The apophysis is a secondary ossification center Secondary ossification center Development of the Limbs found on non-weight-bearing segments of bones. It is the site of ligament or tendon insertion and is involved in the peripheral growth of bones. These secondary growth centers are generally open during childhood and do not close until early adulthood. Chronic apophyseal injury (traction apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease) almost always happens in adolescent athletes during periods of growth. Types of chronic apophyseal injury include Sever disease (posterior calcaneal apophysitis Calcaneal Apophysitis Ankle and Foot Pain), Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease ( tibial tuberosity Tibial tuberosity Leg: Anatomy apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease), little league elbow ( medial epicondyle Medial epicondyle Arm: Anatomy apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease), and Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome (inferior patella Patella The flat, triangular bone situated at the anterior part of the knee. Knee Joint: Anatomy apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease). Diagnosis is generally made clinically. Chronic apophyseal injuries are generally treated with a conservative approach and rarely require surgical intervention.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The apophysis, a secondary ossification center Secondary ossification center Development of the Limbs, may be susceptible to repetitive or acute physical loading, which may lead to injury.
| Disease | Risk factor |
|---|---|
| Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease ( tibial tubercle Tibial Tubercle Osgood-Schlatter Disease apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease) |
|
| Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease ( Apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease of the inferior pole of the patella Patella The flat, triangular bone situated at the anterior part of the knee. Knee Joint: Anatomy) | Sports that involve running and jumping place repetitive tension on the patellar ligament Patellar ligament A band of fibrous tissue that attaches the apex of the patella to the lower part of the tubercle of the tibia. The ligament is actually the caudal continuation