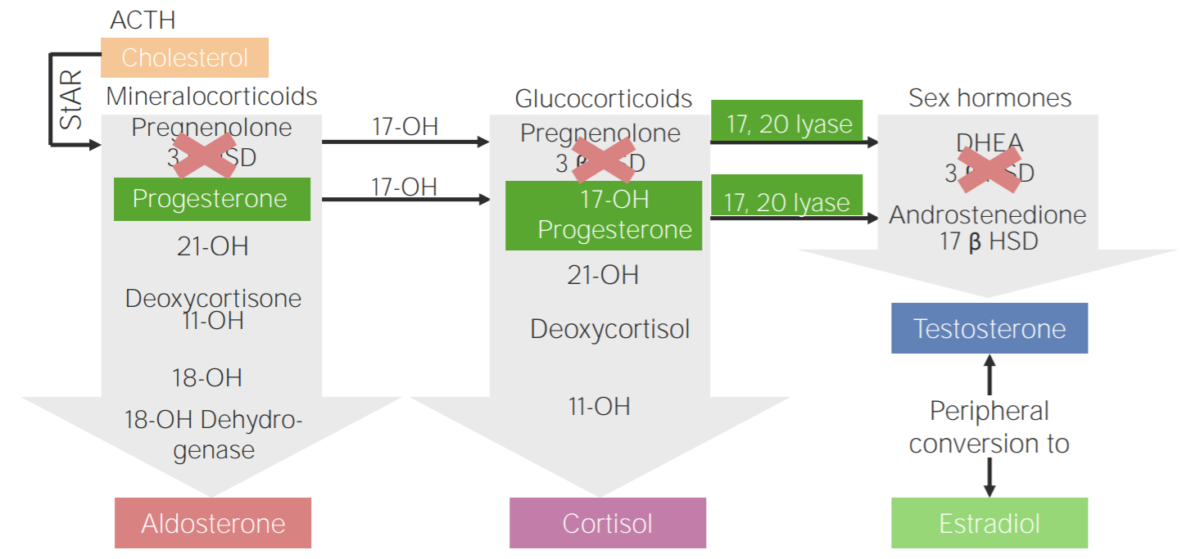
3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency (3BHSD):
Diagram of the pathophysiology of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency
3β HSD: 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
11-OH: 11β-hydroxylase
17-OH: 17α-hydroxylase
17-OH progesterone: 17-hydroxyprogesterone
17β HSD: 17β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase
18-OH: 18-hydroxylase
21-OH: 21-hydroxylase
ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone
DHEA: dehydroepiandrosterone
StAR: steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
| Enzyme deficiency | Gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics mutated | Cortisol Cortisol Glucocorticoids | Aldosterone Aldosterone A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that regulates electrolyte and water balance by increasing the renal retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. Hyperkalemia | 11-deoxycorticosterone | Androgens Androgens Androgens are naturally occurring steroid hormones responsible for development and maintenance of the male sex characteristics, including penile, scrotal, and clitoral growth, development of sexual hair, deepening of the voice, and musculoskeletal growth. Androgens and Antiandrogens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21-hydroxylase | CYP21A2 | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Increased |
| 11β-hydroxylase | CYP11B1 | Increased | |||
| 17α-hydroxylase 17α-hydroxylase A microsomal cytochrome p450 enzyme that catalyzes the 17-alpha-hydroxylation of progesterone or pregnenolone and subsequent cleavage of the residual two carbons at C17 in the presence of molecular oxygen and NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase. This enzyme, encoded by cyp17 gene, generates precursors for glucocorticoid, androgen, and estrogen synthesis. Defects in cyp17 gene cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia and abnormal sexual differentiation. Gonadal Hormones | CYP17A1 | Decreased | |||
| 3BHSD | HSD3B2 | Decreased |
There is a classic form of CAH due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency and a non-classic form. The classic form has 2 different types: simple virilizing and salt wasting.
