Chlamydial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are a group of infectious diseases caused by a small, gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium belonging to the Chlamydiaceae family. The 3 species that can infect humans are Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia trachomatis Type species of Chlamydia causing a variety of ocular and urogenital diseases. Chlamydia, C. pneumoniae, and C. psittaci. The most common infection is an STI STI Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections that spread either by vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or oral sex. Symptoms and signs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, dysuria, skin lesions (e.g., warts, ulcers) on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some infections can lead to infertility and chronic debilitating disease. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), caused by serotypes D through K of C. trachomatis, which is the most common sexually transmitted bacterial infection in the United States. It can cause cervicitis Cervicitis Inflammation of the uterine cervix. Gonorrhea, urethritis Urethritis Inflammation involving the urethra. Similar to cystitis, clinical symptoms range from vague discomfort to painful urination (dysuria), urethral discharge, or both. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is defined as a polymicrobial infection of the upper female reproductive system. The disease can affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and adjacent structures. Pelvic inflammatory disease is closely linked with sexually transmitted diseases, most commonly caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Gardnerella vaginalis. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, laryngitis, epididymitis Epididymitis Epididymitis and orchitis are characterized by acute inflammation of the epididymis and the testicle, respectively, due to viral or bacterial infections. Patients typically present with gradually worsening testicular pain and scrotal swelling along with systemic symptoms such as fever, depending on severity. Epididymitis and Orchitis, proctitis Proctitis Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum, the distal end of the large intestine. