Cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess is a primary headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess disorder characterized by moderate-to-severe unilateral headaches that occur in conjunction with autonomic symptoms. Cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess can last from weeks to months, during which the affected individual may experience attacks up to several times a day, followed by a pain-free remission period. Autonomic symptoms typically manifest as ocular and nasal phenomena (e.g., ptosis Ptosis Cranial Nerve Palsies, miosis Miosis Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities, nasal congestion, rhinorrhea Rhinorrhea Excess nasal drainage. Respiratory Syncytial Virus) on the same side as the headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess. Men are more commonly affected by cluster headaches than women. The diagnosis is clinical and often easy to establish owing to the distinct features of the presenting headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess. The 1st-line treatment involves administration of oxygen by nasal cannula Nasal Cannula Respiratory Failure and/or abortive therapy using a triptan. Preventative strategies (e.g., glucortoicoids, verapamil Verapamil A calcium channel blocker that is a class IV anti-arrhythmia agent. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs) are crucial, as cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess is a chronic condition associated with significant morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status and a high rate of suicide Suicide Suicide is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Patients with chronic medical conditions or psychiatric disorders are at increased risk of suicidal ideation, attempt, and/or completion. The patient assessment of suicide risk is very important as it may help to prevent a serious suicide attempt, which may result in death. Suicide.
Last updated: Apr 13, 2025
Cluster headaches are named based on their tendency to occur in clusters lasting from weeks to months, and interrupted by periods of remission. The defining features include:
Cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess belongs to 2 distinct classification schemes: primary headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess disorders and trigeminal autonomic cephalgias (TACs).
Primary headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess disorders:
Trigeminal autonomic cephalgias:
The pathophysiology of cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess is multifactorial and the precise mechanisms are poorly understood. The prevailing theories of pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways mechanisms are outlined below.
Afferent Afferent Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology nerves of the trigeminal system have neuronal connections with the ANS ANS The ans is a component of the peripheral nervous system that uses both afferent (sensory) and efferent (effector) neurons, which control the functioning of the internal organs and involuntary processes via connections with the CNS. The ans consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic Nervous System: Anatomy. If stimulated, the trigeminal afferents can activate cranial autonomic outflow via the trigeminal-autonomic reflex.
Features of cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess suggest the involvement of the hypothalamus Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is a collection of various nuclei within the diencephalon in the center of the brain. The hypothalamus plays a vital role in endocrine regulation as the primary regulator of the pituitary gland, and it is the major point of integration between the central nervous and endocrine systems. Hypothalamus, which has direct connections to the trigeminal system. Hypothalamic activation also acts as the body’s biological clock and participates in numerous neurohormonal pathways. Factors suggesting hypothalamic involvement include:
There is an overlap in the presenting symptoms and signs of cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess and other primary headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess syndromes, as well as that of other TACs. The distinguishing features are presented below.
Autonomic manifestations accompanying pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways in the trigeminal (V1) distribution are typical of cluster headaches.
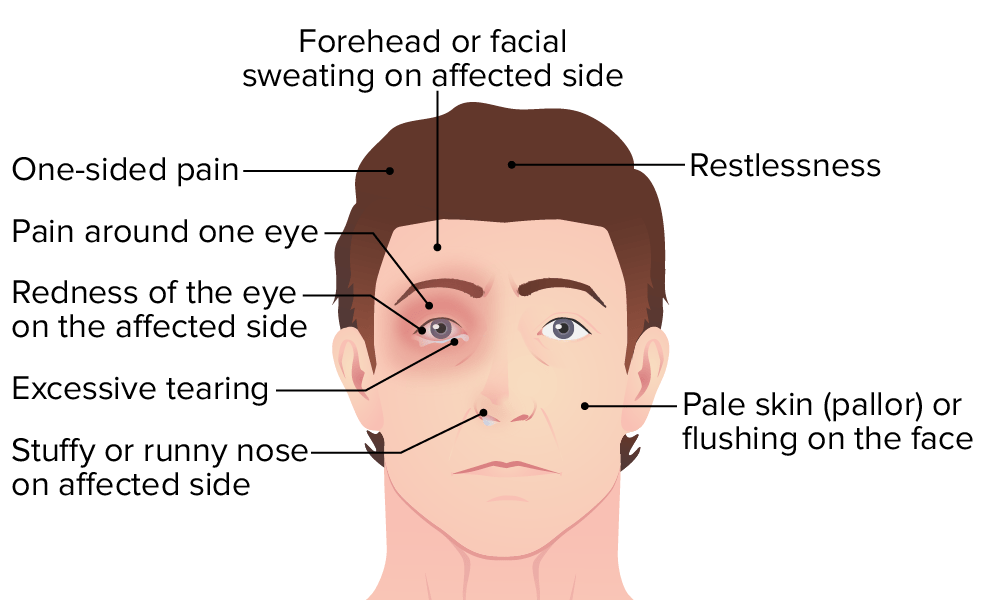
Illustration showing the symptoms of cluster headache
Image by Lecturio.General:
Episodic cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess:
Meets the criteria stated above plus the following criteria:
Chronic cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess:
Meets the criteria stated above plus the following criteria:
While abortive therapy may successfully terminate an isolated attack, preventative therapy is the mainstay of cluster headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess management. Preventive strategies should be started at the onset of headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess episodes.