Class 2 antiarrhythmics include beta-blockers, which exert their therapeutic effects by blocking epinephrine Epinephrine The active sympathomimetic hormone from the adrenal medulla. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. Sympathomimetic Drugs and norepinephrine Norepinephrine Precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and is a widespread central and autonomic neurotransmitter. Norepinephrine is the principal transmitter of most postganglionic sympathetic fibers, and of the diffuse projection system in the brain that arises from the locus ceruleus. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS from binding to the beta-adrenergic receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors in cardiac tissue. The outcome is an antiarrhythmic effect, which results from decreased sinoatrial node Sinoatrial node The small mass of modified cardiac muscle fibers located at the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium. Contraction impulses probably start in this node, spread over the atrium (heart atrium) and are then transmitted by the atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His) to the ventricle (heart ventricle). Heart: Anatomy activity and increased atrioventricular conduction time and refractory period. Additional effects include decreased cardiac contractility, afterload Afterload Afterload is the resistance in the aorta that prevents blood from leaving the heart. Afterload represents the pressure the LV needs to overcome to eject blood into the aorta. Cardiac Mechanics, and blood pressure. Class 2 antiarrhythmics are used in the management of atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation, atrial flutter Atrial flutter Atrial flutter is a regular supraventricular tachycardia characterized by an atrial heart rate between 240/min and 340/min (typically 300/min), atrioventricular (AV) node conduction block, and a "sawtooth" pattern on an electrocardiogram (ECG). Atrial