Child abuse is an act or failure to act that results in harm to a child’s health or development. The abuse encompasses neglect as well as physical, sexual, and emotional harm. Seen in all subsets of society, child abuse is a cause of significant morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status and mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status in the pediatric population. Diagnosis is made with a thorough interrogation of events and physical examination, and treatment is multidisciplinary and long term. Physicians Physicians Individuals licensed to practice medicine. Clinician–Patient Relationship are legally mandated to report all cases of abuse.
Last updated: Mar 29, 2023
Child abuse refers to an act or failure to act that results in actual or potential harm to a minor’s health, development, or dignity by the parent or caregiver responsible for the child’s welfare. In the majority of the United States, a minor is defined as a child below 18 years of age, unless emancipated by law.
There are 4 main types of child abuse:
Failure to thrive Failure to Thrive Failure to thrive (FTT), or faltering growth, describes suboptimal weight gain and growth in children. The majority of cases are due to inadequate caloric intake; however, genetic, infectious, and oncological etiologies are also common. Failure to Thrive is the most common presentation of child abuse. Frequent emergency department visits or a delay in presentation with injuries inconsistent with history are red flags. The following features in history and physical examination increase the likelihood ratio of abuse:
History:
Physical examination:
Shaken baby syndrome:
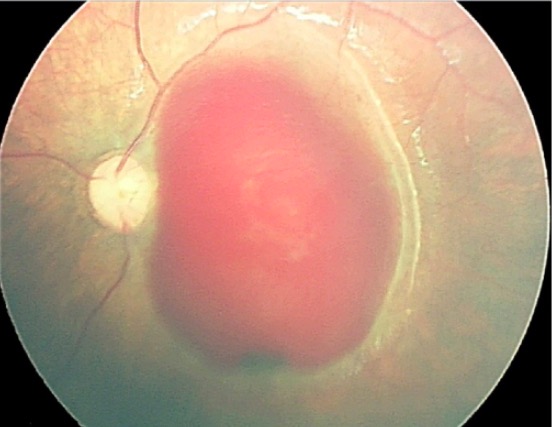
Retinography made by RetCam of the posterior pole of the left eye of an abused child:
Note the extensive subinternal limiting membrane hemorrhage.
History:
Physical examination (always done with a chaperone):
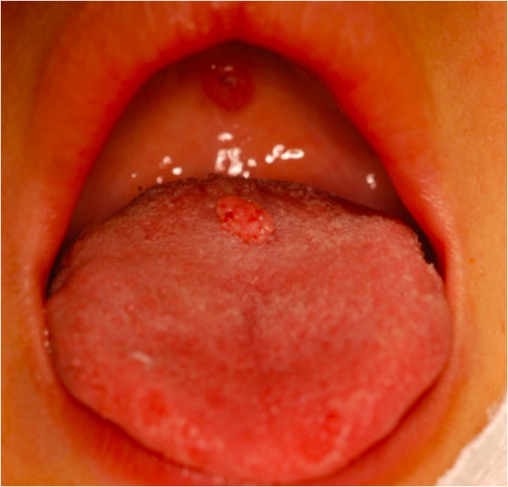
Condyloma acuminata on the tongue of a sexually abused child
Image: “Lesion located on the tongue with a pedicled base” by Araçatuba Dental School, Univ, Estadual Paulista (UNESP), Rua José Bonifácio 1193, 16015-050 Araçatuba, SP, Brazil. License: CC BY 2.0History:
Physical examination:
History:
Physical examination:
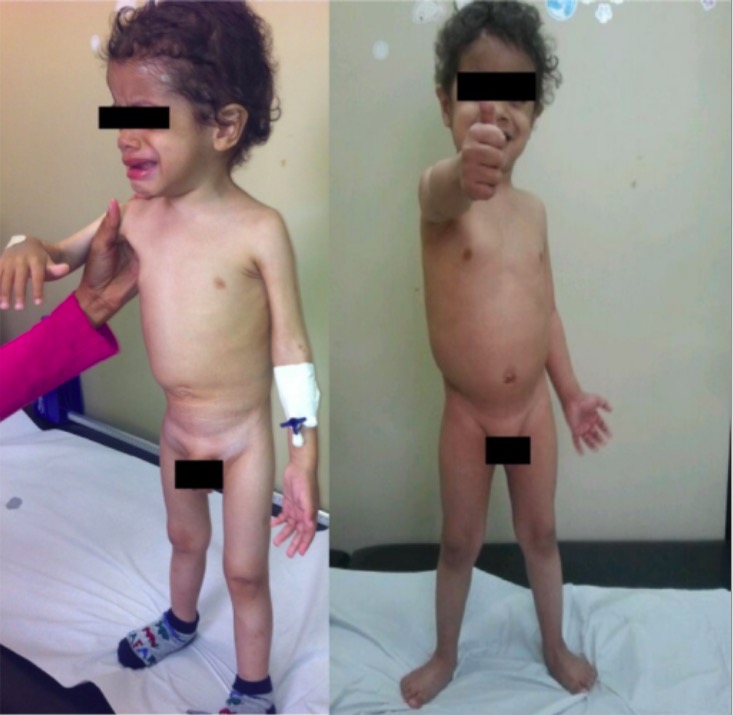
Severe protein-calorie malnutrition due to abuse by starvation
Image: “Patient 2” by Marcela Montenegro Braga Barroso et al. License: CC BY 4.0Red flags that specify a nonaccidental trauma can be best remembered by the mnemonics TEN-4 and FACES P:
Physicians Physicians Individuals licensed to practice medicine. Clinician–Patient Relationship must have a high index of suspicion in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with risk factors and red flags as determined from the history and physical examination. To confirm suspicion, a thorough physical examination, including ophthalmological and neurological exam, must be done.
To gather as much information as possible, the physician must:
Investigation includes:
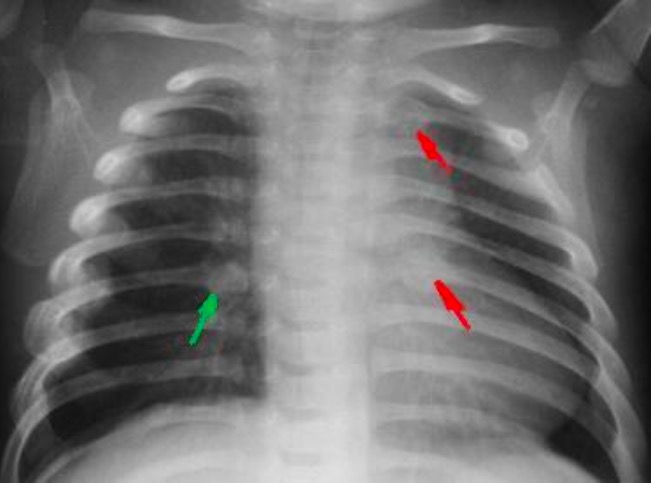
Rib fractures in an infant secondary to child abuse
Image: “Fractured ribs” by National Institute of Health. License: Public Domain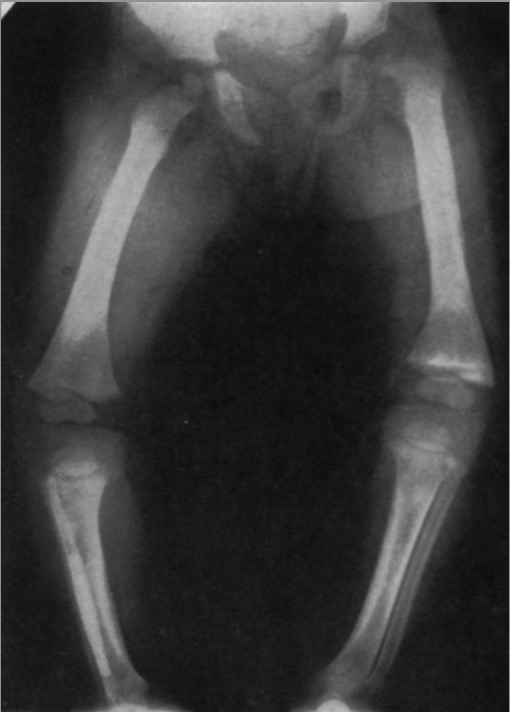
X-ray showing partial separation of a left upper femoral epiphysis
Image: “X-ray showing partial separation of a left upper femoral epiphysis” by Jennifer Crane. License: CC BY 4.0In cases of sexual abuse Sexual Abuse Sexual abuse and assault are major public health problems that affect many people from all walks of life, including people of all ages and genders, but it is more prevalent in women and girls, with reports of up to 1 in 3 experiencing sexual assault at some time in their life. Sexual Abuse:
Physicians Physicians Individuals licensed to practice medicine. Clinician–Patient Relationship are legally mandated to report all cases to child protective services. Documentation Documentation Systematic organization, storage, retrieval, and dissemination of specialized information, especially of a scientific or technical nature. It often involves authenticating or validating information. Advance Directives at every step and visit is essential to support suspicion.
The following conditions are part of the differential diagnosis of child abuse and must be kept in mind when documenting to report: