Organisms can be mostly classified into 2 groups, prokaryotes and eukaryotes, which have fundamental differences at the cellular level. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that include 2 of the 3 domains of life: bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology and archaea. Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular organisms and include plants, animals, fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology, and protozoa Protozoa Nitroimidazoles. Prokaryotic cells consist of a single cytoplasm-filled compartment enclosed by a cell membrane Cell Membrane A cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the cell contents from the outside environment. A cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and proteins that function to protect cellular DNA and mediate the exchange of ions and molecules. The Cell: Cell Membrane and cell wall, while eukaryotic cells contain a well-organized nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles contained by a membrane, along with other membrane-bound organelles Organelles A cell is a complex unit that performs several complex functions. An organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that fulfills a specific role or function. Organelles are enclosed within their own lipid bilayers or are unbound by membranes. The Cell: Organelles.
Last updated: Mar 27, 2025
Eukaryotic organisms include:
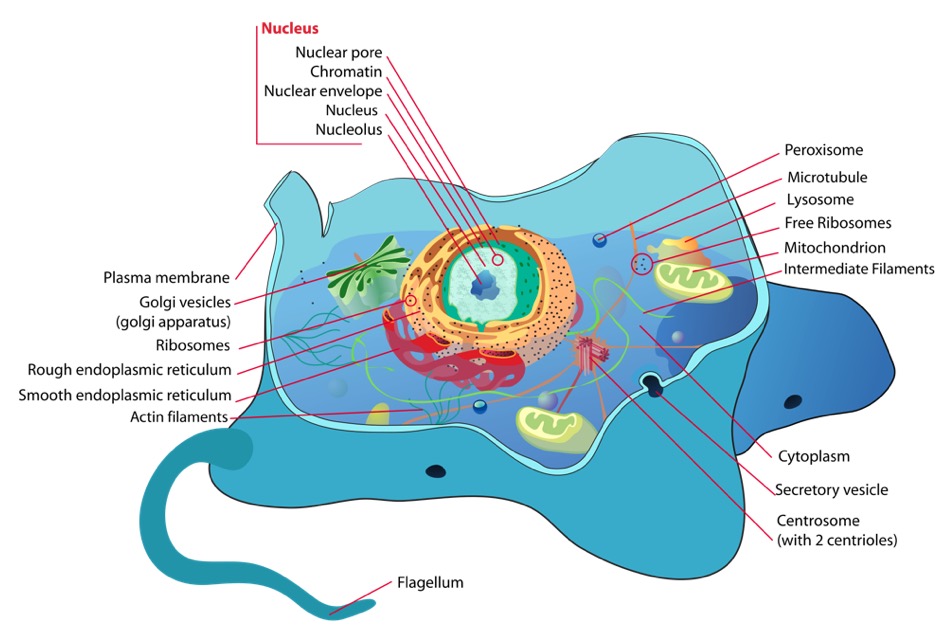
An eukaryotic cell and its components
Image: “Animal cell structure” by Mariana Ruiz. License: Public DomainProkaryotic organisms include bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology and archea.
The cellular organization is unicellular.
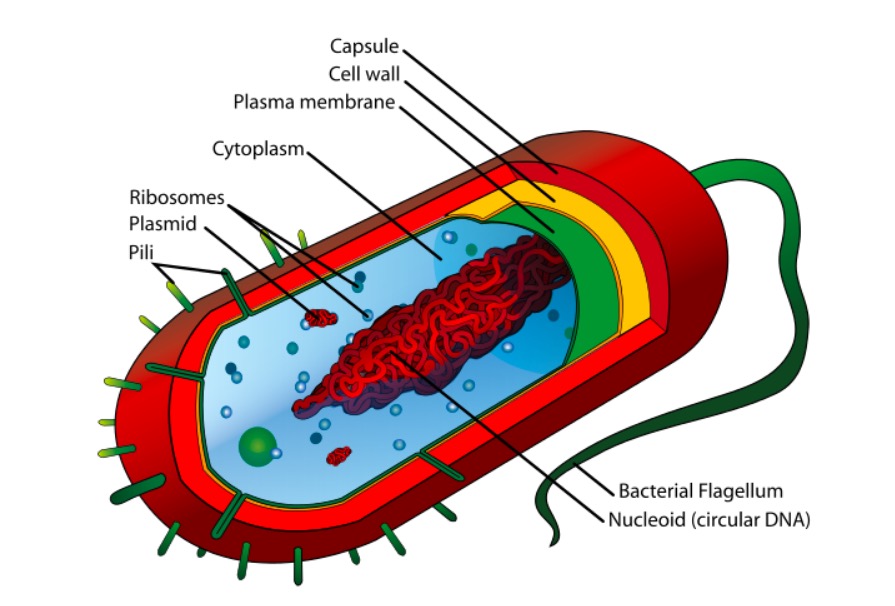
Structure of a prokaryotic cell
Image: “Average prokaryote cell” by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal. License: Public Domain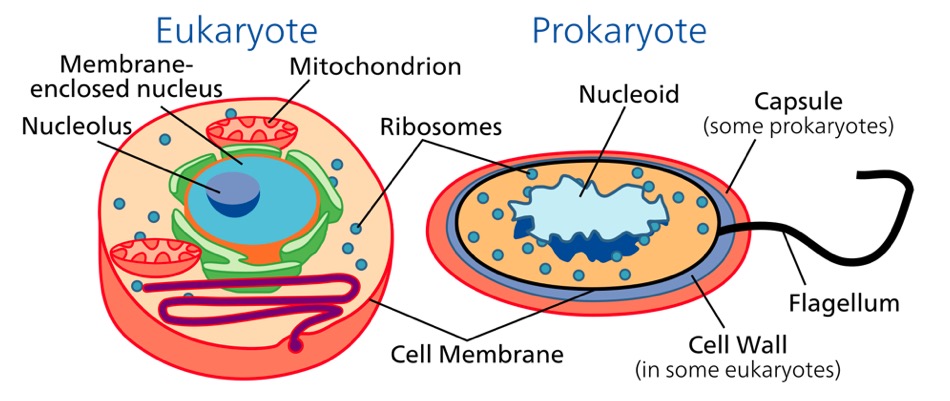
Eukaryote and prokaryote cell comparison
Image: “The cells of eukaryotes (left) and prokaryotes (right)” by Science Primer. License: Public Domain