Flutter, supraventricular tachycardia Tachycardia Abnormally rapid heartbeat, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute for adults. Tachycardia accompanied by disturbance in the cardiac depolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) is called tachyarrhythmia. Sepsis in Children, and ventricular arrhythmias. Adverse effects include bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias, hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension, bronchospasm Bronchospasm Asthma Drugs, fluid retention, and fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia. Beta-blockers should not be used in individuals with decompensated heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR), shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock, and severe bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias.
Last updated: Jul 21, 2023
Class 2 antiarrhythmics include beta-blockers, which competitively inhibit epinephrine Epinephrine The active sympathomimetic hormone from the adrenal medulla. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. Sympathomimetic Drugs and norepinephrine Norepinephrine Precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and is a widespread central and autonomic neurotransmitter. Norepinephrine is the principal transmitter of most postganglionic sympathetic fibers, and of the diffuse projection system in the brain that arises from the locus ceruleus. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS from binding to the beta-adrenergic receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors on vascular and cardiac cells.
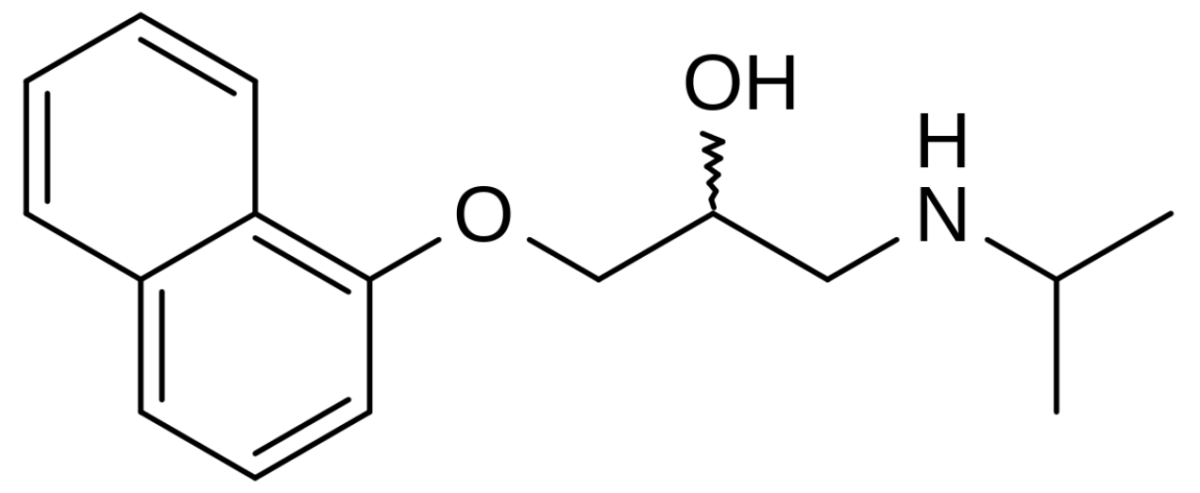
Chemical structure of propranolol
Image: “Chemical structure of propranolol” by catclock. License: Public Domain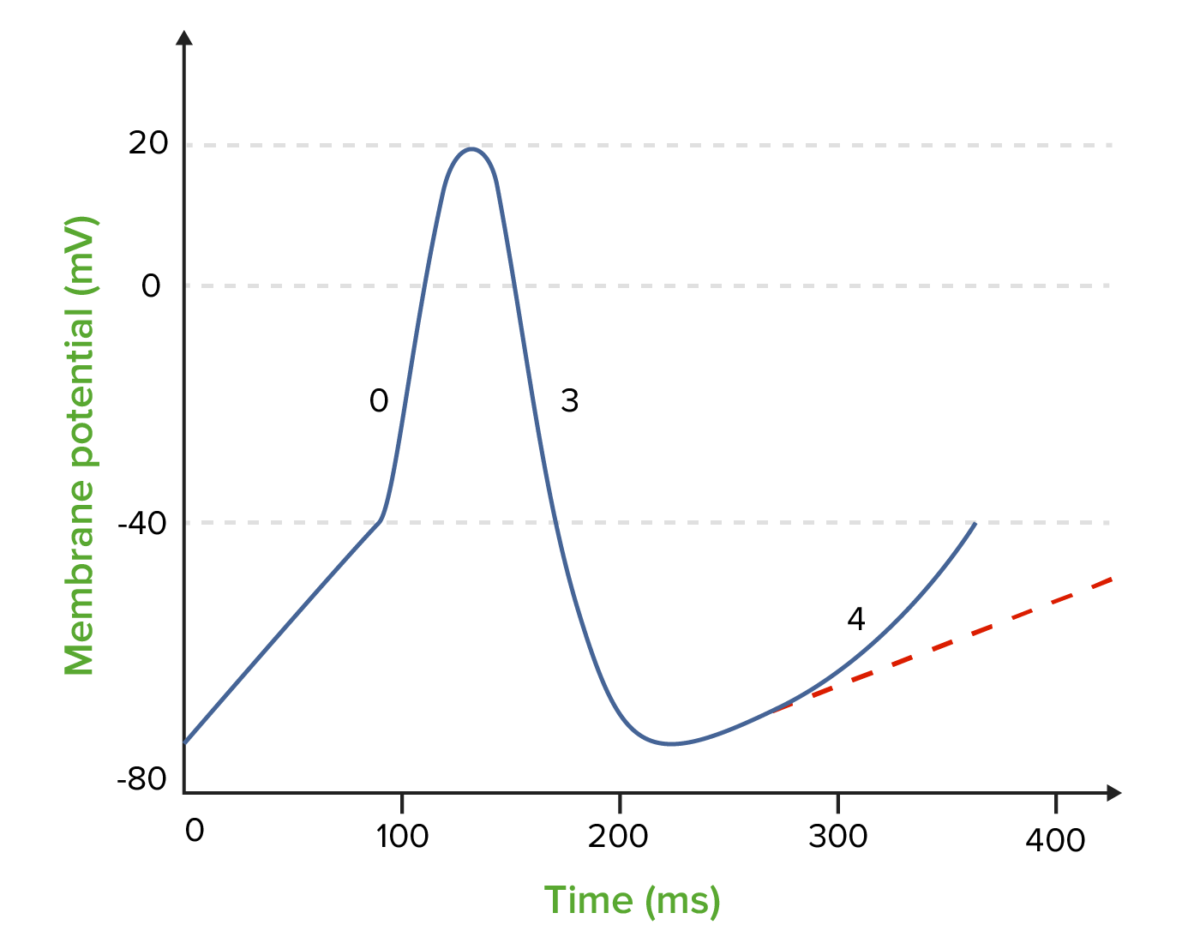
The effect of class 2 antiarrhythmics (beta-blockers) on the nodal action potential:
The dotted line shows the decreased slope and increased duration of phase 4.
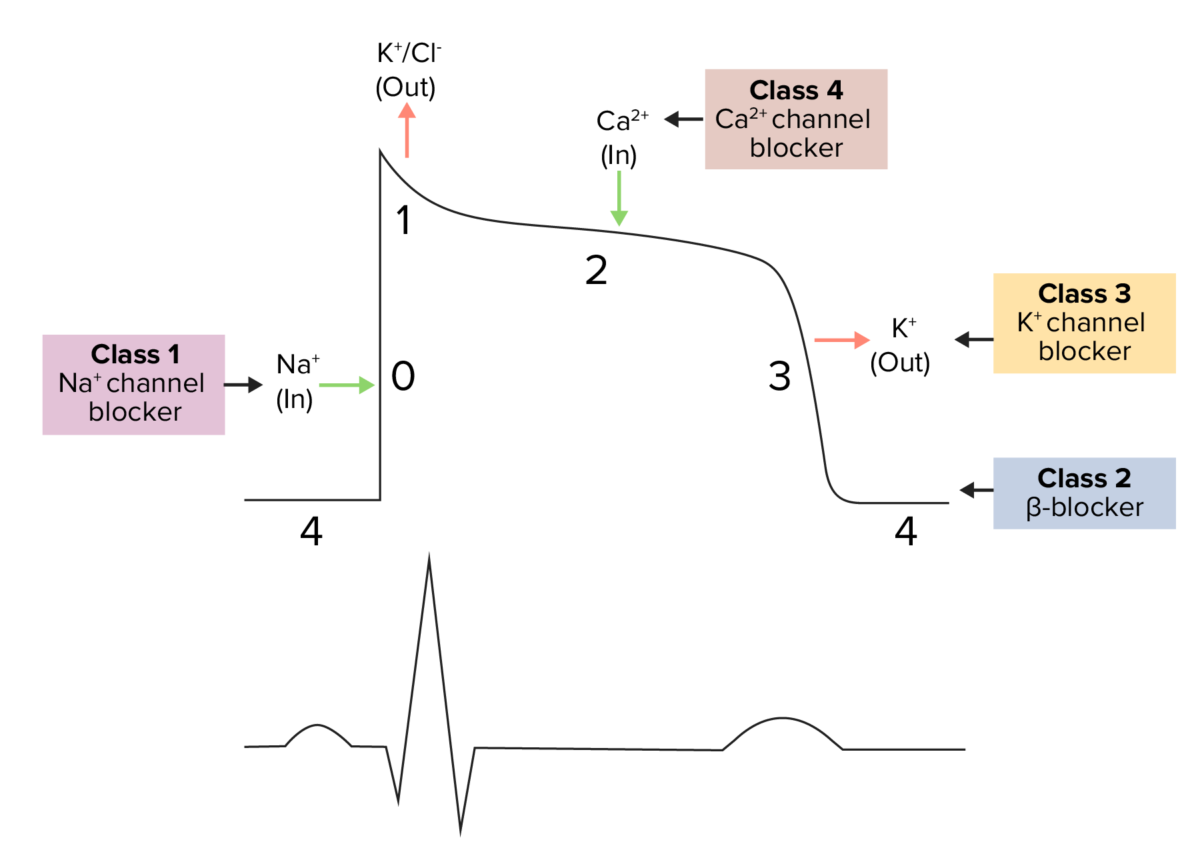
Diagram demonstrating a cardiac action potential and the phases of action for different antiarrhythmic drug classes:
The cycle begins with phase 4, the resting potential. Phase 0 is when rapid depolarization occurs due to an influx of sodium ions into the cell. Repolarization follows, with an efflux of potassium through the fast potassium channels in phase 1, calcium influx in phase 2 causing a plateau (site of action for calcium channel blockers), and efflux of potassium through delayed potassium channels in phase 3.
| Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors location | Response to stimulus | Response to blockade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | |||
| Heart | SA node | ↑ HR | ↓ HR |
| Atria | ↑ Contractility and conduction speed | ↓ Contractility and conduction speed | |
| AV node and His-Purkinje fibers | ↑ Automaticity and conduction speed | ↓ Automaticity and conduction speed | |
| Ventricles | ↑ Contractility, automaticity, conduction speed | ↓ Contractility, automaticity, conduction speed | |
| Kidney | JG cells | ↑ Renin Renin A highly specific (leu-leu) endopeptidase that generates angiotensin I from its precursor angiotensinogen, leading to a cascade of reactions which elevate blood pressure and increase sodium retention by the kidney in the renin-angiotensin system. Renal Sodium and Water Regulation release | ↓ Renin Renin A highly specific (leu-leu) endopeptidase that generates angiotensin I from its precursor angiotensinogen, leading to a cascade of reactions which elevate blood pressure and increase sodium retention by the kidney in the renin-angiotensin system. Renal Sodium and Water Regulation release |
| B2 receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | |||
| Arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology |
|
Vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs | Vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction The physiological narrowing of blood vessels by contraction of the vascular smooth muscle. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure |
| Lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy | Bronchiolar smooth muscle | Bronchodilation | Bronchoconstriction |
| Bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess | Wall | Relaxation | Contraction |
| Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy | Hepatic tissue | Stimulates glycogenolysis Glycogenolysis The release of glucose from glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase (phosphorolysis). The released glucose-1-phosphate is then converted to glucose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase before entering glycolysis. Glycogenolysis is stimulated by glucagon or epinephrine via the activation of phosphorylase kinase. Glycogen Metabolism |
|
| A1 receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | |||
| Arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology | Peripheral | Vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction The physiological narrowing of blood vessels by contraction of the vascular smooth muscle. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure | Vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs |
| Bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess | Sphincter | Contraction | Relaxation |
Some beta-blockers can exhibit the following properties and effects:
| Beta-blocker property | Effect |
|---|---|
| ISA | Partial stimulation of B receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors → suboptimal lowering of HR (avoid post-MI) |
| MSA MSA A syndrome complex composed of three conditions which represent clinical variants of the same disease process: striatonigral degeneration; shy-drager syndrome; and the sporadic form of olivopontocerebellar atrophies. Clinical features include autonomic, cerebellar, and basal ganglia dysfunction. Pathologic examination reveals atrophy of the basal ganglia, cerebellum, pons, and medulla, with prominent loss of autonomic neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord. Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes | Drug can ↓ cardiac conduction velocity by blocking myocyte Na+ channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane |
| NO | Drug stimulates NO production → peripheral vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs |
Class 2 antiarrhythmics can be classified based on their beta-receptor selectivity:
Class 2 antiarrhythmics are used in the management of:
Beta-blockers, as a class, encompass FDA approvals for treating:
| Medication | Arrhythmia | Angina | MI MI MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction | HF | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension | MSA MSA A syndrome complex composed of three conditions which represent clinical variants of the same disease process: striatonigral degeneration; shy-drager syndrome; and the sporadic form of olivopontocerebellar atrophies. Clinical features include autonomic, cerebellar, and basal ganglia dysfunction. Pathologic examination reveals atrophy of the basal ganglia, cerebellum, pons, and medulla, with prominent loss of autonomic neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord. Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atenolol* |
|
X | X | X | ||
| Betaxolol* | Afib Afib Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation | X | X | |||
| Bisoprolol* |
|
X | X | X | ||
| Metoprolol Metoprolol A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias. Antiadrenergic Drugs* |
|
X | X | X | X | X |
| Esmolol Esmolol Antiadrenergic Drugs* |
|
X | ||||
| Acebutolol* | V | X | X | X | X | |
| Nadolol |
|
X | X | X | ||
| Propranolol Propranolol A widely used non-cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Propranolol has been used for myocardial infarction; arrhythmia; angina pectoris; hypertension; hyperthyroidism; migraine; pheochromocytoma; and anxiety but adverse effects instigate replacement by newer drugs. Antiadrenergic Drugs |
|
X | X | X | X | |
| Timolol | Afib Afib Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation | X | X | X | ||
| Carvedilol | Afib Afib Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation/flutter | X | X | X | X | X |
The following table compares antiarrhythmic classes 1‒4. Class 5 is not included due to the varied mechanisms of action and effects.
| Class | Mechanism of action | Effects | Arrhythmia indications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1A |
|
|
|
| 1B | Ventricular | |||
| 1C | Mostly atrial | |||
| 2 |
|
|
Atrial and ventricular | |
| 3 |
|
|
Atrial and ventricular | |
| 4 |
|
|
Atrial | |