A cataract Cataract Partial or complete opacity on or in the lens or capsule of one or both eyes, impairing vision or causing blindness. The many kinds of cataract are classified by their morphology (size, shape, location) or etiology (cause and time of occurrence). Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a condition defined as painless clouding or opacity Opacity Imaging of the Lungs and Pleura of the lens Lens A transparent, biconvex structure of the eye, enclosed in a capsule and situated behind the iris and in front of the vitreous humor (vitreous body). It is slightly overlapped at its margin by the ciliary processes. Adaptation by the ciliary body is crucial for ocular accommodation. Eye: Anatomy. It causes visual impairment, as the lens Lens A transparent, biconvex structure of the eye, enclosed in a capsule and situated behind the iris and in front of the vitreous humor (vitreous body). It is slightly overlapped at its margin by the ciliary processes. Adaptation by the ciliary body is crucial for ocular accommodation. Eye: Anatomy provides part of the eye’s refractive power. Although all age groups can be affected, the age-related or senile type of cataract Cataract Partial or complete opacity on or in the lens or capsule of one or both eyes, impairing vision or causing blindness. The many kinds of cataract are classified by their morphology (size, shape, location) or etiology (cause and time of occurrence). Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is the most common. Aside from age, there are multiple risk factors, including systemic diseases, medications, or trauma. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with blurry vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam, glare sensitivity, and color vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam change. Ophthalmologic inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination often shows darkening of or opacities in the red reflex Red Reflex Cataracts in Children. Slit-lamp examination Slit-Lamp Examination Blepharitis will show the extent and location of the cataract Cataract Partial or complete opacity on or in the lens or capsule of one or both eyes, impairing vision or causing blindness. The many kinds of cataract are classified by their morphology (size, shape, location) or etiology (cause and time of occurrence). Neurofibromatosis Type 2. The treatment is surgery, which is indicated when loss of vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam function interferes with daily function.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A cataract Cataract Partial or complete opacity on or in the lens or capsule of one or both eyes, impairing vision or causing blindness. The many kinds of cataract are classified by their morphology (size, shape, location) or etiology (cause and time of occurrence). Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a painless opacity Opacity Imaging of the Lungs and Pleura of the lens Lens A transparent, biconvex structure of the eye, enclosed in a capsule and situated behind the iris and in front of the vitreous humor (vitreous body). It is slightly overlapped at its margin by the ciliary processes. Adaptation by the ciliary body is crucial for ocular accommodation. Eye: Anatomy that disrupts the light projecting onto the retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy, resulting in a clouding of vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam. It can cause partial or total blindness Blindness The inability to see or the loss or absence of perception of visual stimuli. This condition may be the result of eye diseases; optic nerve diseases; optic chiasm diseases; or brain diseases affecting the visual pathways or occipital lobe. Retinopathy of Prematurity.
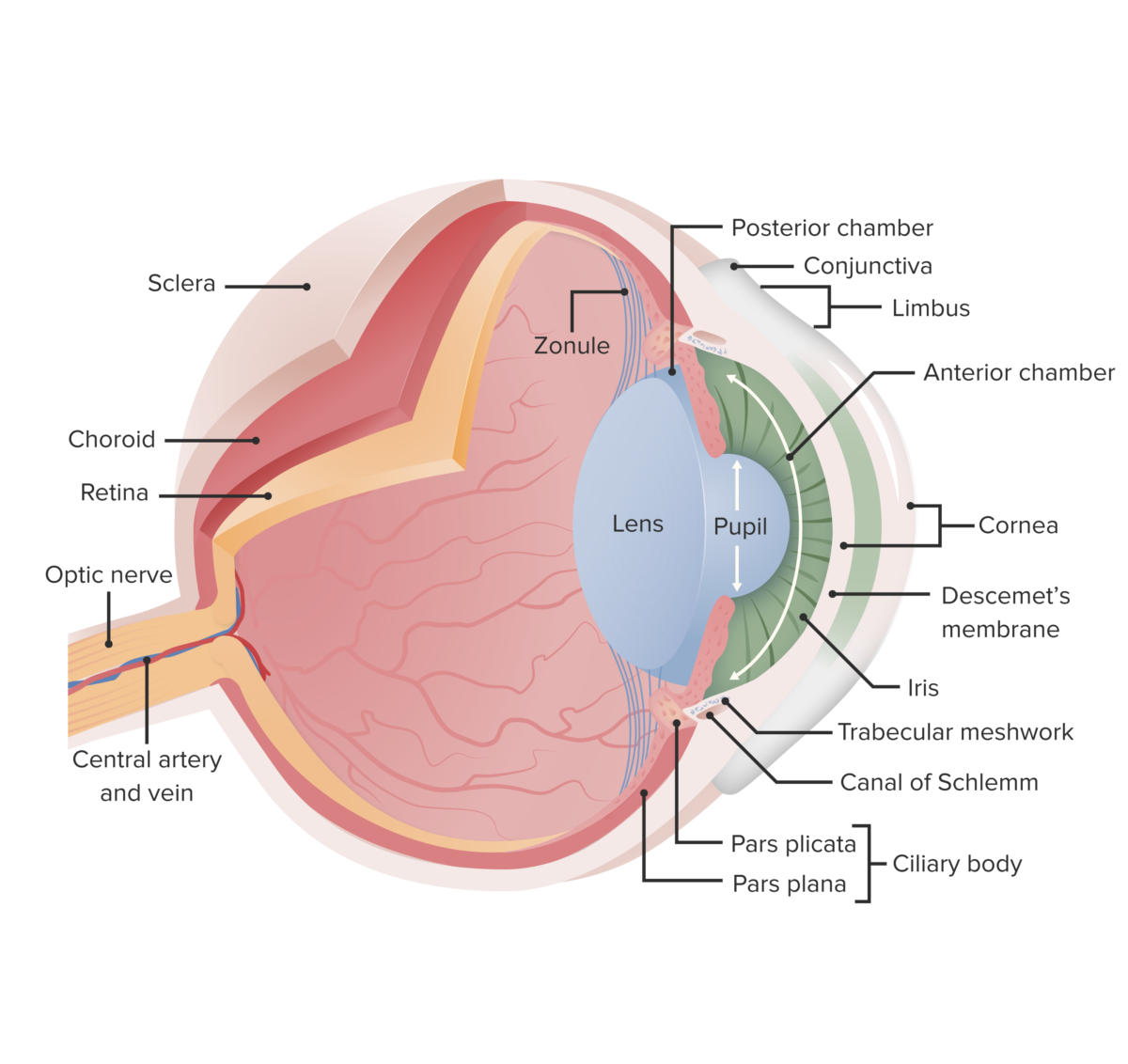
This image displays the essential anatomy of the eye. In cataracts, there is clouding of the lens, which opacifies the light as it projects to the retina; this leads to reduced vision, particularly at night when light levels are low.
Image by Lecturio.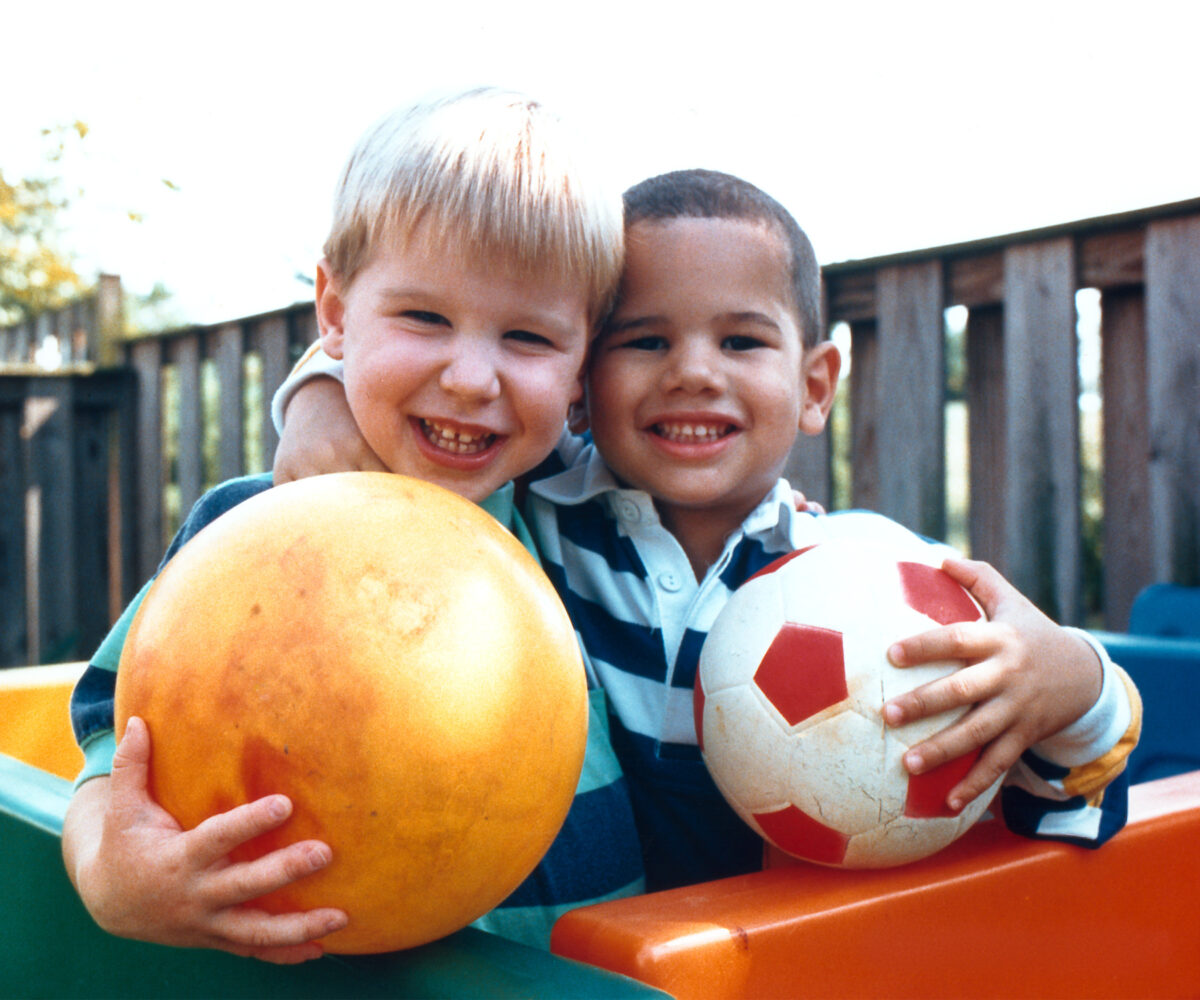
An example of normal vision
Image: “An example of normal vision” by National Eye Institute. License: Public Domain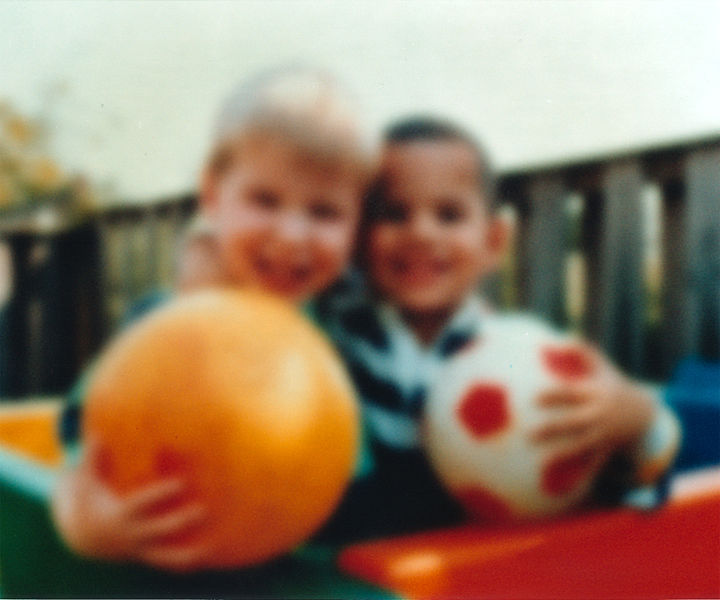
Vision through a cataract lens
Image: “A scene as it might be viewed by a person with cataract” by National Eye Institute. License: Public Domain| Posterior subcapsular cataracts | Nuclear cataracts | Cortical cataracts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causes |
|
Aging |
|
| Symptoms |
|
|
|
| Diagnosis | Granular opacity Opacity Imaging of the Lungs and Pleura in the posterior pole of cortex adjacent to the posterior capsule Capsule An envelope of loose gel surrounding a bacterial cell which is associated with the virulence of pathogenic bacteria. Some capsules have a well-defined border, whereas others form a slime layer that trails off into the medium. Most capsules consist of relatively simple polysaccharides but there are some bacteria whose capsules are made of polypeptides. Bacteroides |
|
|
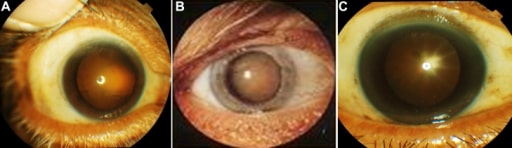
Appearance of lenses in 3 patients.
A: Cortical cataract
B: Nuclear cataract
C: Posterior subcapsular cataract
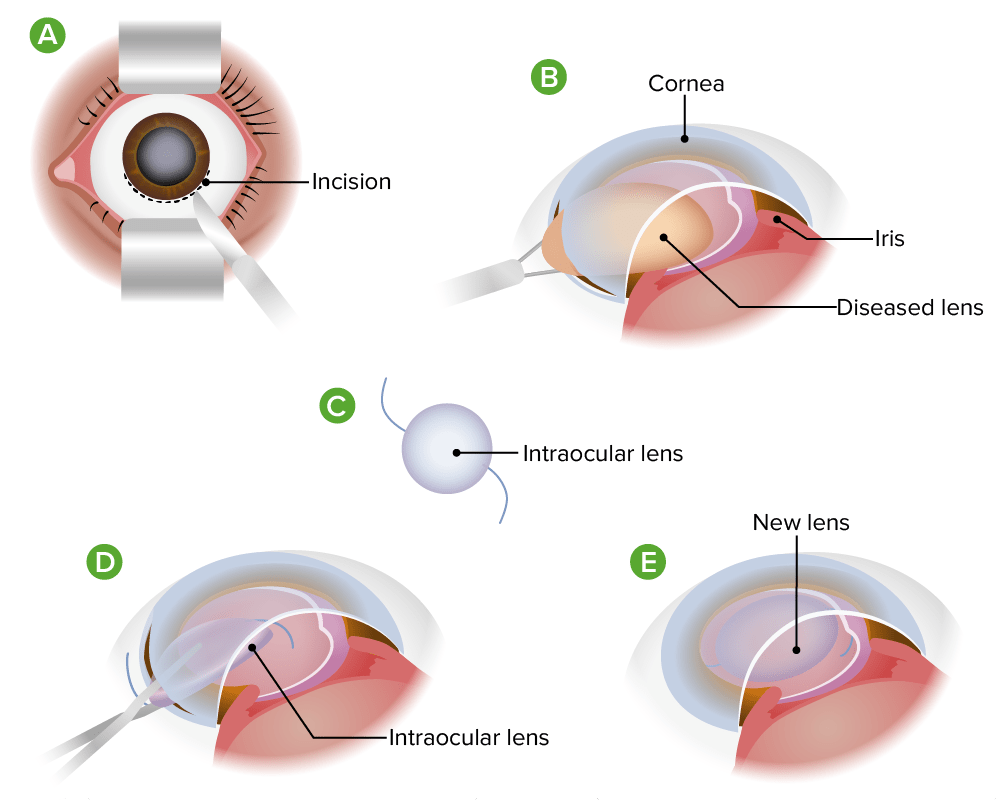
Extracapsular cataract extraction
Image by Lecturio.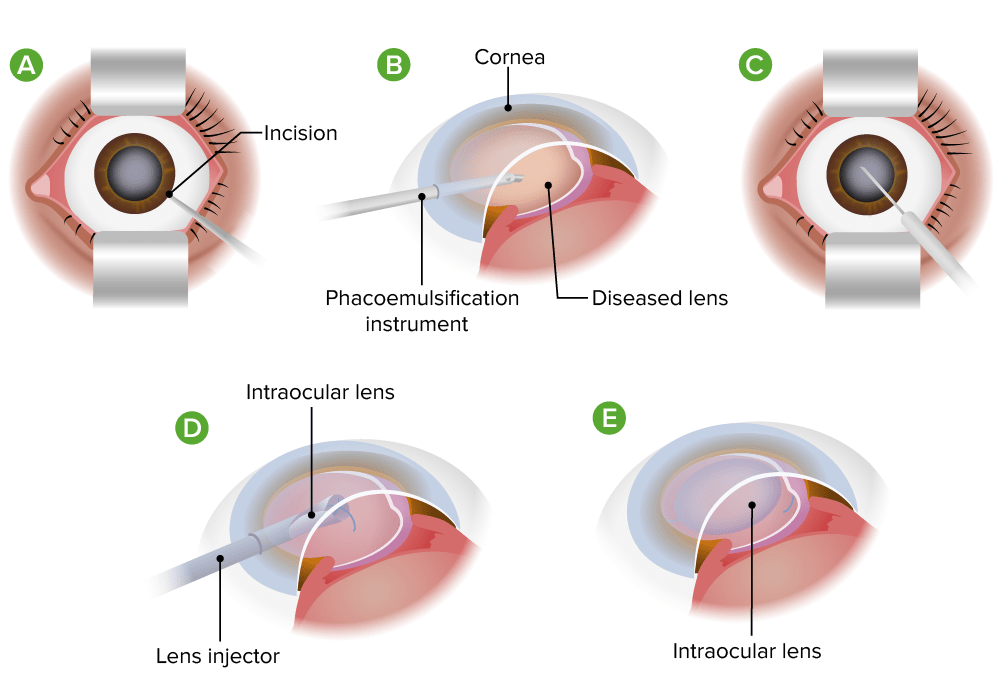
Phacoemulsification for cataracts
Image by Lecturio.