Child and adolescent care is the area of healthcare dedicated to individuals who are beyond the immediate neonatal age through adulthood. These individuals do not present a uniform group, but are a series of patient populations, each with evolving healthcare needs (both preventive and pathologic) unique to them. Appropriate care aims to ensure optimal overall health to promote the physical, emotional, and social well-being of these often-challenging populations. Primary care physicians Physicians Individuals licensed to practice medicine. Clinician–Patient Relationship are usually responsible for child and adolescent care. Well-child visits are scheduled yearly for this purpose. These visits are an opportunity to obtain a detailed clinical history, monitor physiologic and psychologic development, assess growth parameters, and perform a thorough physical examination. Age-specific screenings, counseling, and vaccinations should also be completed at these times.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A comprehensive history should be obtained, particularly for individuals new to the physician.
Birth history is usually obtained only at 1st visit, or if pertinent.
As part of the comprehensive physical exam, special consideration should be given to the areas below.
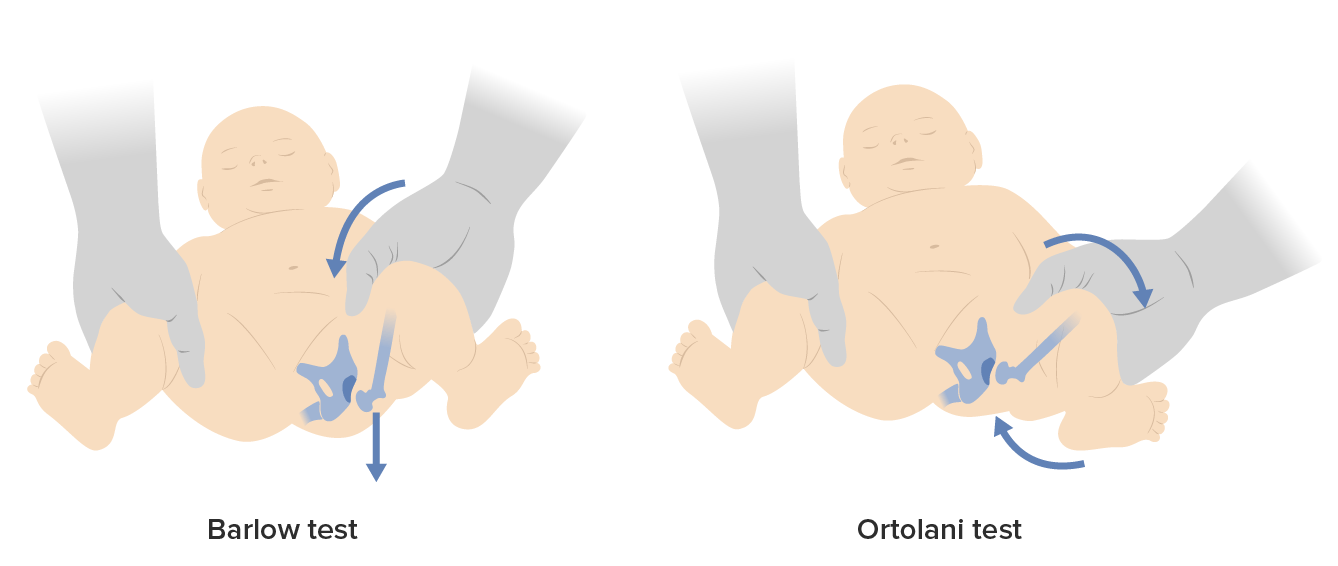
Special tests to assess developmental dysplasia in infants
Image by Lecturio.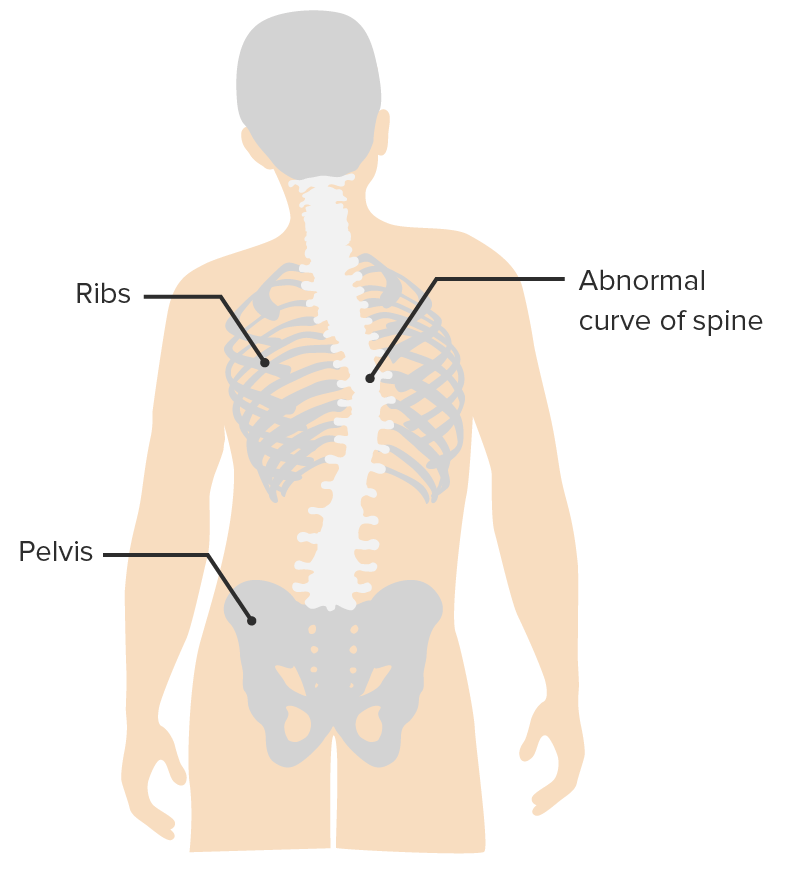
Scoliosis
Image by Lecturio.Immunizations provide children and adolescents protection against multiple vaccine-preventable infectious diseases.
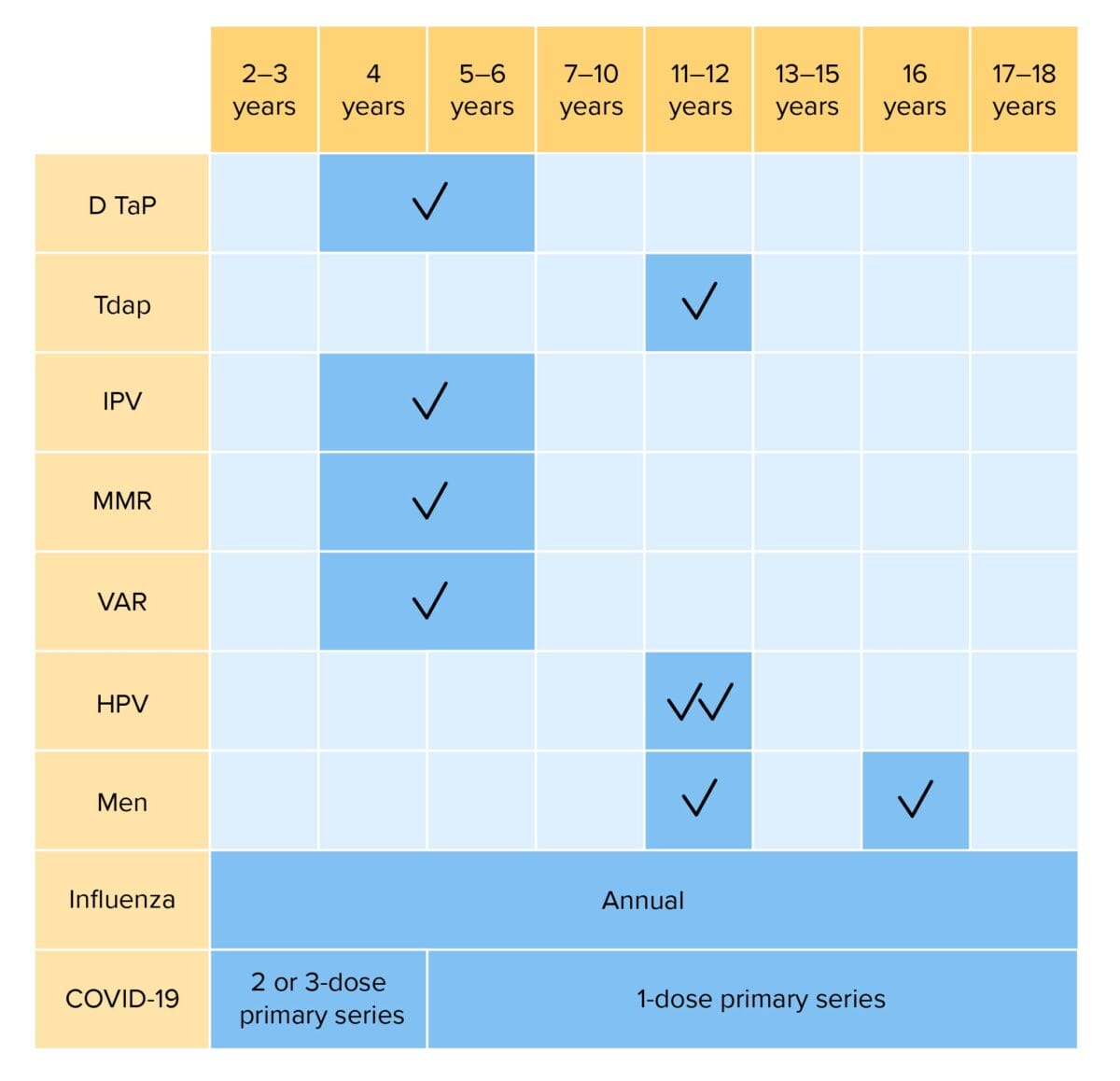
Routine vaccinations for children 2–18 years of age:
DTaP: diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccination
Tdap: tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccination
Hib: Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccination
IPV: inactivated poliovirus vaccination
MMR: measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination
VAR: varicella vaccination
HPV: human papillomavirus vaccination
Men: meningococcal vaccination
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination (bivalent)
Surveillance Surveillance Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth and screening Screening Preoperative Care for additional physical and psychosocial problems are an essential component of child and adolescent care.
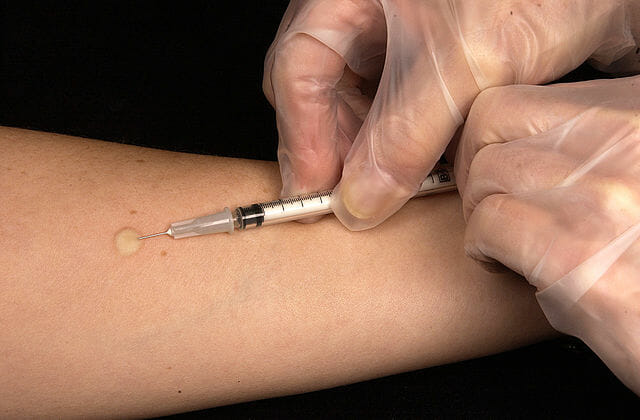
Mantoux test:
The Mantoux skin test consists of an intradermal injection of ⅒ of a mL of PPD tuberculin. The circular shape is known as a wheal response.
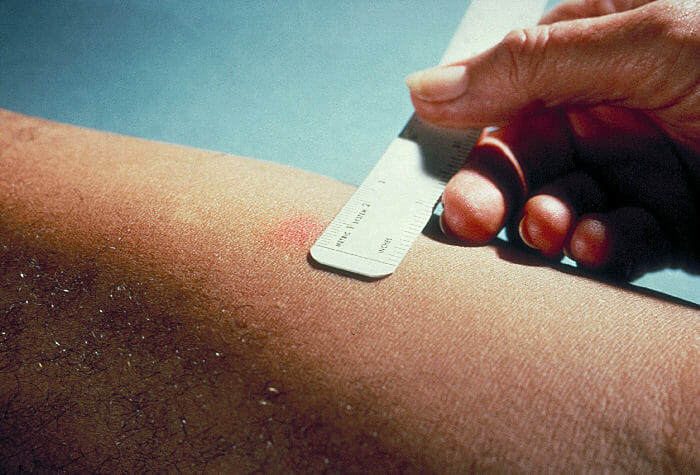
Mantoux test:
The size of induration is measured 48–72 hours after injection. Erythema (redness) should not be measured.
Age-appropriate topics should be discussed for guidance in the home setting.