Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Furthermore, of that percentage, 25% may develop complications of the suppurative lymph nodes. Given the growth of H. ducreyi on a special medium (often not readily available), chancroid is diagnosed based upon clinical appearance and tests to rule out both syphilis and herpes (the most common causes of genital ulcers). Although the disease can resolve spontaneously, antibiotics (azithromycin or ceftriaxone) are the treatment of choice. Treatment should involve both patients and their sexual contacts.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Chancroid Chancroid Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Chancroid ( soft chancre Soft chancre Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Chancroid) is a sexually transmitted disease Sexually Transmitted Disease Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that spread either by vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or oral sex. Symptoms and signs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, dysuria, skin lesions (e.g., warts, ulcers) on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some infections can lead to infertility and chronic debilitating disease. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) caused by a bacterium, Haemophilus ducreyi Haemophilus ducreyi A species of Haemophilus that appears to be the pathogen or causative agent of the sexually transmitted disease, chancroid. Haemophilus, characterized by painful genital ulcers and suppurative inguinal adenopathy.
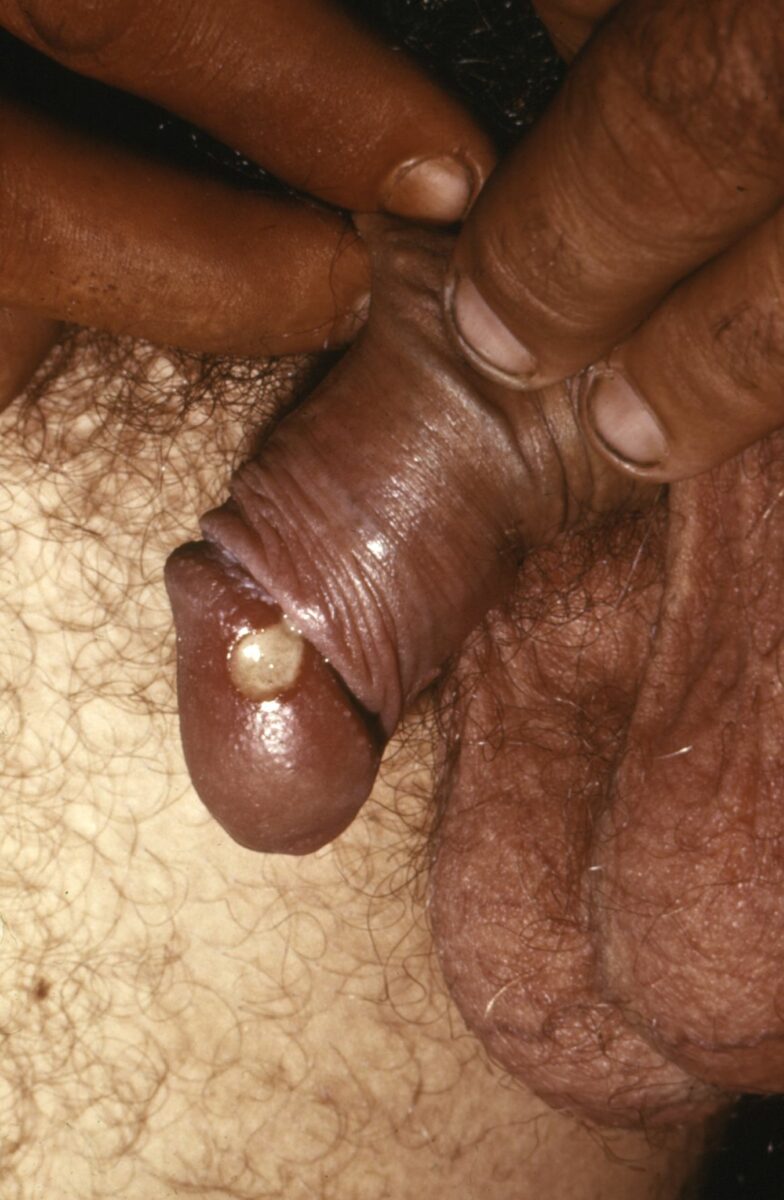
Chancroid: 1 cm (0.39 in) lesion on the glans of the penis confirmed to be from Haemophilus ducreyi
Image: “Chancroid lesion haemophilus ducreyi PHIL 3728 lores” by Joe Miller. License: Public Domain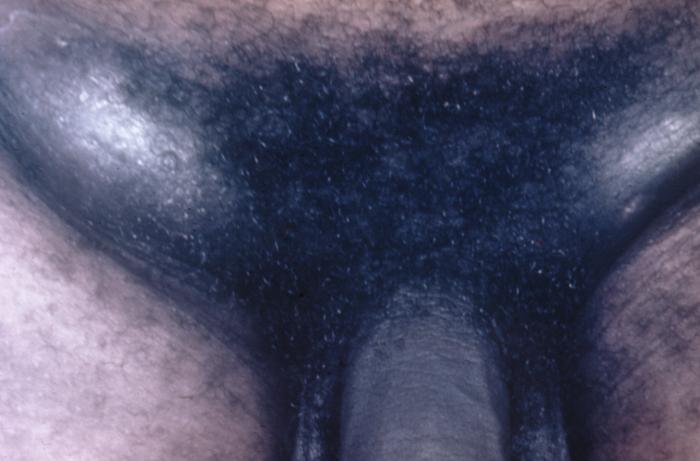
Inguinal lymphadenopathy:
lymph nodes in the groin, which in half of presented cases develop into buboes that can enlarge until they burst through the overlying skin.
