Chronic pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis is due to persistent inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation, fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans, and irreversible cell damage to the pancreas Pancreas The pancreas lies mostly posterior to the stomach and extends across the posterior abdominal wall from the duodenum on the right to the spleen on the left. This organ has both exocrine and endocrine tissue. Pancreas: Anatomy, resulting in a loss of endocrine and exocrine gland function. The most common etiologies are alcohol abuse and pancreatic duct obstruction. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship often present with recurrent epigastric abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, and features of malabsorption Malabsorption General term for a group of malnutrition syndromes caused by failure of normal intestinal absorption of nutrients. Malabsorption and Maldigestion syndrome ( diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea, steatorrhea Steatorrhea A condition that is characterized by chronic fatty diarrhea, a result of abnormal digestion and/or intestinal absorption of fats. Diarrhea, and weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery). Characteristic computed tomography (CT) findings include pancreatic atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation, dilated pancreatic ducts, and pancreatic calcifications. Therapy focuses on alcohol cessation, diet changes, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management, and treatment of pancreatic insufficiency.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Common etiologies of chronic pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis are summarized with the “TIGAR-O” mnemonic:
| T | Toxic/metabolic |
|
|---|---|---|
| I | Idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis | May be early- or late-onset |
| G | Genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis |
|
| A | Autoimmune |
|
| R | Recurrent acute pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis | The strongest risk factor for developing chronic pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis |
| O | Obstructive |
|
Gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics abbreviations:
PRSS1 → cationic trypsinogen Trypsinogen The inactive proenzyme of trypsin secreted by the pancreas, activated in the duodenum via cleavage by enteropeptidase. Pancreatic Parameters:
CFTR → cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans transmembrane conductance regulator gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics:
SPINK1 → pancreatic secretory trypsin Trypsin A serine endopeptidase that is formed from trypsinogen in the pancreas. It is converted into its active form by enteropeptidase in the small intestine. It catalyzes hydrolysis of the carboxyl group of either arginine or lysine. Proteins and Peptides inhibitor gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics:
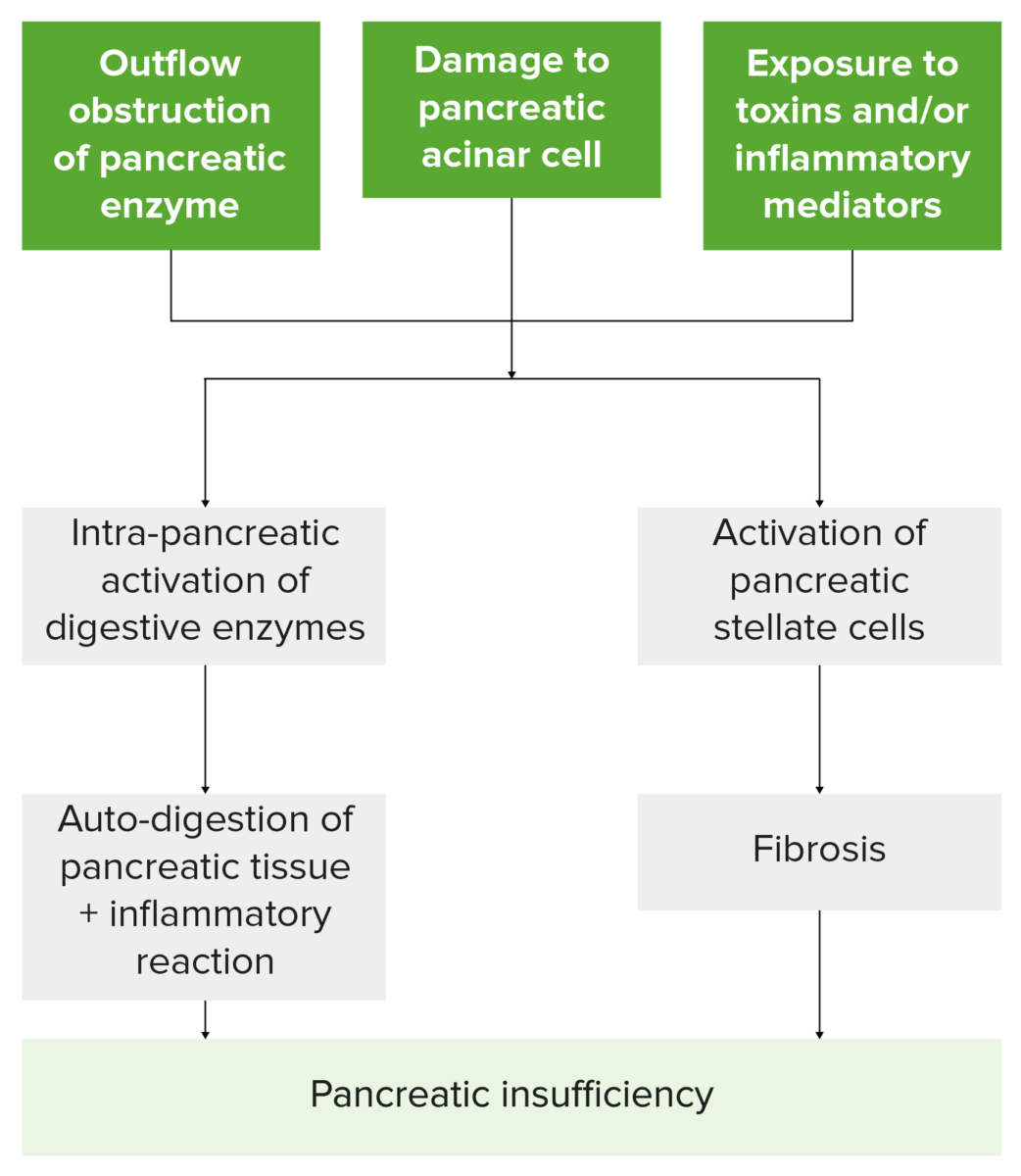
Flowchart summarizing how insults to the pancreas lead to pancreatic insufficiency. Note that injury leads to the activation of pancreatic stellate cells and digestive enzymes, resulting in damaged pancreatic tissue, inflammation, fibrosis, and the loss of exocrine and endocrine cell function.
Image by Lecturio.Laboratory testing is used as an adjunct to imaging.
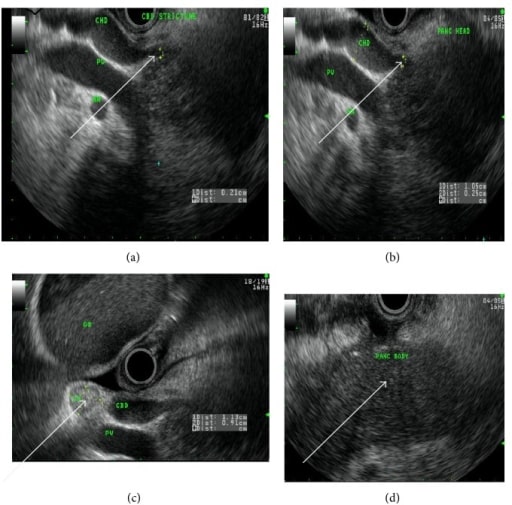
A 50-year-old woman with autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Endoscopic ultrasound image arrows showing (a) common bile duct stricture, (b) dilated common hepatic duct, (c) reactive lymph node, and (d) homogenous pancreatic body.
Image: “fig2” by Lahey Clinic, Burlington, MA 01805, USA. License: CC BY 3.0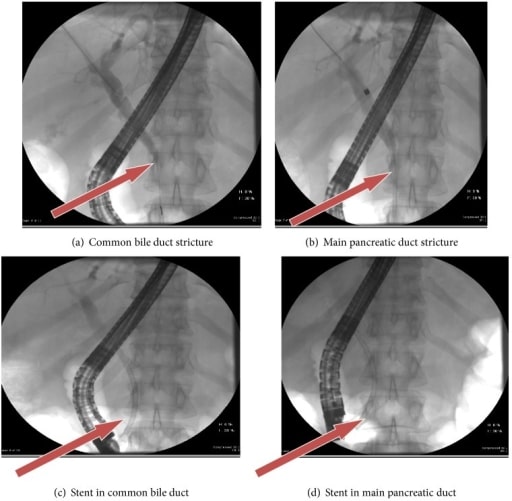
A 50-year-old woman with autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Arrows in ERCP show common bile duct and main pancreatic duct strictures pre-stent insertion (a and b) and post-stent insertion (c and d).
Image: “fig3” by Lahey Clinic, Burlington, MA 01805, USA. License: CC BY 3.0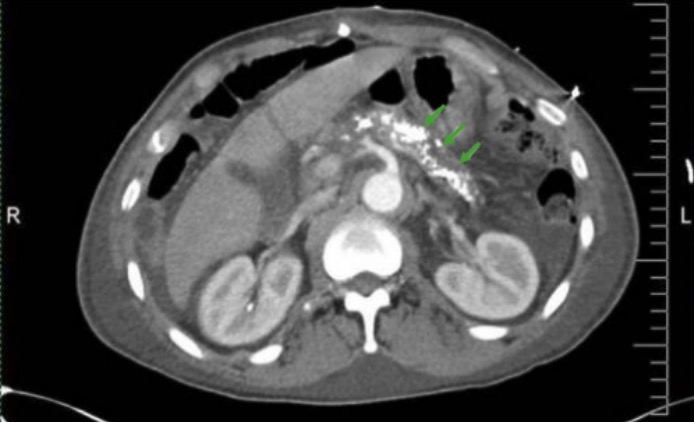
Abdominal CT scan showing pancreatic calcifications in chronic pancreatitis (green arrows)
Image: “CT Abdomen” by Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, BDB 380, USA. License: CC BY 3.0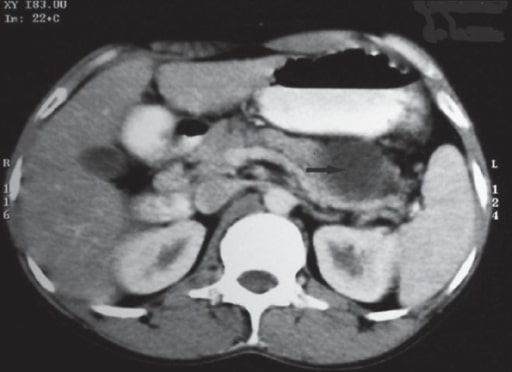
Pancreatic pseudocyst:
CT scan of the abdomen, after oral and IV contrast, showing a cystic lesion in the region of the tail of pancreas, suggestive of pancreatic pseudocyst