of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris. The patella is embedded in that tendon. As such, the patellar ligament can be thought of as connecting the quadriceps femoris tendon to the tibia, and therefore it is sometimes called the patellar tendon. Osgood-Schlatter Disease and can lead to irritation or even avulsion of the apophysis of the inferior pole of the patella Patella The flat, triangular bone situated at the anterior part of the knee. Knee Joint: Anatomy. |
| Pelvic apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease (multiple sites) |
|
| Little league elbow ( medial epicondyle Medial epicondyle Arm: Anatomy apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease) | Repetitive throwing (pitching) places repetitive strain on the apophysis of the medial epicondyle Medial epicondyle Arm: Anatomy—a traction injury. |
| Sever disease ( calcaneal apophysitis Calcaneal Apophysitis Ankle and Foot Pain) |
|
| Iselin disease (5th metatarsal traction apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease) |
|
Injuries related to sports and activities in school-age children are the common presentation:
| Disease | Epidemiology |
|---|---|
| Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease |
|
| Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease | Similar to Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease but commonly occurs in children slightly younger, between ages 10 and 13 |
| Pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease | Age range is wide; related to variation in apophysis growth |
| Little league elbow |
|
| Sever disease |
|
| Iselin disease |
|
The majority of traction apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease presents with localized swelling Swelling Inflammation and pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways at the site of the apophysis that worsens with resisted motion or muscle activation of the associated muscle–tendon complex.
| Disease | Clinical presentation |
|---|---|
| Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease |
|
| Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease |
|
| Pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease (multiple locations) |
|
| Little league elbow |
|
| Sever disease |
|
| Iselin disease |
|
There are specific apophyseal disorders of the pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy with associated muscles. These disorders can present secondary to repetitive trauma, direct trauma Direct Trauma Toddler’s Fractures, or acute avulsion:
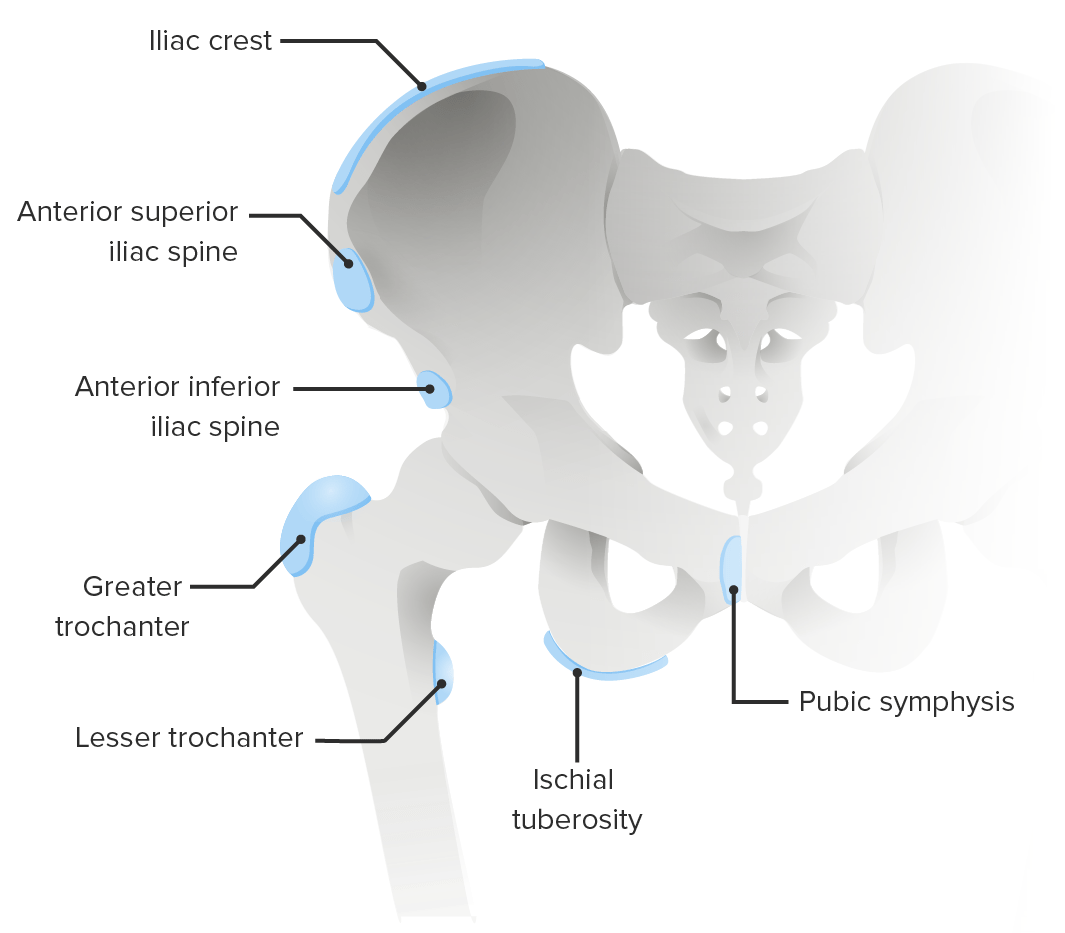
Common sites of apophyseal disorders of the pelvis
Image by Lecturio.| Disease | Radiographic findings |
|---|---|
| Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease | Soft-tissue swelling Swelling Inflammation and fragmentation of the tibial tubercle Tibial Tubercle Osgood-Schlatter Disease |
| Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease | Soft-tissue swelling Swelling Inflammation and calcification or fragmentation of the inferior pole of the patella Patella The flat, triangular bone situated at the anterior part of the knee. Knee Joint: Anatomy |
| Pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy/hip apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease |
|
| Little league elbow | Can show fragmentation or widening of the medial epicondyle Medial epicondyle Arm: Anatomy apophysis |
| Sever disease | Frequently normal on plain radiography |
| Iselin disease | Normal or widened apophysis of the proximal 5th metatarsal |
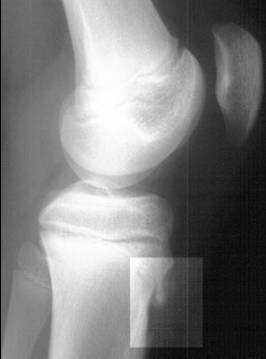
Lateral radiograph demonstrating fragmentation of the tibial tubercle, indicating Osgood-Schlatter disease
Image: “Osgood-Schlatter disease X-ray” by Kristin M Houghton; Radiograph courtesy of BC Children’s Hospital. License: CC BY 2.0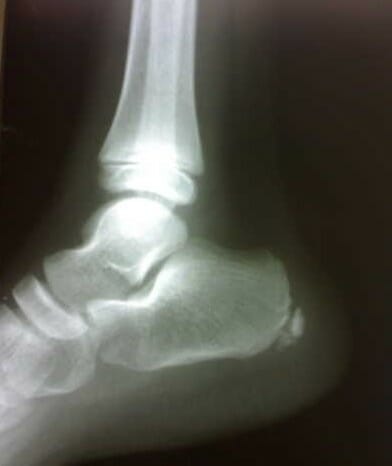
Radiograph of the right foot showing sclerosis and fragmentation of the calcaneal apophysis, indicating Sever disease
Image: “Figure 1 Lateral radiograph of the right foot” by Sitati, F. C. and Kingori, J. License: CC BY 2.0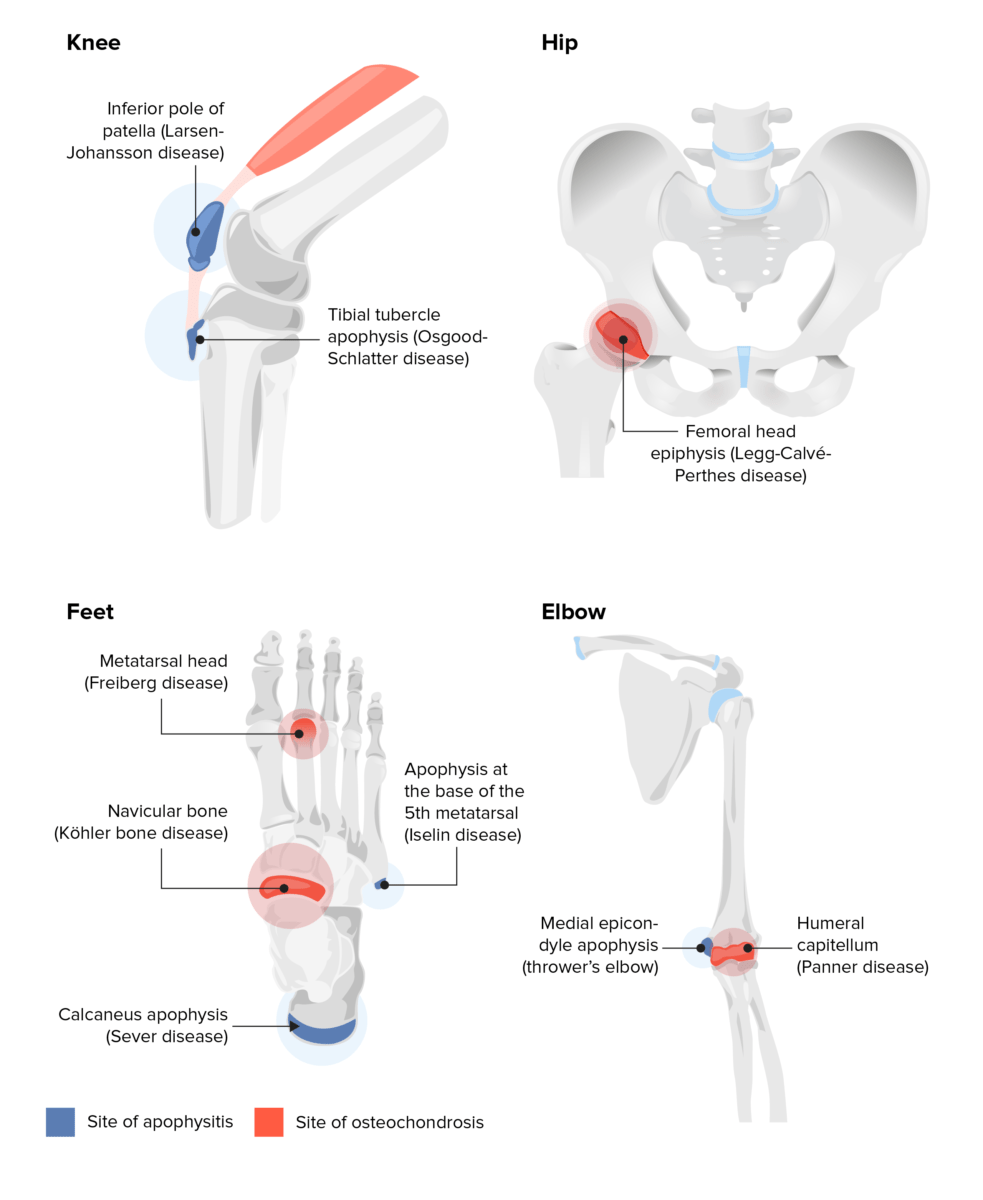
Sites of apophysitis and osteochondrosis
Image by Lecturio.| Disease | Treatment | Indication for orthopedic referral |
|---|---|---|
| Osgood-Schlatter disease Osgood-Schlatter Disease Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Osgood-Schlatter Disease |
|
|
| Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease |
|
|
| Little league elbow |
|
|
| Hip apophysitis Apophysitis Osgood-Schlatter Disease |
|
|
| Sever disease |
|
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship not responding to activity modifications and initial therapy |
| Iselin disease |
|
|