Classical CAH is the most severe form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
Nonclassic CAH is the milder, more common form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
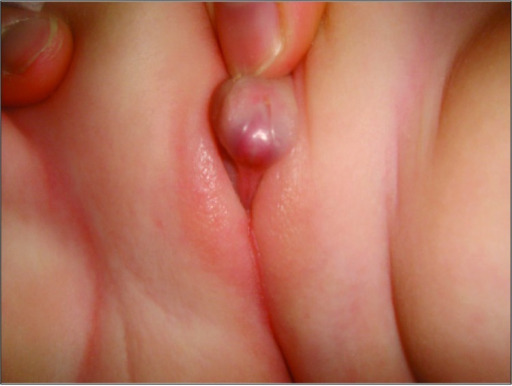
Appearance of ambiguous genitalia in a patient with congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Image: “A rare combination: congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21 hydroxylase deficiency and Turner syndrome” by Kendirci HN, Aycan Z, Çetinkaya S, Baş VN, Ağladıoğlu SY, Önder A. License: CC BY 2.5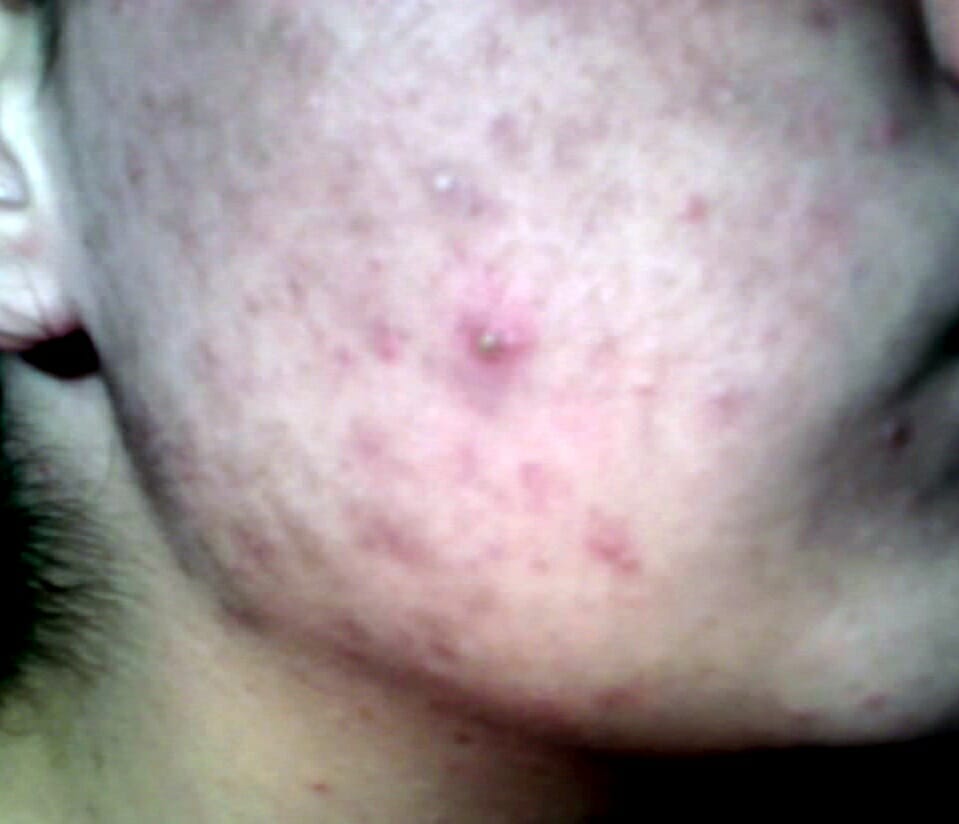
Acne on the forehead of a girl during puberty: seen in non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia more, a common form of 21-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency
Image: “Teenager-with-acne” by Diariodaj. License: Public DomainThe following table outlines important findings in the 3 most common types of CAH.
| Type of CAH | Steroids Steroids A group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus. Benign Liver Tumors/precursors | Electrolytes Electrolytes Electrolytes are mineral salts that dissolve in water and dissociate into charged particles called ions, which can be either be positively (cations) or negatively (anions) charged. Electrolytes are distributed in the extracellular and intracellular compartments in different concentrations. Electrolytes are essential for various basic life-sustaining functions. Electrolytes |
|---|---|---|
| 21-hydroxylase |
|
|
| 11β-hydroxylase |
|
|
| 17α-hydroxylase 17α-hydroxylase A microsomal cytochrome p450 enzyme that catalyzes the 17-alpha-hydroxylation of progesterone or pregnenolone and subsequent cleavage of the residual two carbons at C17 in the presence of molecular oxygen and NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase. This enzyme, encoded by cyp17 gene, generates precursors for glucocorticoid, androgen, and estrogen synthesis. Defects in cyp17 gene cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia and abnormal sexual differentiation. Gonadal Hormones |
|
The general treatment goals are to mitigate the effects of respective steroid deficiencies and excessive amounts of steroids Steroids A group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus. Benign Liver Tumors and to aid secondary sexual development Secondary Sexual Development Delayed Puberty.