Chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is one of the most common and challenging complaints that may present in an inpatient and outpatient setting. The differential diagnosis of chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is large and includes cardiac, gastrointestinal, pulmonary, musculoskeletal, and psychiatric etiologies. Assessing for life-threatening causes, such as acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and pulmonary embolism Pulmonary Embolism Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a potentially fatal condition that occurs as a result of intraluminal obstruction of the main pulmonary artery or its branches. The causative factors include thrombi, air, amniotic fluid, and fat. In PE, gas exchange is impaired due to the decreased return of deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Pulmonary Embolism, should be a priority. From there, a careful history, examination, and diagnostic workup will help in determining the diagnosis and subsequent appropriate management.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The anatomy of the chest and thorax includes: heart, lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy, breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy, and chest wall Chest wall The chest wall consists of skin, fat, muscles, bones, and cartilage. The bony structure of the chest wall is composed of the ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae. The chest wall serves as armor for the vital intrathoracic organs and provides the stability necessary for the movement of the shoulders and arms. Chest Wall: Anatomy.
Description of chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways:
Typical chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways descriptions and their clinical significance:
Risk factors:
Vital sign abnormalities and their possible diseases:
Examples of important findings in the physical exam:
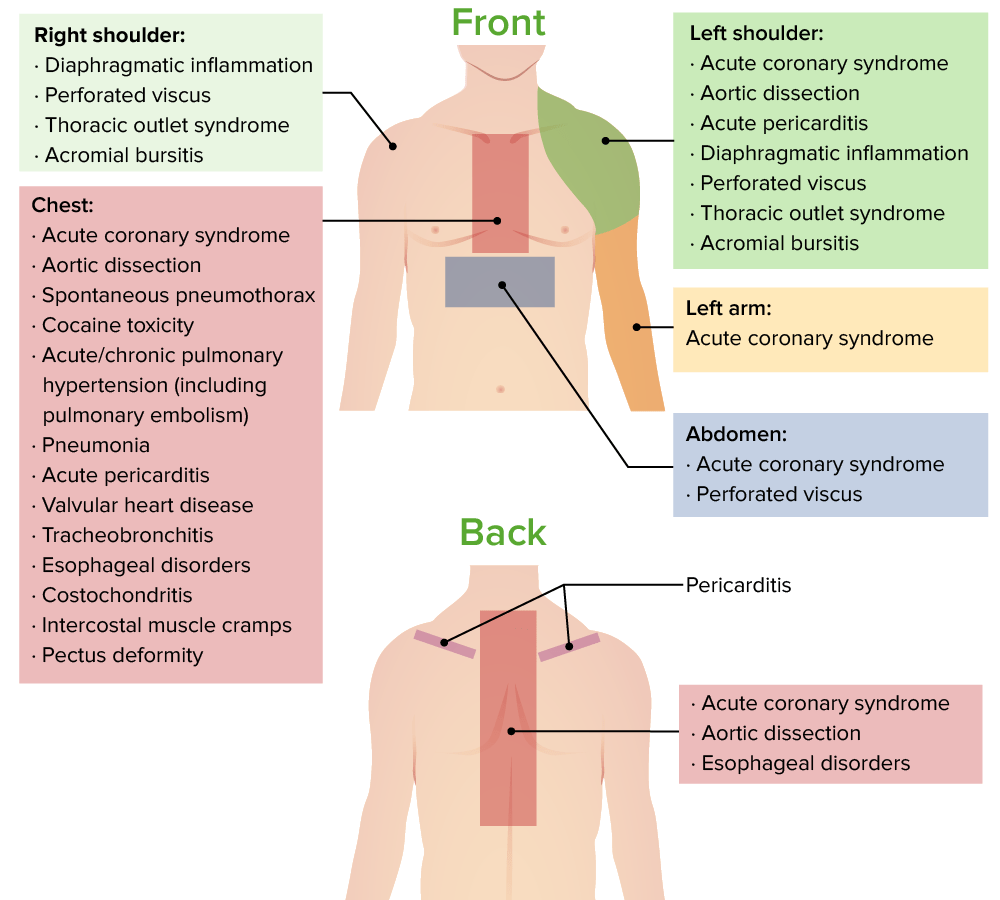
Causes of chest pain and sites of referred pain
Image by Lecturio.Directed toward the most likely diagnosis:
Disease and consultants: