Chédiak-Higashi syndrome ( CHS CHS Cannabinoids) is an autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance disorder caused by mutations affecting a lysosomal trafficking regulator protein. This protein plays a crucial role in the inability of neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation to kill phagocytosed microbes. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with CHS CHS Cannabinoids exhibit recurrent pyogenic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, easy bleeding and bruising, and neurologic manifestations. The syndrome is also associated with oculocutaneous albinism Oculocutaneous albinism Heterogeneous group of autosomal recessive disorders comprising at least four recognized types, all having in common varying degrees of hypopigmentation of the skin, hair, and eyes. The two most common are the tyrosinase-positive and tyrosinase-negative types. Albinism. The diagnosis is made based on analysis of the patient’s blood or bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis smear and genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies. The treatment of choice is allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Signs and symptoms that usually appear soon after birth include the following:
Late-onset neurological manifestations that appear in individuals who survive early childhood with curative treatment:
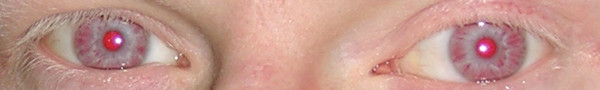
Hypopigmented eyes and eyelashes in a patient with oculocutaneous albinism:
This may be seen in Chédiak-Higashi syndrome.
Chédiak-Higashi syndrome ( CHS CHS Cannabinoids) can progress to the accelerated phase Accelerated phase The phase of chronic myeloid leukemia following the chronic phase, where there are increased systemic symptoms, worsening cytopenias, and refractory leukocytosis. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia characterized by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis A group of related disorders characterized by lymphocytosis; histiocytosis; and hemophagocytosis. The two major forms are familial and reactive. Epstein-Barr Virus (HLH), where hyperactive WBCs cause excessive inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and tissue damage. It develops in 80-85% of CHS CHS Cannabinoids patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship and is usually lethal. Signs and symptoms include:
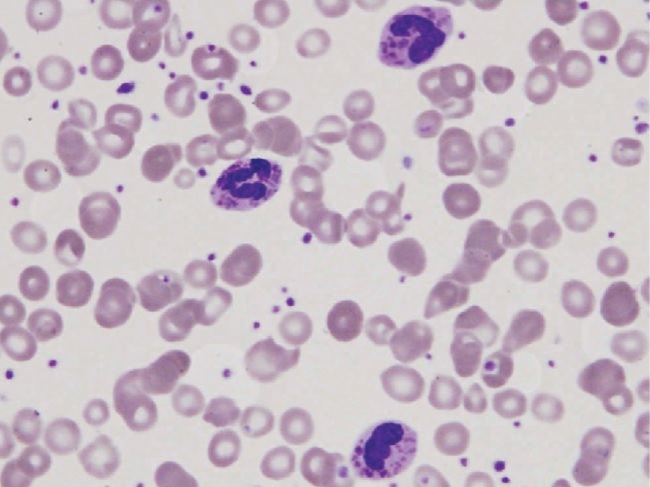
Peripheral blood smear in a patient with Chédiak-Higashi syndrome depicting 3 polymorphonuclear leukocytes with large granules. These findings are typical.
Image: “Peripheral blood smear of our patient with Chediak-Higashi” by Morrone K. License: CC BY 3.0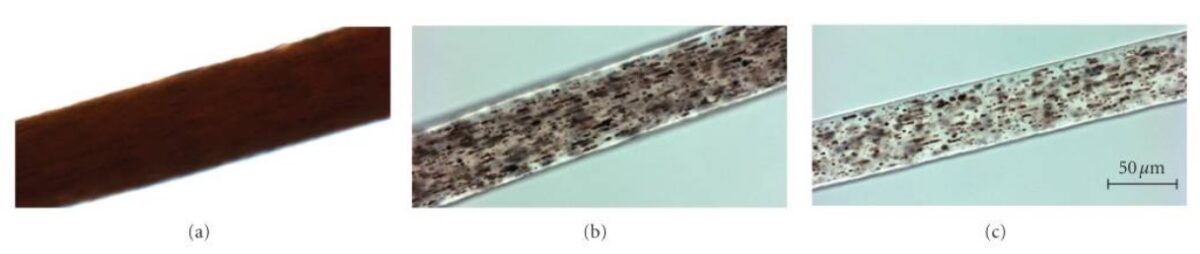
Hair shaft samples under high-powered light microscopy:
(a): African American control hair sample, demonstrating evenly distributed pigment in the hairshaft
(b): hair sample of a severely affected Chédiak-Higashi syndrome patient demonstrating an atypical granular distribution of “pigmented clumps” in the hair shaft
(c): hair sample from an African American patient with Chédiak-Higashi syndrome demonstrating a similar atypical granular pigmentation pattern