Cerebral venous thrombosis Venous thrombosis The formation or presence of a blood clot (thrombus) within a vein. Budd-Chiari Syndrome (CVT) is a blood clot in the cerebral veins Veins Veins are tubular collections of cells, which transport deoxygenated blood and waste from the capillary beds back to the heart. Veins are classified into 3 types: small veins/venules, medium veins, and large veins. Each type contains 3 primary layers: tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Veins: Histology or dural sinuses that predominantly affects younger adults. Risk factors include hypercoagulable Hypercoagulable Hypercoagulable states (also referred to as thrombophilias) are a group of hematologic diseases defined by an increased risk of clot formation (i.e., thrombosis) due to either an increase in procoagulants, a decrease in anticoagulants, or a decrease in fibrinolysis. Hypercoagulable States states, infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, head trauma Head trauma Head trauma occurs when external forces are directed to the skull and brain structures, resulting in damage to the skull, brain, and intracranial structures. Head injuries can be classified as open (penetrating) or closed (blunt), and primary (from the initial trauma) or secondary (indirect brain injury), and range from mild to severe and life-threatening. Head Trauma, inflammatory conditions, and medications. CVT may have varied clinical presentations. Symptoms include headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess, focal neurologic deficits Neurologic Deficits High-Risk Headaches, seizures Seizures A seizure is abnormal electrical activity of the neurons in the cerebral cortex that can manifest in numerous ways depending on the region of the brain affected. Seizures consist of a sudden imbalance that occurs between the excitatory and inhibitory signals in cortical neurons, creating a net excitation. The 2 major classes of seizures are focal and generalized. Seizures, and general signs of increased ICP Increased ICP Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with this suspected diagnosis should undergo urgent neuroimaging Neuroimaging Non-invasive methods of visualizing the central nervous system, especially the brain, by various imaging modalities. Febrile Infant with brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification magnetic resonance venography Venography Budd-Chiari Syndrome. Anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs is the mainstay of treatment. CVT can be fatal during the acute phase Acute phase Short Bowel Syndrome; however, the overall long-term outcome is favorable in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who survive.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Cerebral venous thrombosis Venous thrombosis The formation or presence of a blood clot (thrombus) within a vein. Budd-Chiari Syndrome (CVT) is a blood clot in the cerebral veins Veins Veins are tubular collections of cells, which transport deoxygenated blood and waste from the capillary beds back to the heart. Veins are classified into 3 types: small veins/venules, medium veins, and large veins. Each type contains 3 primary layers: tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Veins: Histology or dural sinuses.
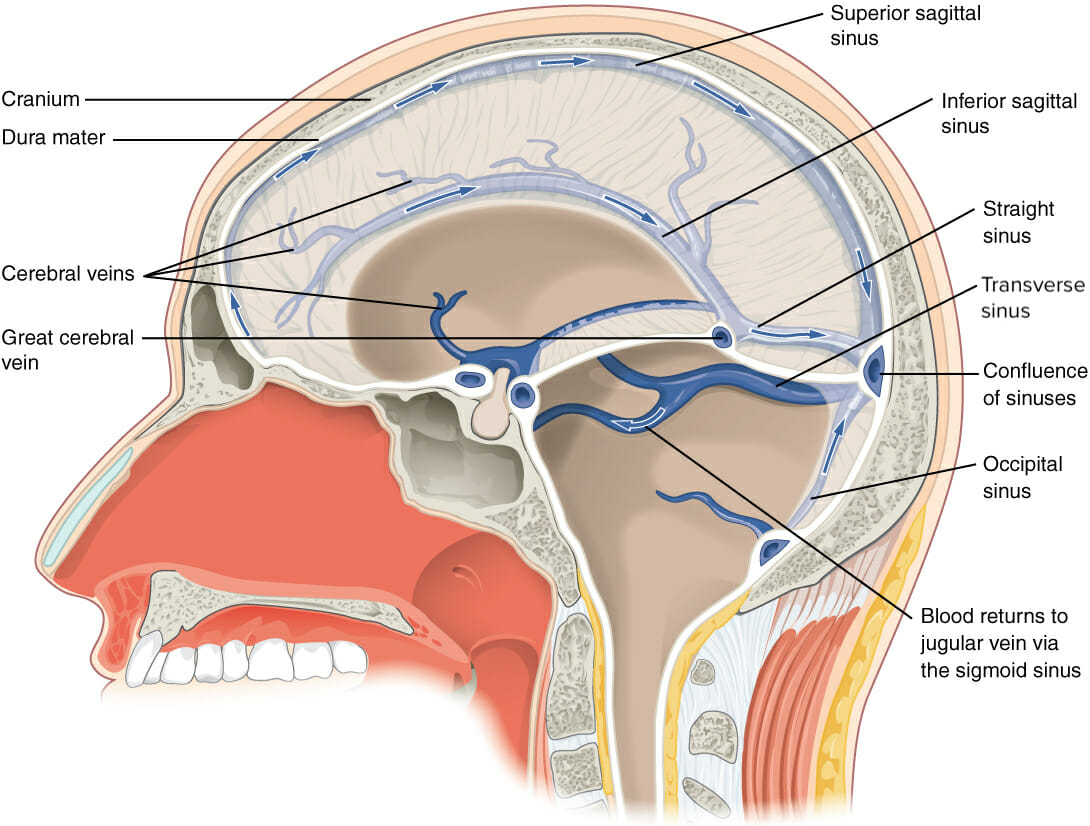
This sagittal view through the skull illustrates the venous drainage system. The arrows demonstrate the flow of blood from the cerebral veins and sinuses to the confluence of sinuses and its ultimate return to the jugular vein via the sigmoid sinus.