Diagnosis is made by clinical judgment Judgment The process of discovering or asserting an objective or intrinsic relation between two objects or concepts; a faculty or power that enables a person to make judgments; the process of bringing to light and asserting the implicit meaning of a concept; a critical evaluation of a person or situation. Psychiatric Assessment and tests to rule out the 2 most common causes of genital ulcers, herpes simplex Herpes Simplex A group of acute infections caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 or type 2 that is characterized by the development of one or more small fluid-filled vesicles with a raised erythematous base on the skin or mucous membrane. It occurs as a primary infection or recurs due to a reactivation of a latent infection. Congenital TORCH Infections virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology ( HSV HSV Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae. Herpes simplex virus commonly causes recurrent infections involving the skin and mucosal surfaces, including the mouth, lips, eyes, and genitals. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2) and syphilis Syphilis Syphilis is a bacterial infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum pallidum (T. p. pallidum), which is usually spread through sexual contact. Syphilis has 4 clinical stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Syphilis.[2,3,8]
| Disease | Are ulcers painful? | Typical ulcer size and number | Other characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genital herpes Genital Herpes Genital herpes infections are common sexually transmitted infections caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2. Primary infection often presents with systemic, prodromal symptoms followed by clusters of painful, fluid-filled vesicles on an erythematous base, dysuria, and painful lymphadenopathy. Labial and Genital Herpes | Yes | 1‒2 mm, multiple | |
| Syphilis Syphilis Syphilis is a bacterial infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum pallidum (T. p. pallidum), which is usually spread through sexual contact. Syphilis has 4 clinical stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Syphilis | No | 1‒2 cm, usually one | |
| Chancroid Chancroid Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Chancroid | Yes | 1‒2 cm, usually multiple | |
| Lymphogranuloma venereum Lymphogranuloma venereum Subacute inflammation of the inguinal lymph glands caused by certain immunotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis. It is a sexually transmitted disease in the U.S. But is more widespread in developing countries. It is distinguished from granuloma venereum, which is caused by calymmatobacterium granulomatis. Chlamydial Infections | No | 2‒10 mm, usually one | |
| Granuloma inguinale Granuloma inguinale Donovanosis (also known as granuloma inguinale) is an STD caused by Klebsiella granulomatis and is mainly seen in tropical regions. The condition is characterized by chronic, progressive, ulcerating disease mostly affecting the genital region. Donovanosis ( donovanosis Donovanosis Donovanosis (also known as granuloma inguinale) is an STD caused by Klebsiella granulomatis and is mainly seen in tropical regions. The condition is characterized by chronic, progressive, ulcerating disease mostly affecting the genital region. Donovanosis) | No | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables | |
| Behçet’s syndrome | Yes | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables | |
| Lipschütz ulcer (acute genital ulceration Ulceration Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers) | Yes | > 1 cm, multiple and bilateral |
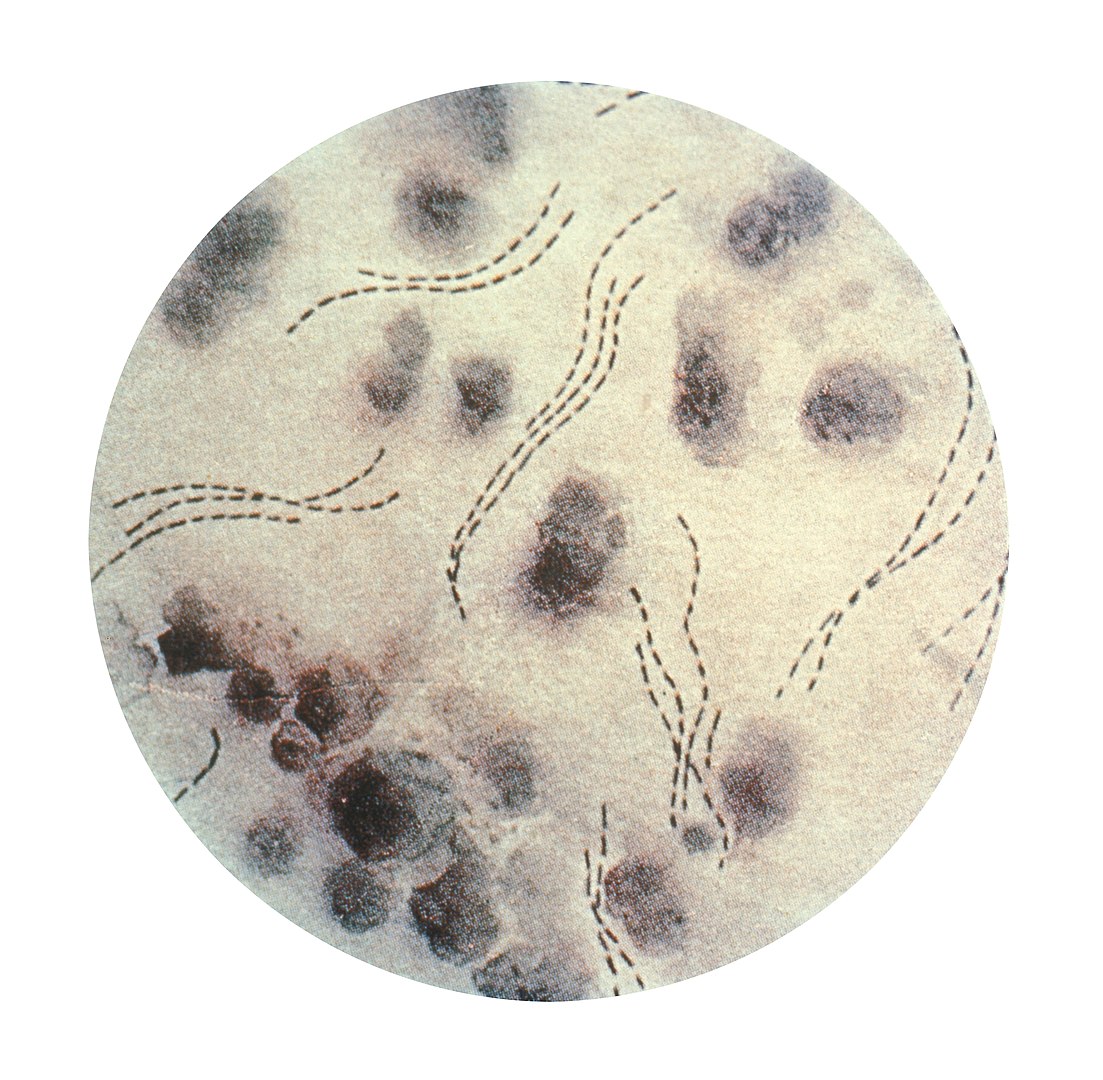
Haemophilus ducreyi bacteria
Image: “Haemophilus ducreyi 01” by CDC. License: Public DomainManagement may vary depending on practice location. The following information is based on US and European recommendations; however, please review your local guidelines.
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose
chancroid
Chancroid
Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy.
Chancroid, a
sexually transmitted infection
Sexually Transmitted Infection
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections that spread either by vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or oral sex. Symptoms and signs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, dysuria, skin lesions (e.g., warts, ulcers) on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some infections can lead to infertility and chronic debilitating disease.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) caused by the bacterium
Haemophilus ducreyi
Haemophilus ducreyi
A species of Haemophilus that appears to be the pathogen or causative agent of the sexually transmitted disease, chancroid.
Haemophilus, characterized by painful genital ulcers and suppurative
inguinal lymphadenopathy
Inguinal Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | A57 | Chancroid Chancroid Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Chancroid |
| SNOMED CT | 23670000 | Chancroid Chancroid Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Chancroid (disorder) |
Medications:
These codes are for the antibiotics used to treat
chancroid
Chancroid
Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or “soft chancre”). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy.
Chancroid. A single dose of
azithromycin
Azithromycin
A semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic structurally related to erythromycin. It has been used in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infections, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis.
Macrolides and Ketolides or
ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone
A broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic and cefotaxime derivative with a very long half-life and high penetrability to meninges, eyes and inner ears.
Cephalosporins is the recommended and most effective treatment.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 18631 | Azithromycin Azithromycin A semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic structurally related to erythromycin. It has been used in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infections, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis. Macrolides and Ketolides (ingredient) |
| RxNorm | 2240 | Ceftriaxone Ceftriaxone A broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic and cefotaxime derivative with a very long half-life and high penetrability to meninges, eyes and inner ears. Cephalosporins (ingredient) |