Calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes channel blockers (CCBs) are a class of medications that inhibit voltage-dependent L-type calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells. The inhibition of these channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane produces vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs and myocardial depression. There are 2 major classes of CCBs: dihydropyridines Dihydropyridines Pyridine moieties which are partially saturated by the addition of two hydrogen atoms in any position. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs and non-dihydropyridines, which differ in their selectivity for cardiac or vascular smooth muscle cells. Broadly, these agents are used to treat hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, angina, and tachyarrhythmias. Side effects are from vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs ( headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess, peripheral edema Peripheral edema Peripheral edema is the swelling of the lower extremities, namely, legs, feet, and ankles. Edema, reflex tachycardia Tachycardia Abnormally rapid heartbeat, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute for adults. Tachycardia accompanied by disturbance in the cardiac depolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) is called tachyarrhythmia. Sepsis in Children) or a consequence of reduced myocardial contractility and nodal conduction velocity ( bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias).
Last updated: Aug 18, 2022
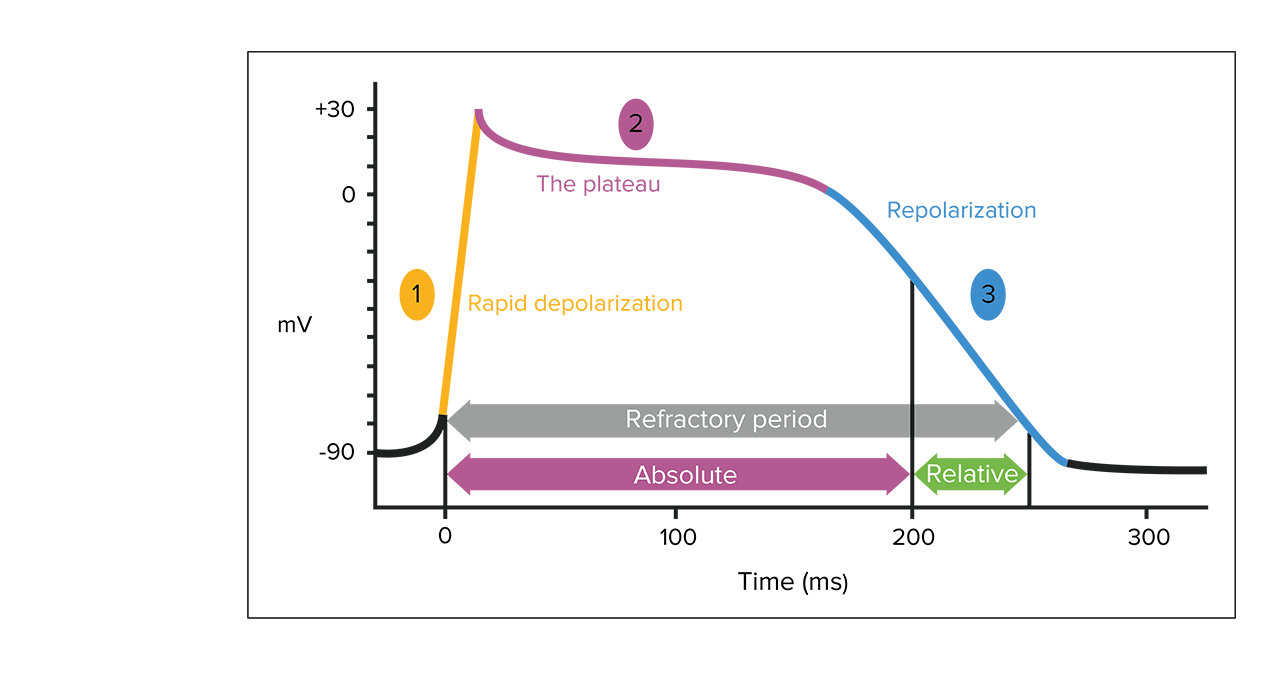
Cardiac myocyte action potential:
1. Sodium channels open, and sodium enters the cell.
2. Sodium channels close; some potassium moves outward. Intracellular calcium increases from entry through L-type calcium channels and release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
3. Calcium channels close and with increased potassium efflux. Cardiac myocytes relax.
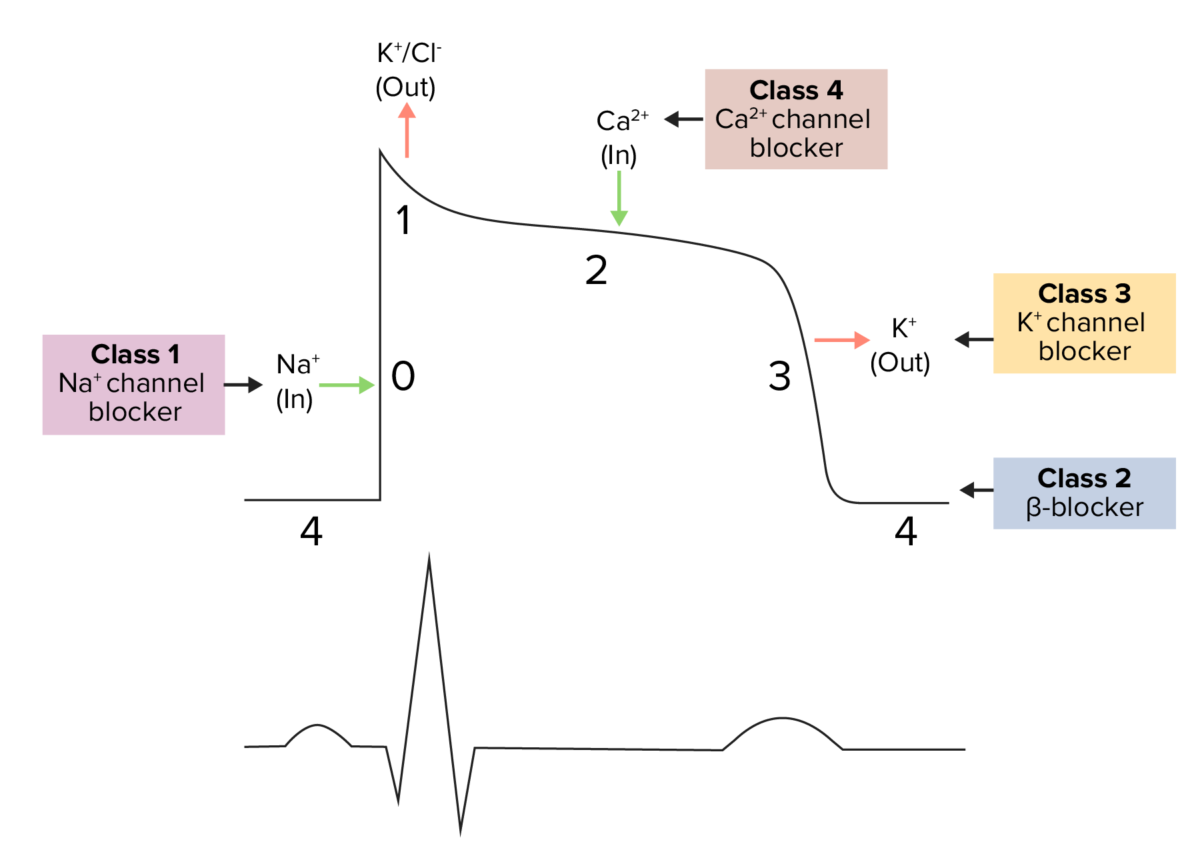
Diagram demonstrating a cardiac action potential and the phases of action for different antiarrhythmic drug classes:
The cycle begins with phase 4, the resting potential. Phase 0 is when rapid depolarization happens due to an influx of sodium ions into the cell. Repolarization follows, with an efflux of potassium through fast potassium channels in phase 1, calcium influx in phase 2 causing a plateau (site of action for calcium channel blockers), and an efflux of potassium through delayed potassium channels in phase 3.
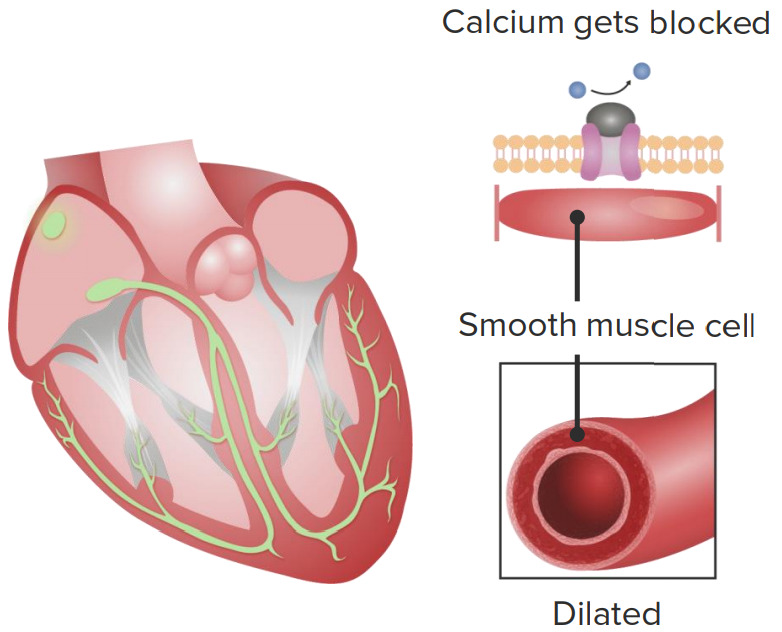
Cardiovascular effects of calcium channel blockers
1. Calcium channel blockers slow down the sinoatrial node, causing lowered heart rate.
2. Calcium channel blockers intake leads to vascular smooth muscle relaxation, causing vasodilation.
| Drug class | Examples | Indications | Key points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dihydropyridines Dihydropyridines Pyridine moieties which are partially saturated by the addition of two hydrogen atoms in any position. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs | Nifedipine, nicardipine, amlodipine Amlodipine A long-acting dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It is effective in the treatment of angina pectoris and hypertension. Hypertension Drugs, felodipine, nimodipine Nimodipine Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
|
|
| Benzothiazepines | Diltiazem |
|
|
| Phenylalkylamines | Verapamil Verapamil A calcium channel blocker that is a class IV anti-arrhythmia agent. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs |
|
|