Image: “Blood drains from the brain through a series of sinuses that connect to the jugular veins” by OpenStax College, edited by Lecturio. License: CC BY 4.0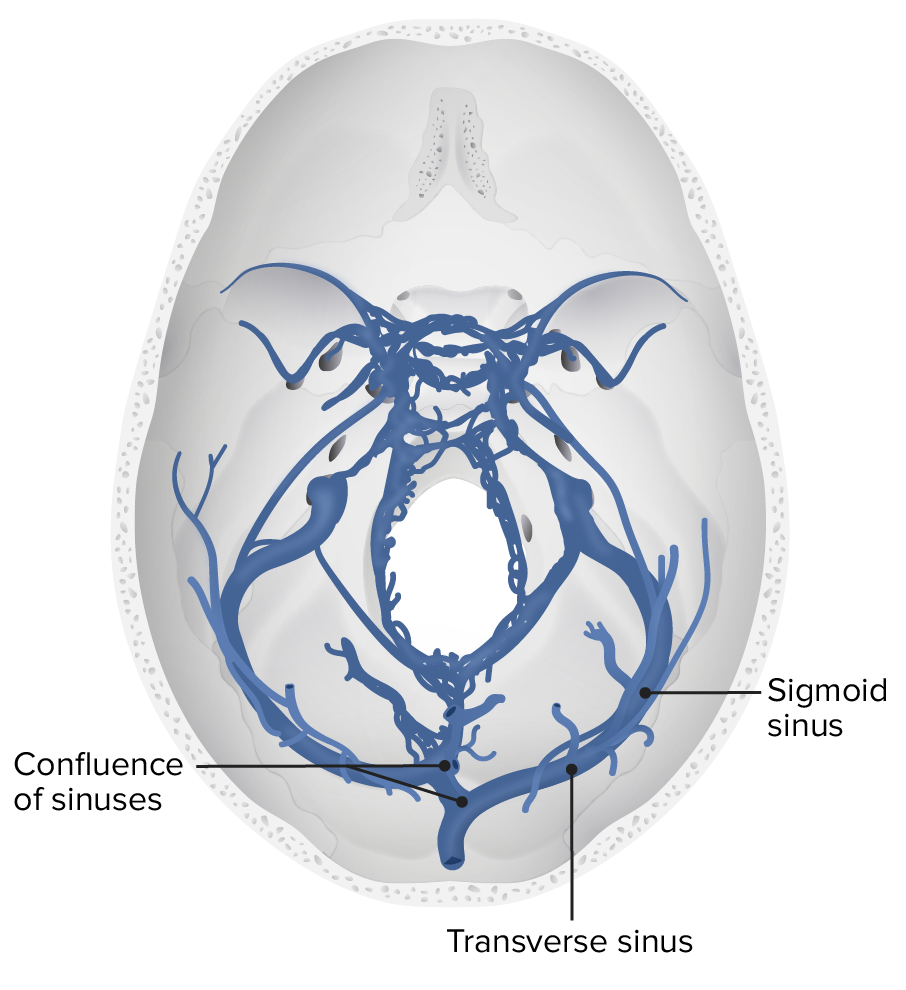
A transverse view of the cerebral deep venous system, specifically the sigmoid and transverse sinuses
Image by Lecturio.Clinical presentations can vary significantly. Some cases may present with isolated ICP ICP Normal intracranial pressure (ICP) is defined as < 15 mm Hg, whereas pathologically increased ICP is any pressure ≥ 20 mm Hg. Increased ICP may result from several etiologies, including trauma, intracranial hemorrhage, mass lesions, cerebral edema, increased CSF production, and decreased CSF absorption. Increased Intracranial Pressure (ICP) signs, while others have ischemic symptoms. The onset of symptoms can also differ (acute, subacute, chronic).
Urgent imaging studies are indicated for those presenting with concerning signs of CVT. Laboratory tests play no role in diagnosing CVT, but they may help identify the underlying cause.
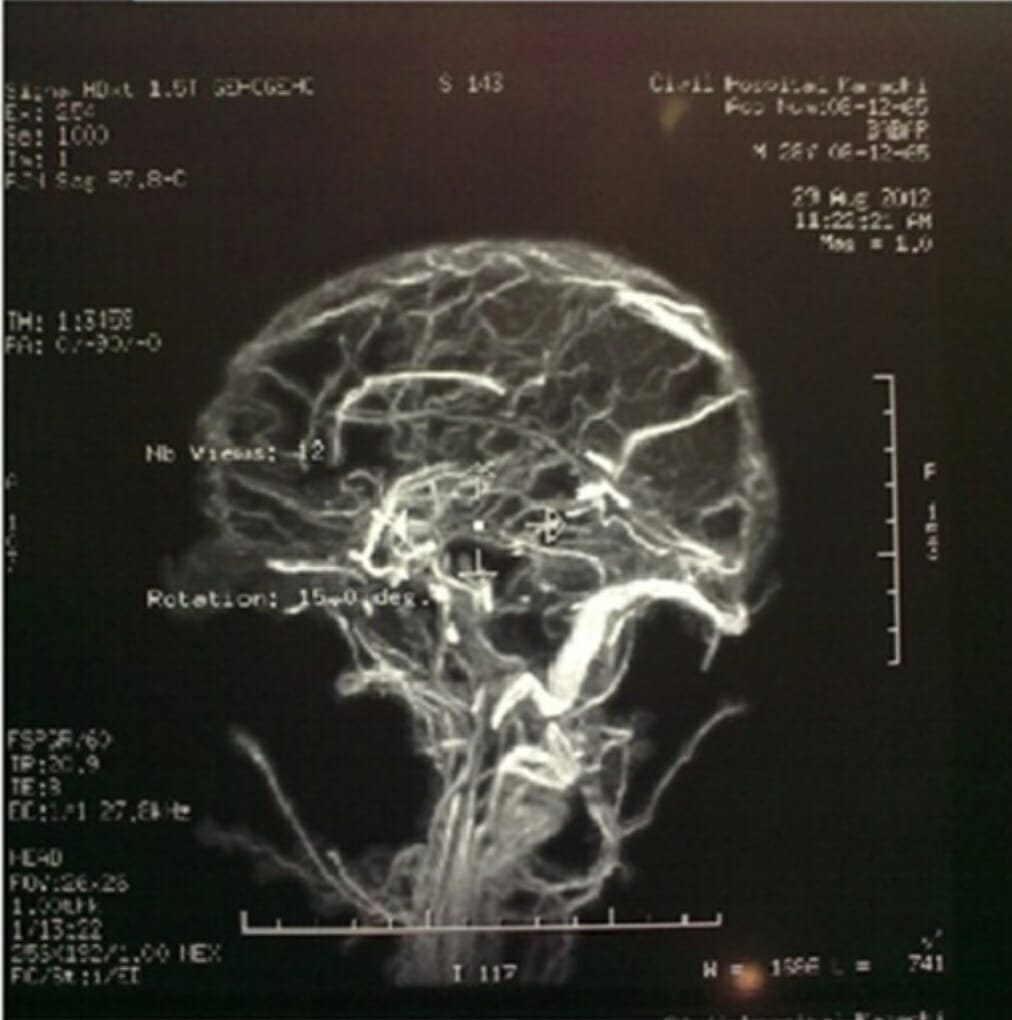
Magnetic resonance venography (MRV) of the brain reveals extensive cerebral venous thrombosis.
Image: “Magnetic Resonance Venography” by Department of Medicine, Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan. License: CC BY 4.0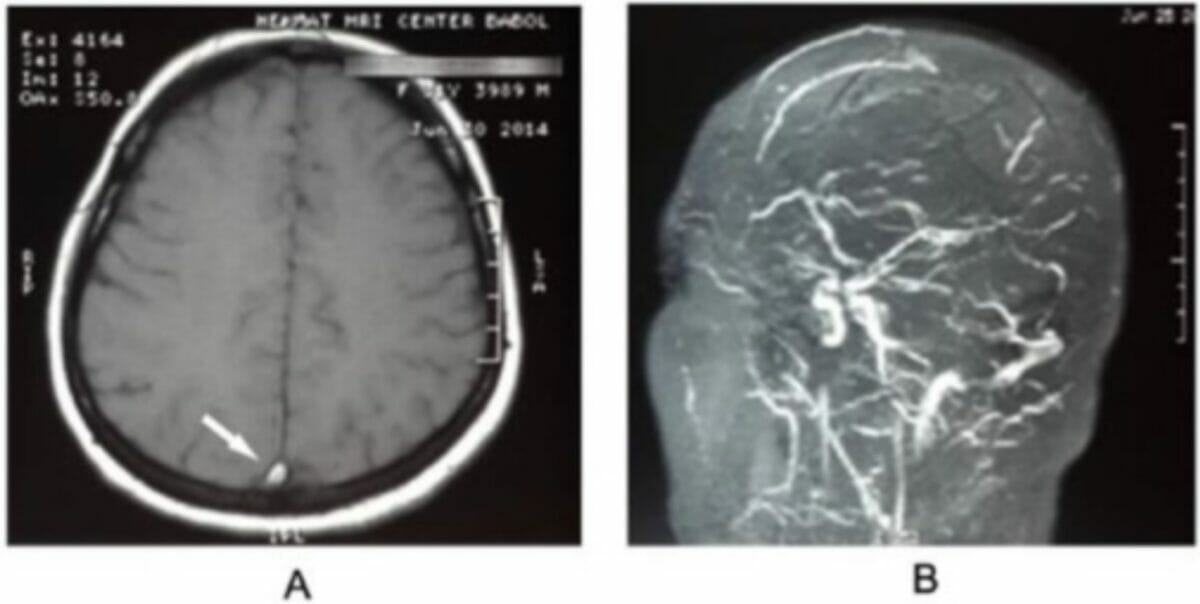
Transverse sinus thrombosis:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain shows an empty delta sign (panel A, arrow), and magnetic resonance venography (panel B) confirms a diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis.
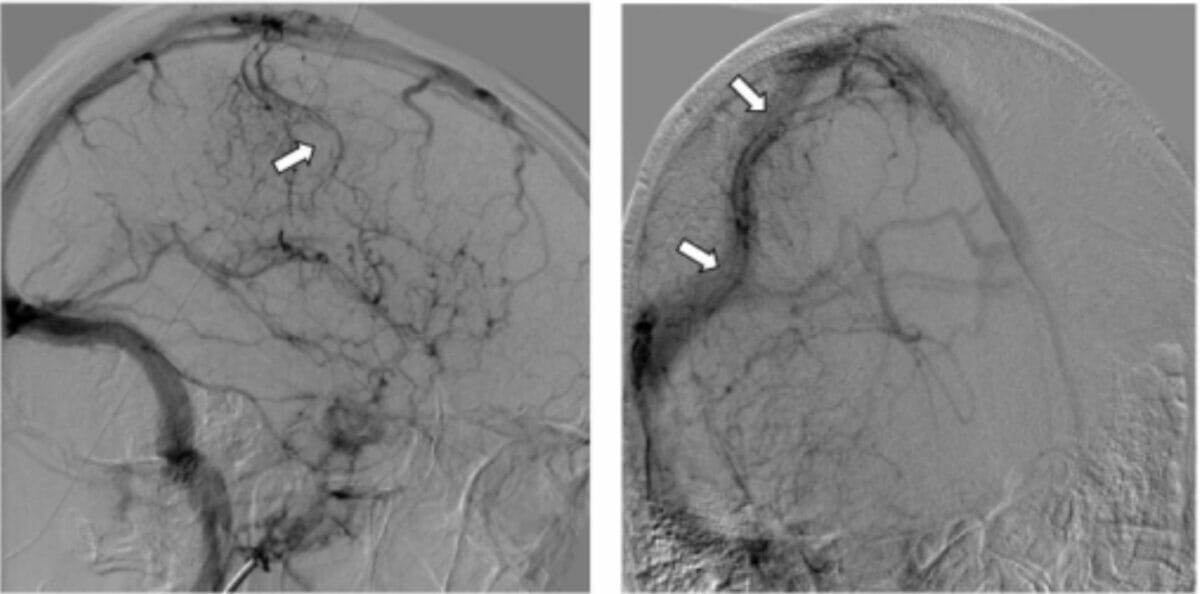
Cerebral angiography:
Venous phase image of the right internal carotid artery shows a tubular filling defect within the superficial cortical vein of Trolard (arrow) and engorgement of the surrounding venules (arrows), suggestive of thrombosis.