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, and lymphogranuloma venereum. The serotypes A, B, Ba, and C of C. trachomatis cause trachoma, a chronic keratoconjunctivitis that remains the leading infectious cause of blindness Blindness The inability to see or the loss or absence of perception of visual stimuli. This condition may be the result of eye diseases; optic nerve diseases; optic chiasm diseases; or brain diseases affecting the visual pathways or occipital lobe. Retinopathy of Prematurity worldwide. The other species of Chlamydia Chlamydia Chlamydiae are obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria. They lack a peptidoglycan layer and are best visualized using Giemsa stain. The family of Chlamydiaceae comprises 3 pathogens that can infect humans: Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, and Chlamydia pneumoniae. Chlamydia mainly cause respiratory infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Diagnosis is based on nucleic acid amplification Nucleic acid amplification Laboratory techniques that involve the in-vitro synthesis of many copies of DNA or RNA from one original template. Septic Arthritis tests. Management is with antibiotics. Untreated chlamydial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease may have serious consequences, including sterility, ectopic pregnancies, spontaneous abortions, and infertility due to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease Chronic Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Chlamydial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are infectious diseases caused by bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology belonging to the Chlamydiaceae family.
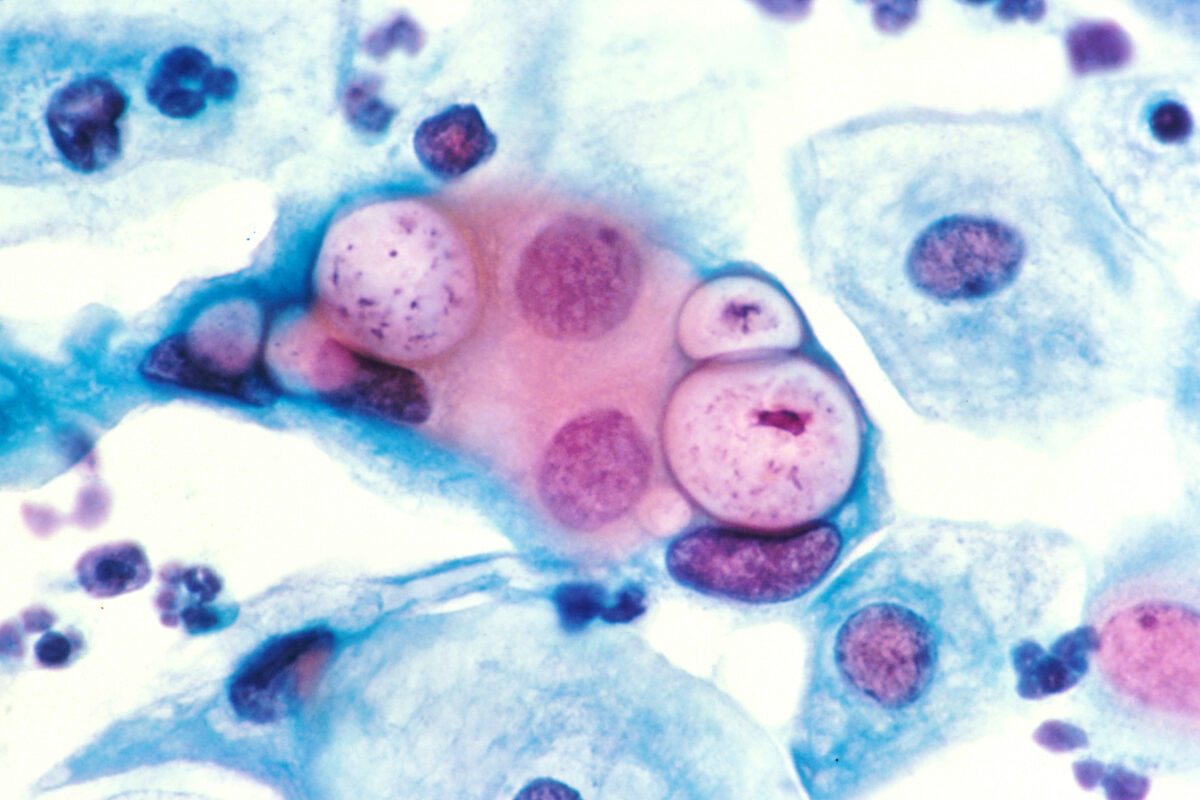
Papanicolaou stain of a cervicovaginal cytology preparation showing 3 chlamydial intranuclear inclusions within squamous epithelial cells that are next to several normal epithelial cells
Image: “Pap smear showing Chlamydia in the vacuoles 500x H&E” by Dr. Lance Liotta Laboratory. License: Public Domain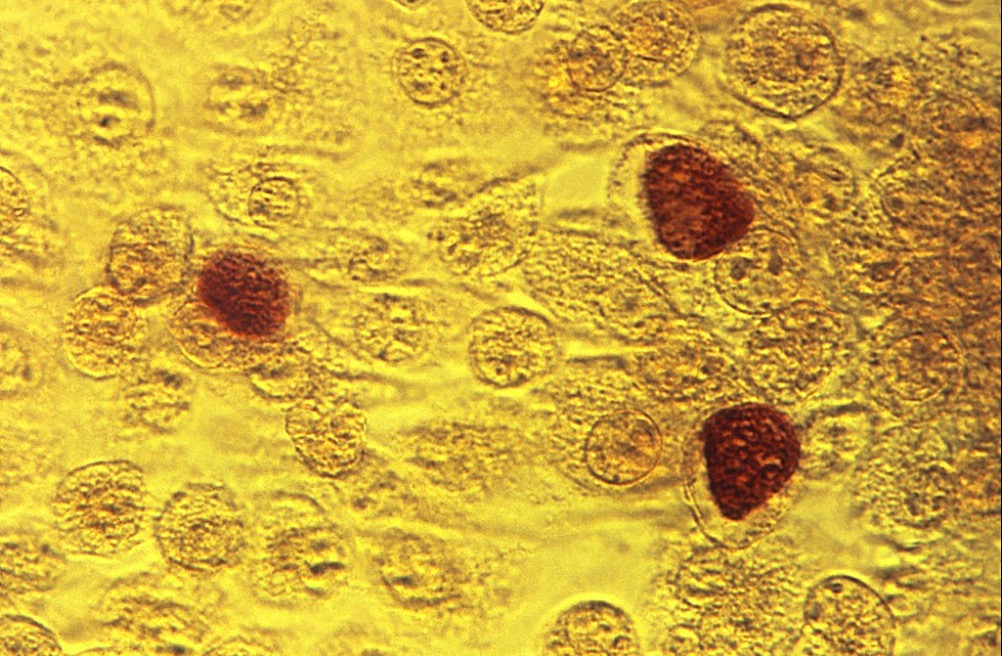
Photomicrograph showcasing McCoy cell monolayers with Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies
Image: “Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies” by CDC/Dr. E. Arum. License: Public DomainGenital disease (serovars d–k):
Infant disease:
Eye disease (serovars a–c):
Lymphogranuloma venereum (serovars l1–l3):
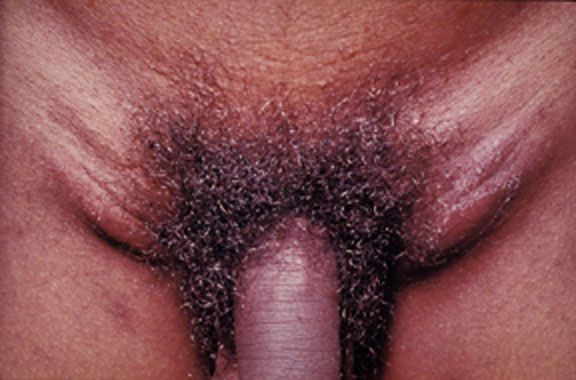
Lymphogranuloma venereum caused by the invasive serovars l1, l2, or l3 of Chlamydia trachomatis. This young adult experienced an acute onset of tender, enlarged lymph nodes in both groins.
Image: “Lymphogranuloma venerum: lymph nodes” by Herbert L. Fred, Hendrik A. van Dijk. License: CC BY 2.0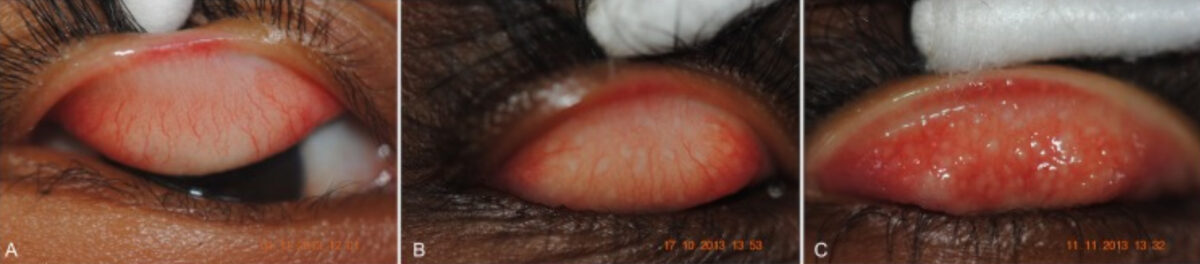
Photographs of conjunctivae showing (A) no evidence of active trachoma, (B) mild trachomatous inflammation-follicular (TF), and (C) more severe TF
Image: “Low Prevalence of Conjunctival infection with Chlamydia trachomatis in a treatment-naïve trachoma-endemic region of the Solomon Islands” by PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. License: CC BY 4.0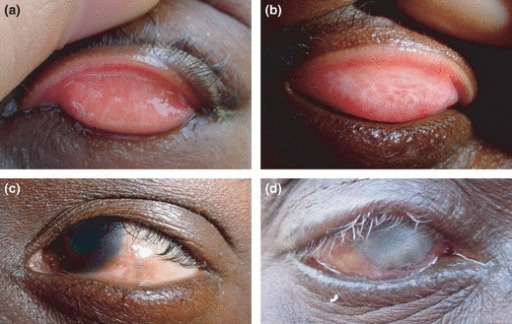
Trachoma
Recurrent episodes of infection with serovars a–c of Chlamydia trachomatis cause conjunctival inflammation in children, who eventually develop scarring and blindness as adults.
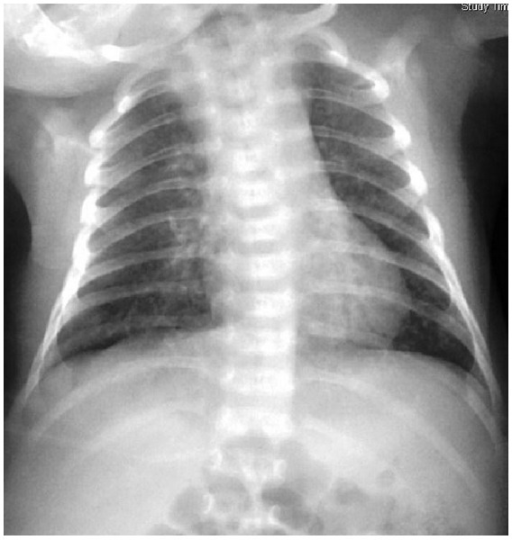
Chlamydia trachomatis neonatal pneumonia: diffuse patchiness on a chest radiogram
Image: “Chlamydial pneumonitis: a creepy neonatal disease” by Hon KL, Leung AK. License: CC BY 3.0History:
Physical exam:
Laboratory studies:
General approach:
Antibiotics:
Trachoma:
Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia:
| C. trachomatis | C. psittaci | C. pneumoniae |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|