During exercise, the metabolic demands of the body increase, and changes in the cardiovascular system are required to maintain adequate perfusion. During isometric contraction, blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure is decreased to the contracting muscle due to direct compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma of the arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology. Once the contraction ends, vasoactive metabolites cause significant vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs, resulting in an increase in blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure to the muscle known as active hyperemia. During endurance exercise, repetitive, coordinated movements over a sustained period result in an increase in HR, stroke volume Stroke volume The amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat, not to be confused with cardiac output (volume/time). It is calculated as the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. Cardiac Cycle, cardiac output Cardiac output The volume of blood passing through the heart per unit of time. It is usually expressed as liters (volume) per minute so as not to be confused with stroke volume (volume per beat). Cardiac Mechanics, and systolic blood pressure primarily via sympathetic stimulation and effects of the skeletal muscle pump Pump ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols. Diastolic blood pressure usually decreases slightly due to significant vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs in the skeletal muscle vascular beds Vascular beds Gas Exchange, resulting in a decrease in systemic vascular resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing.
Last updated: Feb 28, 2023
Blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure to skeletal muscles Skeletal muscles A subtype of striated muscle, attached by tendons to the skeleton. Skeletal muscles are innervated and their movement can be consciously controlled. They are also called voluntary muscles. Muscle Tissue: Histology can increase > 20 fold during strenuous exercise.
During isometric contraction, blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure is decreased in working muscles.
After isometric contraction, blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure is increased in the working muscle.
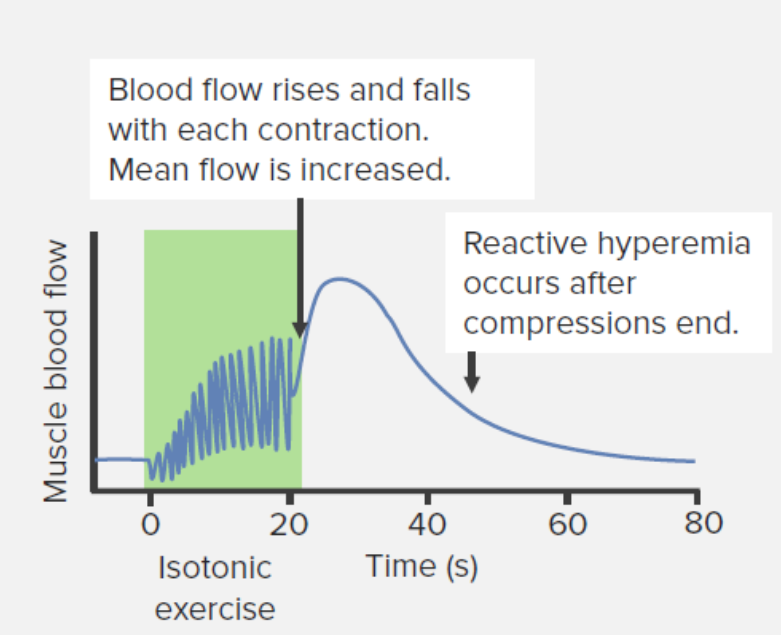
Changes in blood flow to the muscle during and after isotonic resistance exercise
Image by Lecturio.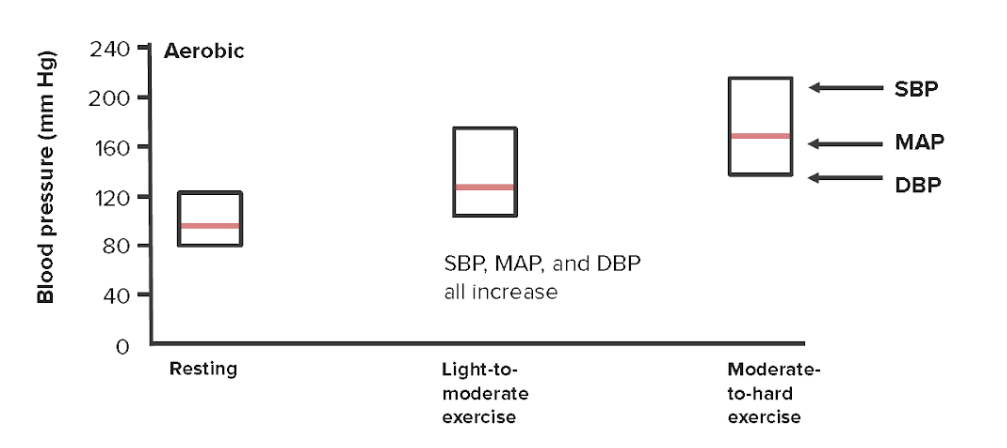
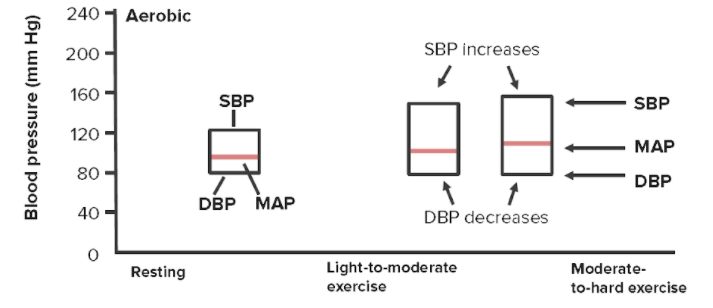
Changes in systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures with increasing physical exertion
SBP = systolic blood pressure
DBP = diastolic blood pressure
MAP = mean arterial pressure
Valsalva: forced expiration Forced expiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing against a closed glottis Glottis The vocal apparatus of the larynx, situated in the middle section of the larynx. Glottis consists of the vocal folds and an opening (rima glottidis) between the folds. Larynx: Anatomy (occurs frequently during exercise). Valsalva causes 4 different changes in blood pressure over time:
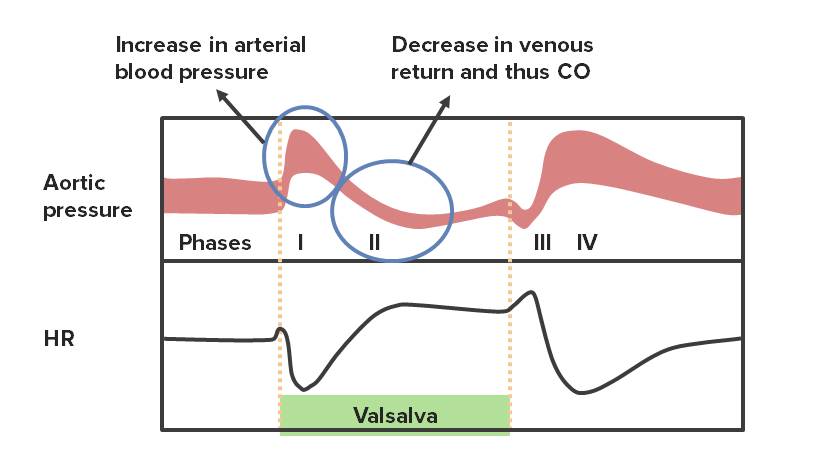
Phases of the Valsalva maneuver with their corresponding changes in HR
CO: cardiac output
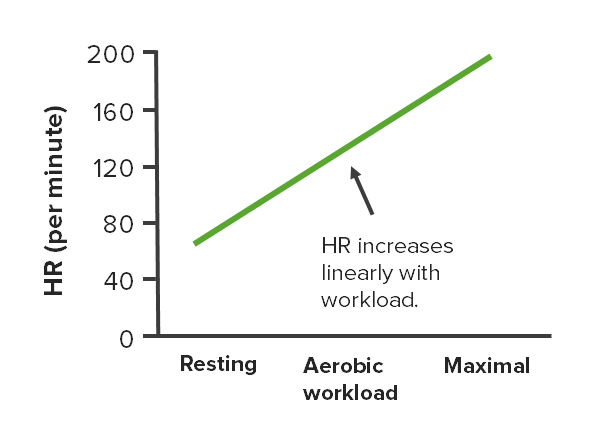
Changes in HR at different intensities of aerobic exercise
Image by Lecturio.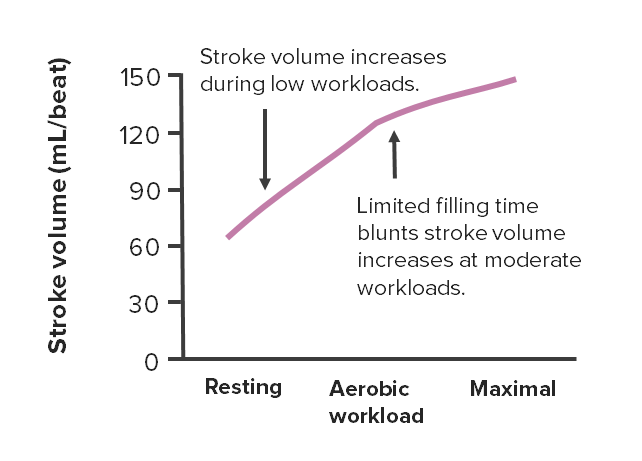
Changes in stroke volume at different intensities of aerobic exercise
Image by Lecturio.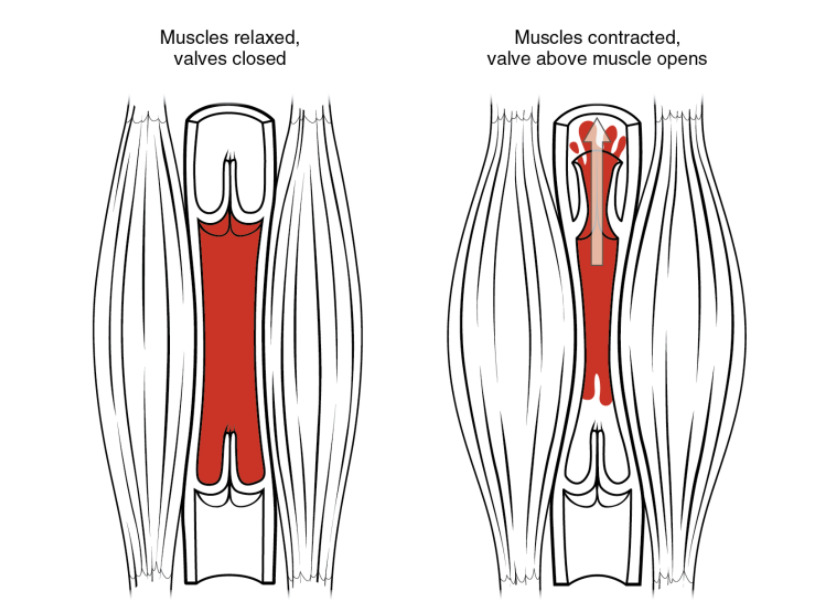
Skeletal muscle pump: As skeletal muscles surrounding a vein contract, the vessel is compressed, forcing blood to move forward. The 1-way valves in the veins prevent backflow and ensure that blood flows only in 1 direction.
Image by Lecturio.With aerobic exercise:
Changes to cardiovascular parameters at different intensities of resistance exercise
SBP: systolic blood pressure
MAP: mean arterial pressure
DBP: diastolic blood pressure
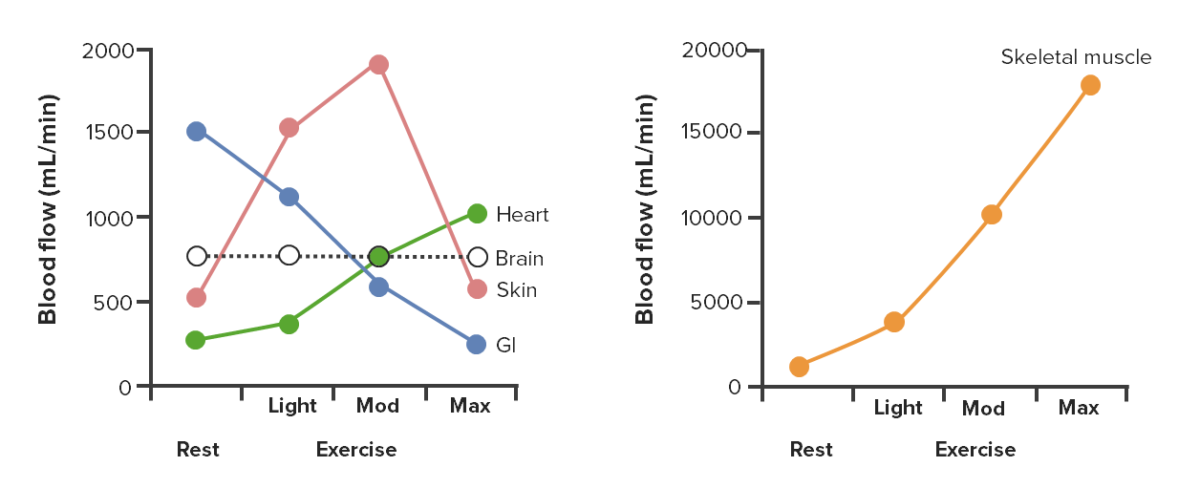
Changes in blood flow distribution during light, moderate (mod), and maximal (max) exercise
Image by Lecturio.| Posture | Supine (e.g., swimming) | Upright |
|---|---|---|
| Effect on preload Preload Cardiac Mechanics and stroke volume Stroke volume The amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat, not to be confused with cardiac output (volume/time). It is calculated as the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. Cardiac Cycle | Higher | Lower |
| Effect on resting HR | Lower | Higher |
Regular Regular Insulin aerobic exercise improves cardiovascular health by ↓ HR, ↑ stroke volume Stroke volume The amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat, not to be confused with cardiac output (volume/time). It is calculated as the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. Cardiac Cycle, and ↑ CO (during exercise)
| At rest | During maximal workload | |
|---|---|---|
| HR | Decreases | Minimal change or slightly reduced to allow for longer filling time |
| Stroke volume Stroke volume The amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat, not to be confused with cardiac output (volume/time). It is calculated as the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. Cardiac Cycle | Increases | Increases:
|
| Cardiac output Cardiac output The volume of blood passing through the heart per unit of time. It is usually expressed as liters (volume) per minute so as not to be confused with stroke volume (volume per beat). Cardiac Mechanics | Minimal change | Increased due to ↑ stroke volume Stroke volume The amount of blood pumped out of the heart per beat, not to be confused with cardiac output (volume/time). It is calculated as the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. Cardiac Cycle |
Other vascular adaptations that occur with chronic endurance training: