A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender. Diagnosis is based on history and physical exam findings. Most chalazia will resolve with conservative management.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Occurs due to gland blockage, which can be associated with:
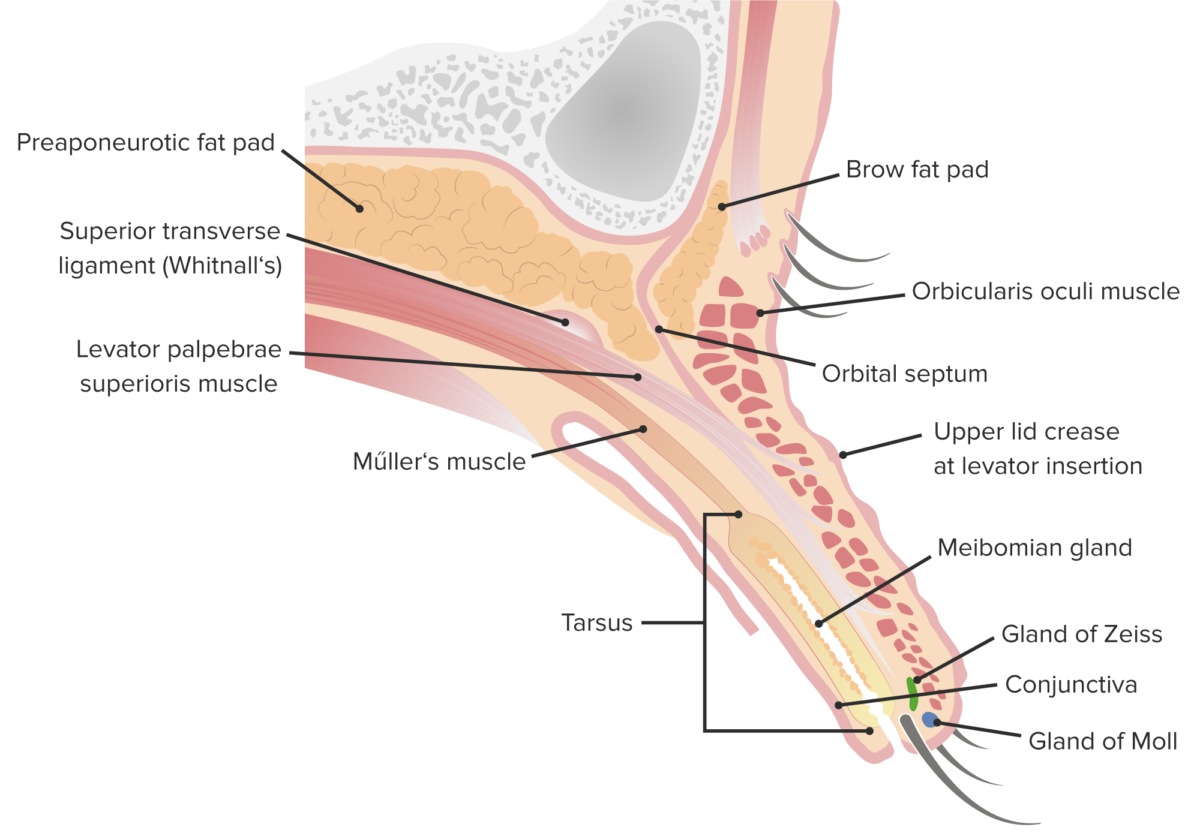
Anatomy of the eyelid: Note the locations of the Meibomian and Zeis glands, which are typically involved in the formation of a chalazion.
Image by Lecturio.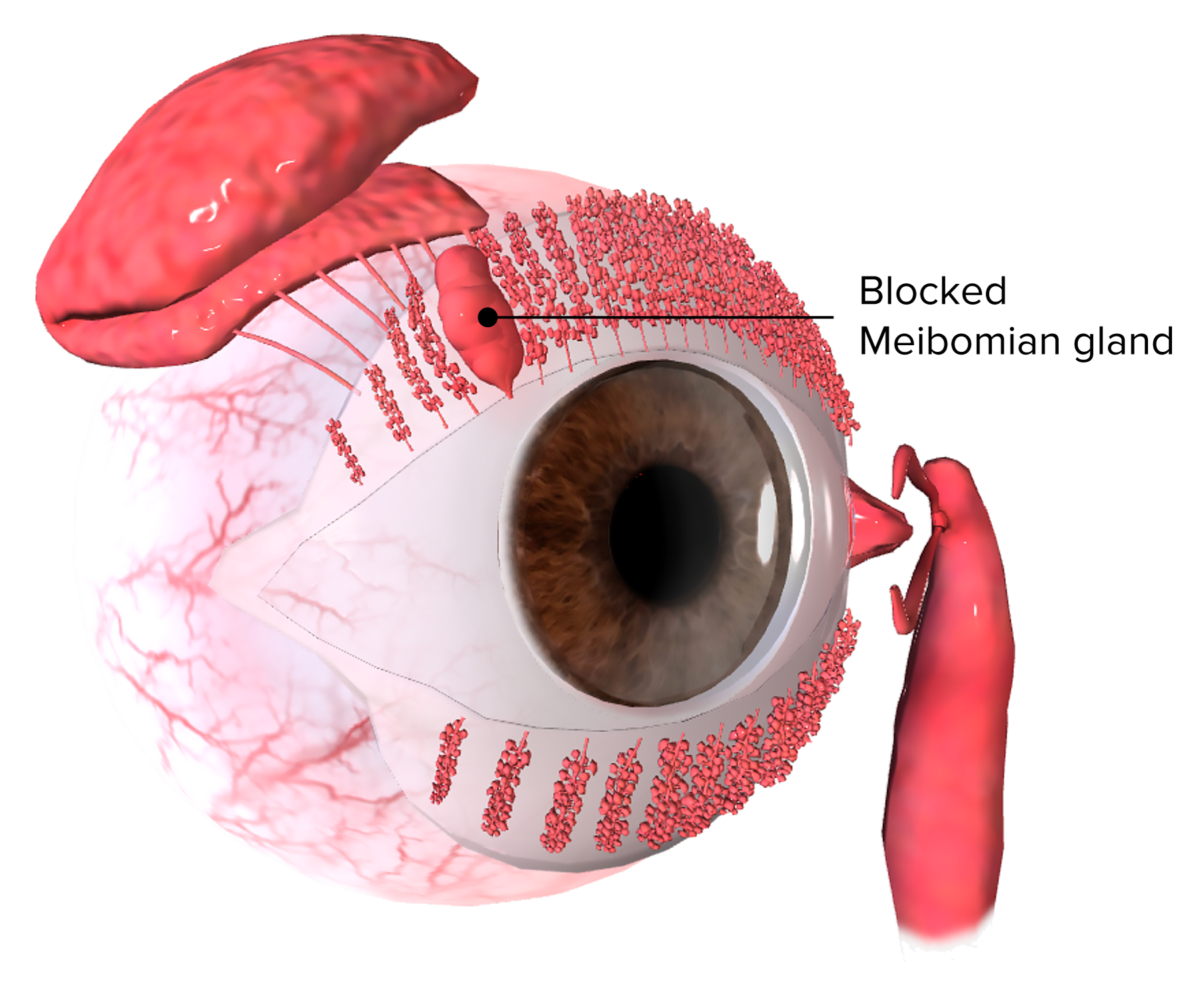
Visualization of a blocked Meibomian gland causing a chalazion
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio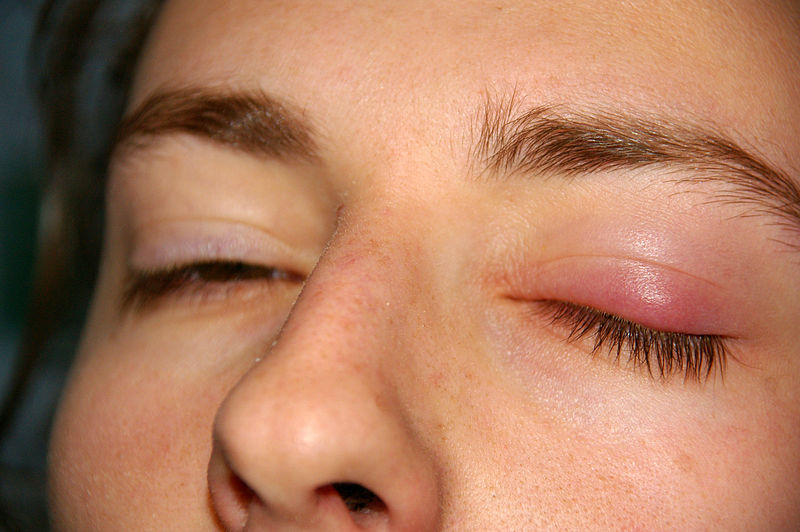
Patient presenting with a chalazion on the left eyelid with mild swelling
Image: “Chalazion” by jd. License: Public DomainDiagnosis is clinical based on the history and physical exam.
Conservative management:[4,5]
Invasive treatment (for a persistent or large, symptomatic chalazion Chalazion A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the Meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender. Chalazion):[4,6]
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose a
chalazion
Chalazion
A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the Meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender.
Chalazion, a blocked
meibomian gland
Meibomian Gland
Chalazion in the eyelid that leads to a granulomatous, non-infectious, and typically painless lump.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | H00.1- | Chalazion Chalazion A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the Meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender. Chalazion |
| SNOMED CT | 35911001 | Chalazion Chalazion A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the Meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender. Chalazion (disorder) |
Procedures/Interventions:
These codes are for the common procedural treatments for a persistent
chalazion
Chalazion
A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the Meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender.
Chalazion, including incision and
curettage
Curettage
A scraping, usually of the interior of a cavity or tract, for removal of new growth or other abnormal tissue, or to obtain material for tissue diagnosis. It is performed with a curet (curette), a spoon-shaped instrument designed for that purpose.
Benign Bone Tumors to remove the granulomatous material, or an intralesional steroid injection to reduce
inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function.
Inflammation.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 67800 | Excision of chalazion Chalazion A chalazion is one of the most common inflammatory lesions of the eyelid. It is caused by obstruction of the Meibomian or Zeis glands, leading to granulomatous inflammation and resulting in a firm, rubbery, slow-growing nodule that is typically non-tender. Chalazion; single |
| CPT | 11900 | Injection, intralesional; up to and including 7 lesions |