Examination of the cardiovascular system (CVS) is a critical component of a thorough physical examination. As with all components of a complete physical examination, the CVS examination consists of inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination, palpation Palpation Application of fingers with light pressure to the surface of the body to determine consistency of parts beneath in physical diagnosis; includes palpation for determining the outlines of organs. Dermatologic Examination, and auscultation. The evaluation of the CVS focuses on the heart, but also includes an assessment of the arterial system throughout the body. A number of cardiovascular conditions can be diagnosed with a physical examination, including valvular heart disease, peripheral artery disease Peripheral artery disease Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is obstruction of the arterial lumen resulting in decreased blood flow to the distal limbs. The disease can be a result of atherosclerosis or thrombosis. Patients may be asymptomatic or have progressive claudication, skin discoloration, ischemic ulcers, or gangrene. Peripheral Artery Disease, and arrhythmia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination is the 1st part of the cardiovascular examination. Take note of pertinent positive and negative findings. Cardiovascular disease can be detected through a thorough inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination of the entire body.
Evaluate for JVD:
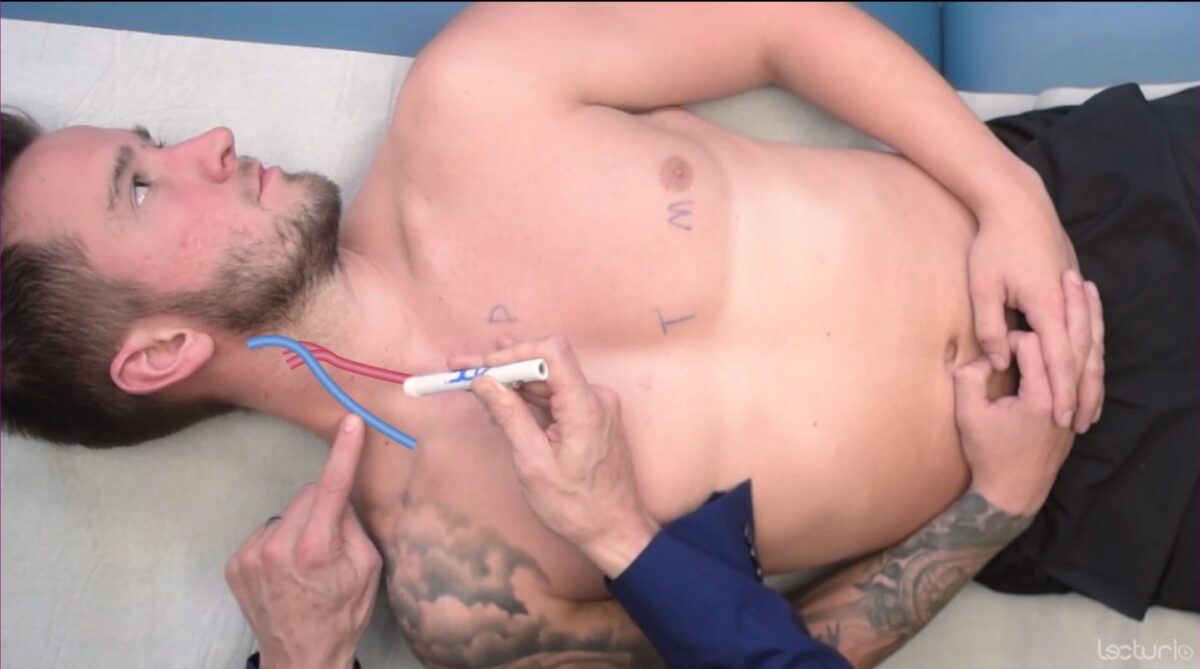
Evaluation of jugular venous distension (JVD) with the individual supine at 30–45 degrees
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The cardiovascular examination includes palpation Palpation Application of fingers with light pressure to the surface of the body to determine consistency of parts beneath in physical diagnosis; includes palpation for determining the outlines of organs. Dermatologic Examination of the pulses and the chest wall Chest wall The chest wall consists of skin, fat, muscles, bones, and cartilage. The bony structure of the chest wall is composed of the ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae. The chest wall serves as armor for the vital intrathoracic organs and provides the stability necessary for the movement of the shoulders and arms. Chest Wall: Anatomy (precordium).
Note the rate, rhythm, strength, character, and compare with contralateral pulses.
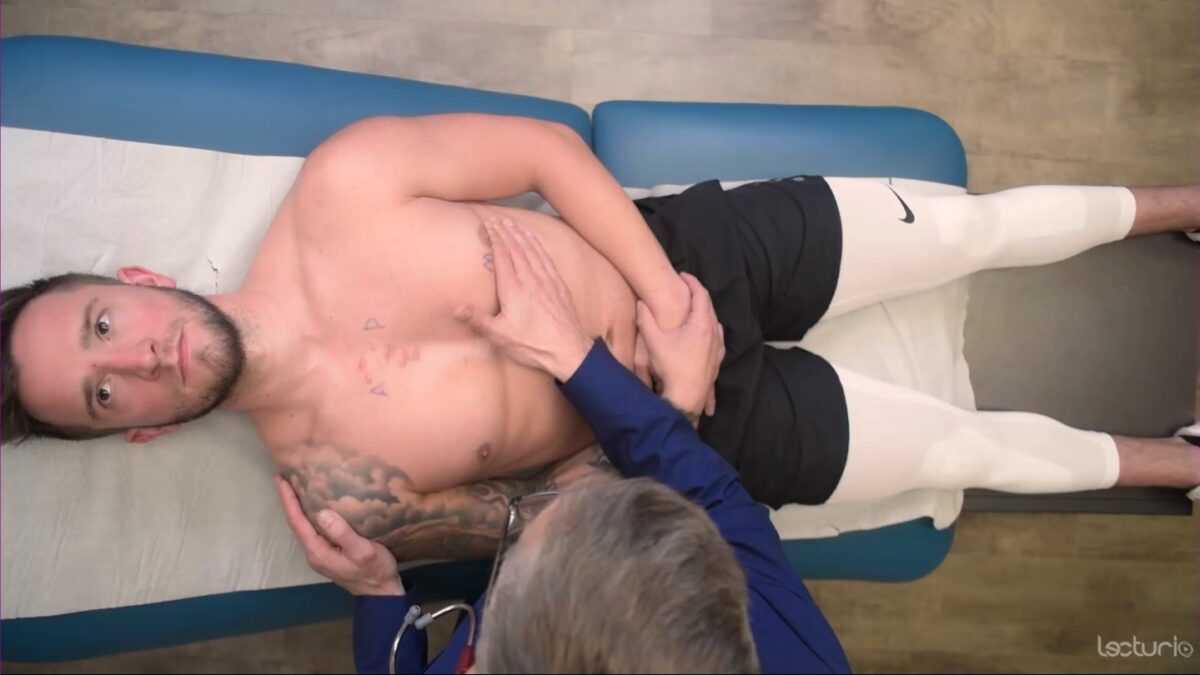
Palpation of the precordium: the heel of the hand over the sternal border with fingers below the left nipple
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Auscultation is best performed on bare skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions. Maintain the individual’s modesty while performing examination maneuvers on the chest.
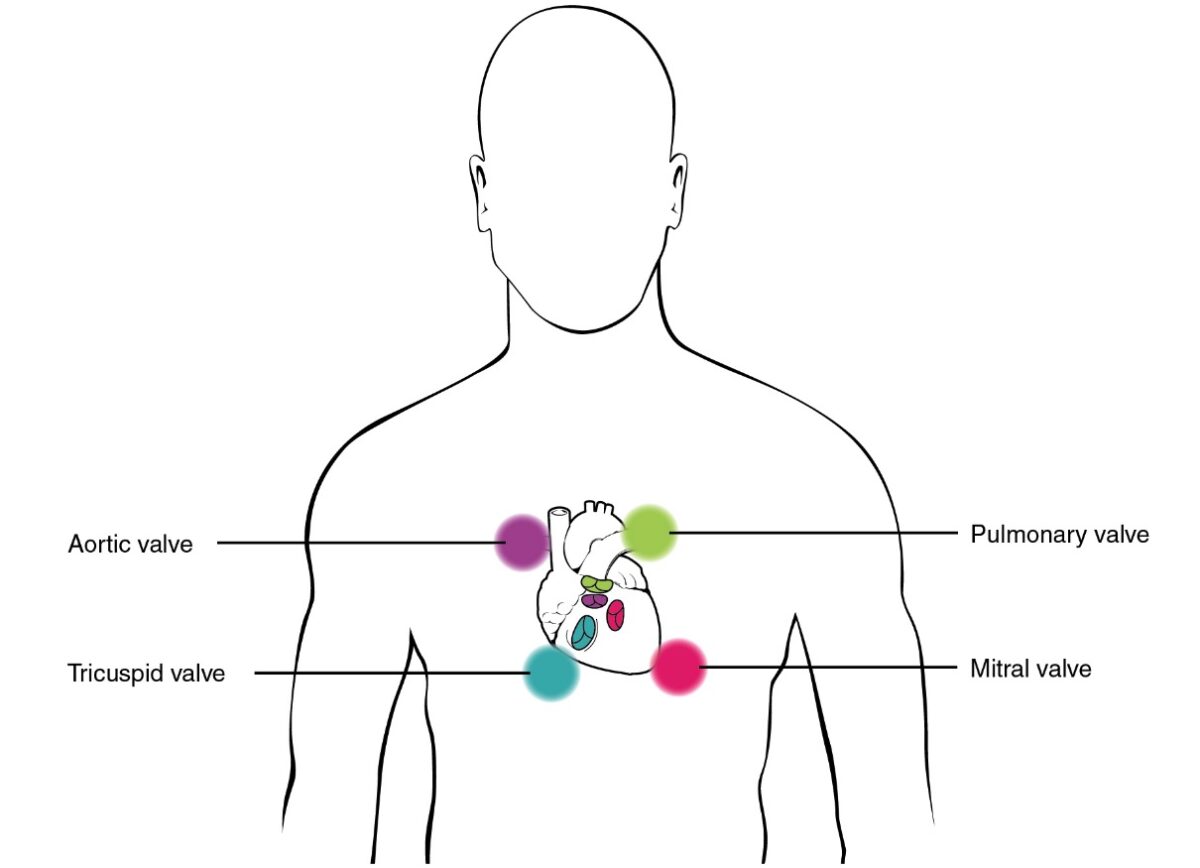
Areas of auscultation
Image: “Proper placement of the bell of the stethoscope facilitates auscultation” by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0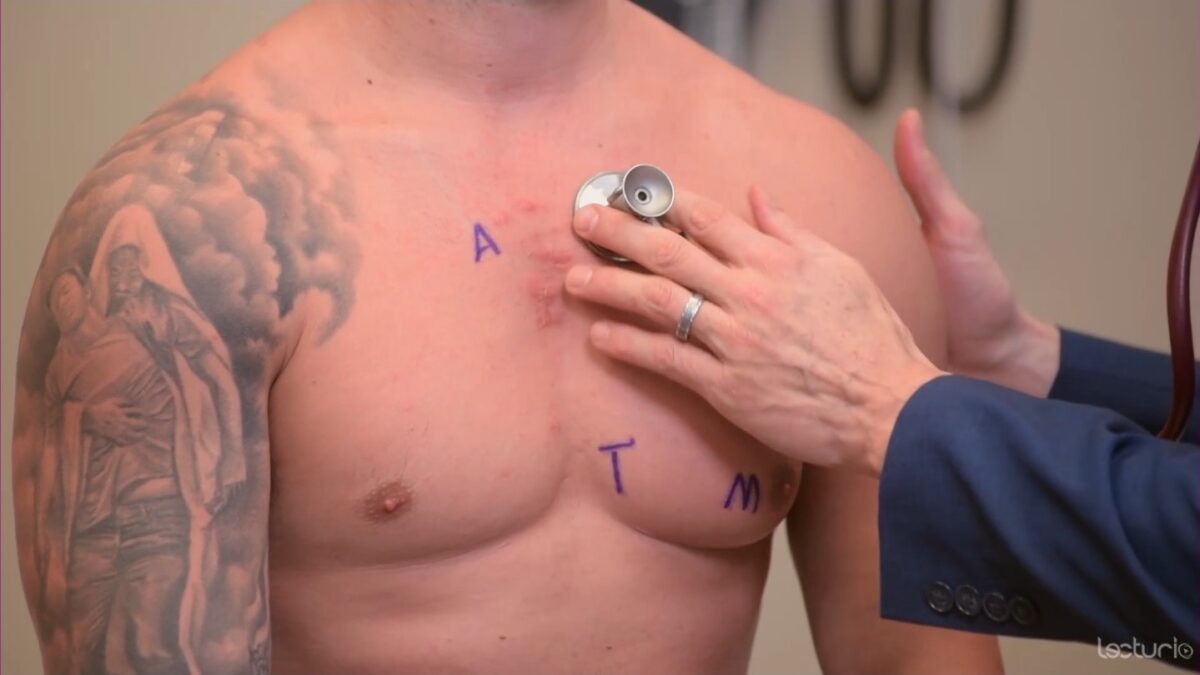
Auscultation using the diaphragm over the pulmonic area
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Audio:
| Ankle-brachial index ratio | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| > 1.4 | Vessel hardening |
| 1.0–1.4 | Normal |
| 0.9–1.0 | Acceptable |
| 0.8–0.9 | Mild arterial disease |
| 0.5–0.8 | Moderate arterial disease |
| < 0.5 | Severe arterial disease |
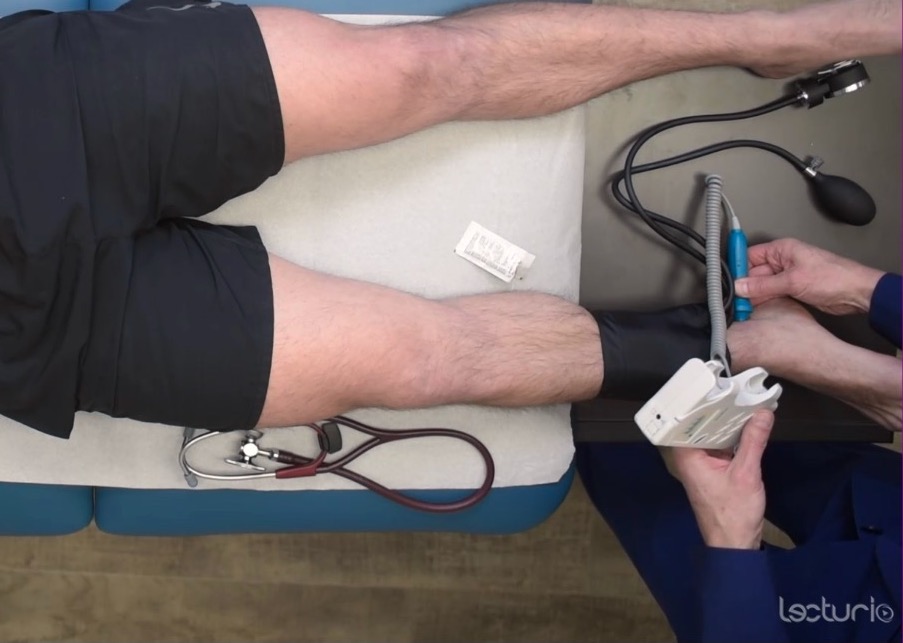
Measuring the systolic pressure at the ankle to calculate the ankle-brachial index
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0