Complex regional pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic regional neuropathic pain Neuropathic pain Caused by lesion or disease affecting the nervous system (PNS or CNS). Pain: Types and Pathways condition characterized by excruciating pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways (out of proportion to apparent tissue damage or inciting trauma), paresthesia, allodynia Allodynia Pain due to a stimulus that does not typically provoke pain. Pain Management, temperature abnormalities, skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions discoloration, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, reduced range of motion Range of motion The distance and direction to which a bone joint can be extended. Range of motion is a function of the condition of the joints, muscles, and connective tissues involved. Joint flexibility can be improved through appropriate muscle strength exercises. Examination of the Upper Limbs, and bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types demineralization. This syndrome is most often associated with an inciting traumatic event Traumatic event An emotionally painful, shocking, stressful, and sometimes life-threatening experience. It can result from witnessing distressing events such as natural disasters, physical or sexual abuse, and terrorism or other acts of violence. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) (e.g., fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures, surgery, burn) and predominantly affects the limb(s). Diagnosis is clinical, but it is supported by imaging and electrodiagnostic testing. Treatment centers around multidisciplinary pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management and maintenance of function.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Complex regional pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways syndrome occurs after an initiating noxious event, such as trauma:
The pathophysiology of CRPS is not completely understood, but there are multiple likely mechanisms.
Inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation (cytokine-mediated):
Neurogenic inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation (neuropeptide-mediated):
Central sensitization Central sensitization Increased responsiveness of nociceptive neurons in the central nervous system to normal or subthreshold input. Pain: Types and Pathways:
Sympathetic dysregulation:
Cortical reorganization:
Genetic predisposition:
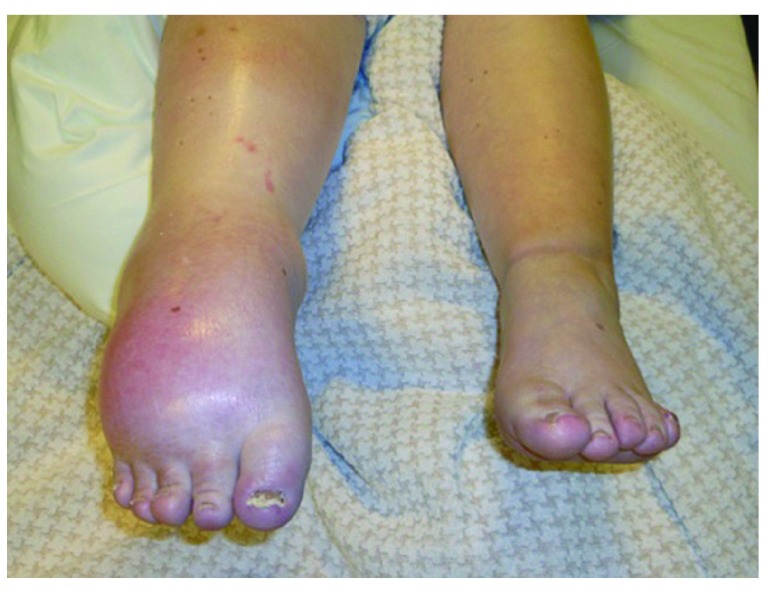
Complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS-1)
The individual presented dystonic equinus of the right ankle and a swollen foot and calf with tightened, pale, gleaming, cold skin.
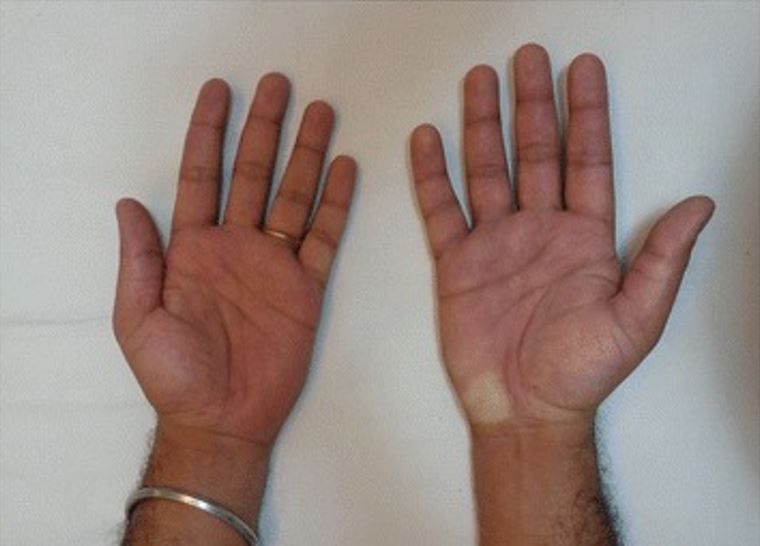
Individual with complex regional pain syndrome, presenting with a swollen right hand, hyperemia and a pale spot on the hypothenar region:
The individual sustained an electrical shock injury to the right hand while repairing a domestic appliance.
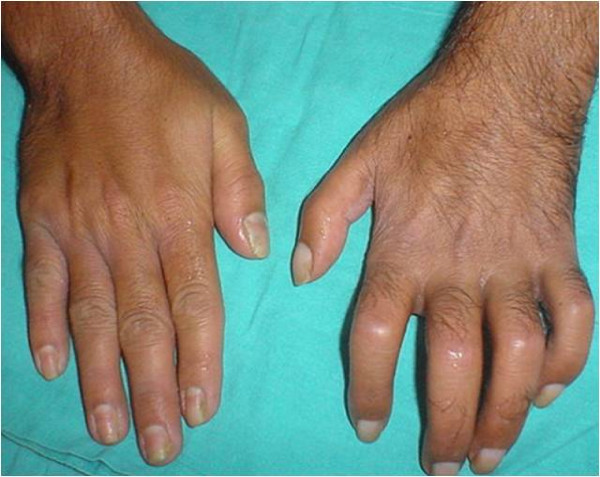
Typical features of complex regional pain syndrome:
On the left hand, note the hypertrichosis, edema, joint stiffness, nail changes, and skin atrophy as compared with the opposite hand.
There are 3 stages of CRPS:
Suspect CRPS when the following historical features are present:
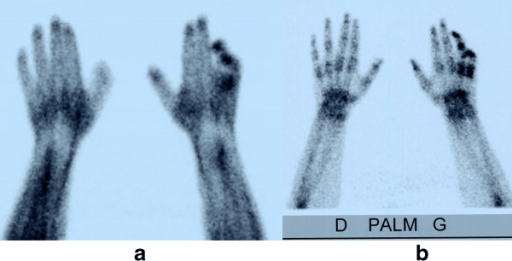
Three-phase bone scintigraphy:
Early and delayed hyperfixation on the 4th and 5th fingers suggest complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS).
a: early phase
b: delayed phase
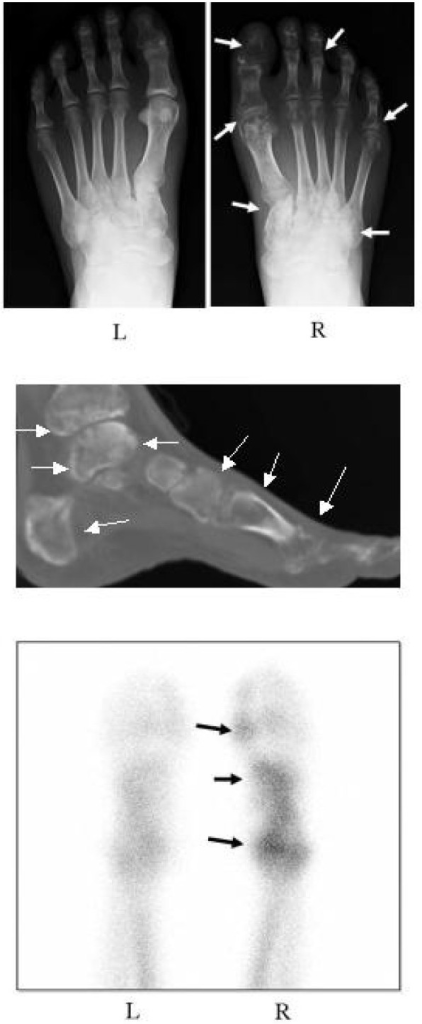
Images of an individual’s feet with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) before treatment with bisphosphonates:
Top picture: Radiograph shows regional osteoporotic changes in the phalanges, metatarsals, and tarsals of the right foot (white arrows). The left foot is normal.
Middle picture: A reconstitution CT shows extensive osteoporotic changes in the foot and ankle (white arrows).
Lower picture: A bone scintigraphy with 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate shows a marked increase in radioactivity in the right foot (black arrows).
| Method | Rationale | Confounding factors |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests | Look for gross bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types pathology (fractures, osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that results from the spread of microorganisms from the blood (hematogenous), nearby infected tissue, or open wounds (non-hematogenous). Infections are most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Osteomyelitis) or other causes of soft tissue Soft Tissue Soft Tissue Abscess swelling Swelling Inflammation. | Sensitivity for CRPS is low, as even trivial injuries can be the trigger Trigger The type of signal that initiates the inspiratory phase by the ventilator Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. |
| 3-phase bone scan Bone Scan Osteosarcoma | Demineralization may be seen even in early stages of CRPS. | Not a sensitive/specific finding, as result may be related to disuse of the extremity rather than a direct result of CRPS |
| Sympathetic block | Provides diagnostic and therapeutic value with individual response | Not diagnostic if pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is unchanged or somatic nerves are blocked at the same time |
| Electromyography Electromyography Recording of the changes in electric potential of muscle by means of surface or needle electrodes. Becker Muscular Dystrophy (EMG) | Can help determine presence of nerve injury Nerve Injury Surgical Complications to confirm diagnosis of CRPS-2 |
|
| Qualitative sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology testing (QST) | The lack of sensitivity to temperature changes suggests dysfunction, which includes the sympathetic nerves. | Little positive and negative predictive value Negative predictive value The NPV is the percentage of people with a negative test result who are actually disease free, among all people with a negative result regardless of whether or not they have the disease. Epidemiological Values of Diagnostic Tests |
The management of CRPS is difficult. Management requires a multidisciplinary approach to pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways in order to be successful.
Control of pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is critical for full compliance Compliance Distensibility measure of a chamber such as the lungs (lung compliance) or bladder. Compliance is expressed as a change in volume per unit change in pressure. Veins: Histology with rehabilitation.
Pharmacologic therapy:
Procedural therapy: