Class 5 antiarrhythmic drugs are a miscellaneous group of medications that do not belong to a traditional class of antiarrhythmics. These drugs have varied mechanisms of action and uses. The medications in this class are digoxin Digoxin A cardiotonic glycoside obtained mainly from digitalis lanata; it consists of three sugars and the aglycone digoxigenin. Digoxin has positive inotropic and negative chronotropic activity. It is used to control ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and in the management of congestive heart failure with atrial fibrillation. Its use in congestive heart failure and sinus rhythm is less certain. The margin between toxic and therapeutic doses is small. Cardiac Glycosides, adenosine, Mg sulfate, and atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs. Digoxin Digoxin A cardiotonic glycoside obtained mainly from digitalis lanata; it consists of three sugars and the aglycone digoxigenin. Digoxin has positive inotropic and negative chronotropic activity. It is used to control ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and in the management of congestive heart failure with atrial fibrillation. Its use in congestive heart failure and sinus rhythm is less certain. The margin between toxic and therapeutic doses is small. Cardiac Glycosides’s antiarrhythmic effect comes from increased vagal tone and direct action on the atrioventricular node Atrioventricular node A small nodular mass of specialized muscle fibers located in the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus. It gives rise to the atrioventricular bundle of the conduction system of the heart. Heart: Anatomy ( AVN Avn Hip Fractures), resulting in decreased AVN Avn Hip Fractures conduction and sinoatrial (SA) automaticity. Digoxin Digoxin A cardiotonic glycoside obtained mainly from digitalis lanata; it consists of three sugars and the aglycone digoxigenin. Digoxin has positive inotropic and negative chronotropic activity. It is used to control ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and in the management of congestive heart failure with atrial fibrillation. Its use in congestive heart failure and sinus rhythm is less certain. The margin between toxic and therapeutic doses is small. Cardiac Glycosides can be used for atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation ( AFib Afib Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation), atrial flutter Atrial flutter Atrial flutter is a regular supraventricular tachycardia characterized by an atrial heart rate between 240/min and 340/min (typically 300/min), atrioventricular (AV) node conduction block, and a "sawtooth" pattern on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Atrial Flutter (AFL), and supraventricular tachycardia Tachycardia Abnormally rapid heartbeat, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute for adults. Tachycardia accompanied by disturbance in the cardiac depolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) is called tachyarrhythmia. Sepsis in Children ( SVT SVT Supraventricular tachycardias are related disorders in which the elevation in heart rate is driven by pathophysiology in the atria. This group falls under the larger umbrella of tachyarrhythmias and includes paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias (PSVTs), ventricular pre-excitation syndromes (i.e. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome), atrial flutter, multifocal atrial tachycardia, and atrial fibrillation. Supraventricular Tachycardias). Adenosine works on purinergic receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors to cause hyperpolarization Hyperpolarization Membrane Potential, which causes decreased AVN Avn Hip Fractures velocity and increased refractoriness, making it a good choice for cardioversion Cardioversion Atrial Fibrillation of SVT SVT Supraventricular tachycardias are related disorders in which the elevation in heart rate is driven by pathophysiology in the atria. This group falls under the larger umbrella of tachyarrhythmias and includes paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias (PSVTs), ventricular pre-excitation syndromes (i.e. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome), atrial flutter, multifocal atrial tachycardia, and atrial fibrillation. Supraventricular Tachycardias. Magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes’s mechanism of action is not well understood, but it does interact with multiple ion transport mechanisms and is helpful for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with QT prolongation and torsades de pointes Torsades de pointes A malignant form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that is characterized by heart rate between 200 and 250 beats per minute, and QRS complexes with changing amplitude and twisting of the points. The term also describes the syndrome of tachycardia with prolonged ventricular repolarization, long qt intervals exceeding 500 milliseconds or bradycardia. Torsades de pointes may be self-limited or may progress to ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular Tachycardia. Finally, atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs antagonizes muscarinic receptors Muscarinic Receptors Asthma Drugs and blocks vagal effects on the heart, making it useful in symptomatic and unstable bradyarrhythmias Bradyarrhythmias Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias.
Last updated: Jul 5, 2023
This is the most commonly used classifications for antiarrhythmic drugs. There are 5 classes based on the drug class’s general effect (mechanism of action):
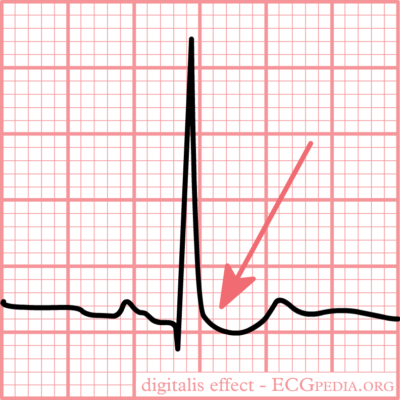
Typical “scooped” ST-segment depression resulting from digoxin use
Image: “Typical for digoxin intoxication is the oddly shaped ST-depression” by I.A.C. van der Bilt, MD. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0Adenosine is a naturally occurring purine nucleoside base.
Cardiac nodal cells:
Vascular smooth muscle cells:
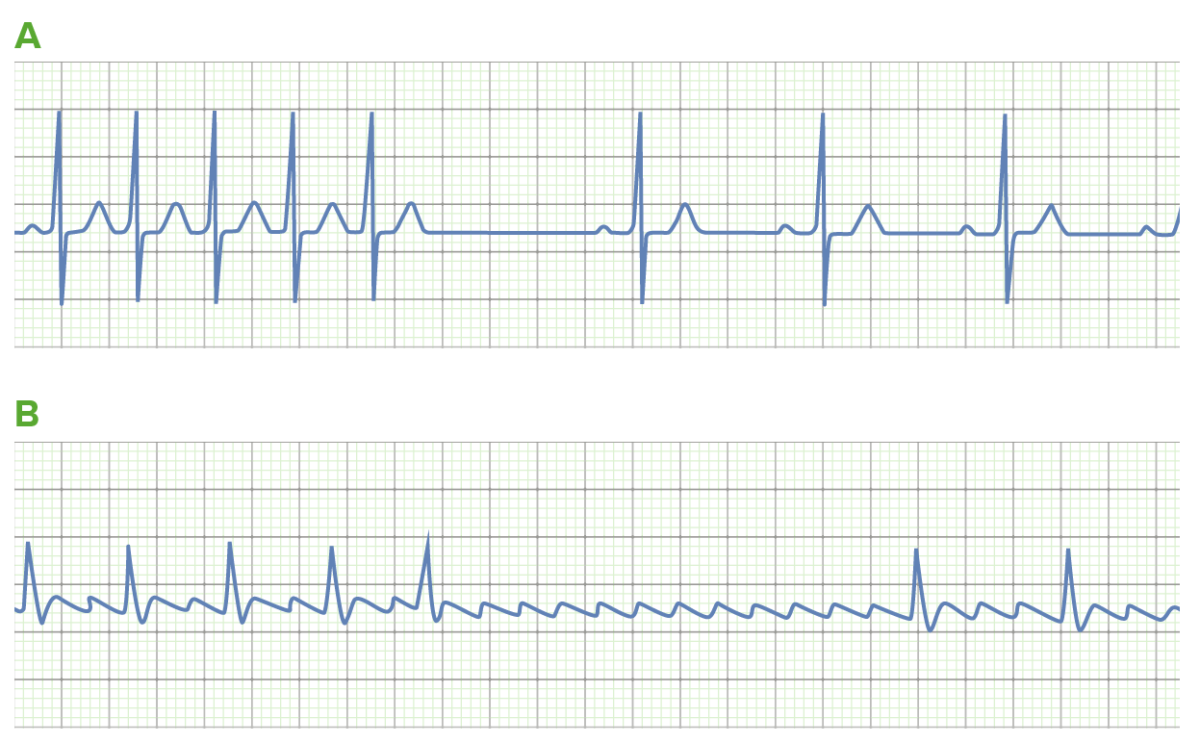
The use of adenosine in tachyarrhythmias:
A: Adenosine can be used to convert supraventricular tachycardias (SVTs), such as atrioventricular node (AVN) reentry tachycardia. Transient blockade of the AVN (noted by the long pause) terminates the reentry circuit, allowing for the resumption of normal sinus rhythm.
B: Sometimes, the underlying rhythm is not certain. Transient AVN blockade may allow for rhythm identification in these cases. This is demonstrated by the uncovering of “sawtooth” flutter waves due to atrial flutter (AFL).
Magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes supplementation for arrhythmias is usually administered IV as Mg sulfate.
Magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes is used as an antiarrhythmic for:
Magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes should be used with caution in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with: