Cardiac glycosides are a class of drugs reversibly inhibiting the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in myocardial cells and increasing vagal tone, which results in increased cardiac contractility and slowed conduction through the atrioventricular node. Digoxin is the only medically used drug in the cardiac glycoside class. Digoxin can be used for rate control in atrial fibrillation/flutter and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). However, the medication needs to be used with caution due to a very narrow therapeutic window Therapeutic Window Dosage Calculation. Digoxin toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation can result in life-threatening arrhythmias as well as GI and neurologic symptoms; an antidote Antidote An antidote is a substance that counteracts poisoning or toxicity. Substances that can cause poisoning include heavy metals (from occupation, treatments, or diet), alcohols, environmental toxins, and medications. Antidotes of Common Poisonings is available.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Digoxin is the prototype drug of the cardiac glycoside class and the only drug in the class used for medicinal purposes.
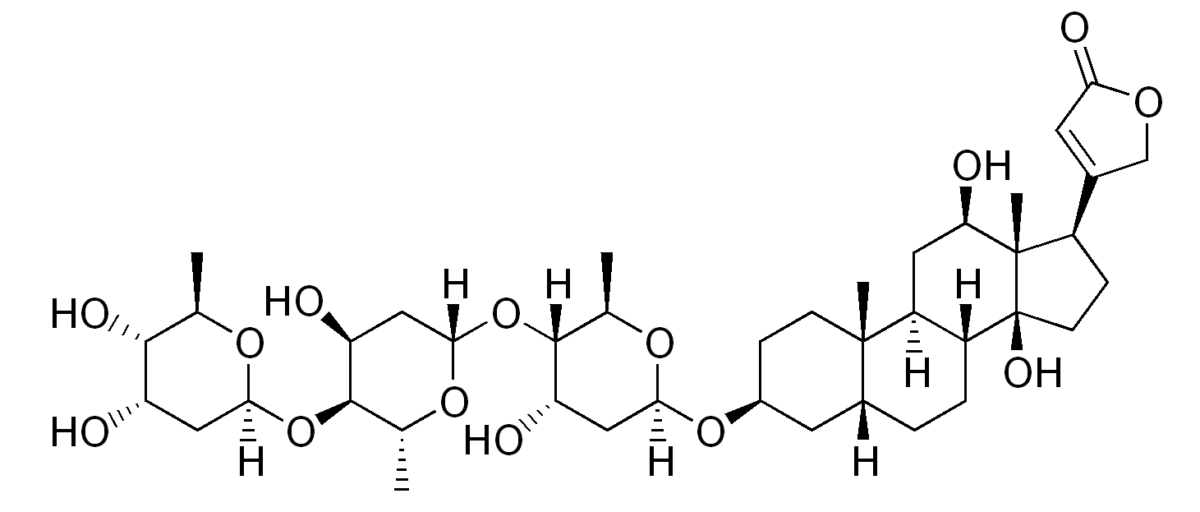
The chemical structure of digoxin:
Notice the steroid nucleus (4 fused rings) with an attached lactone ring (far right) and glycoside attachment (left).
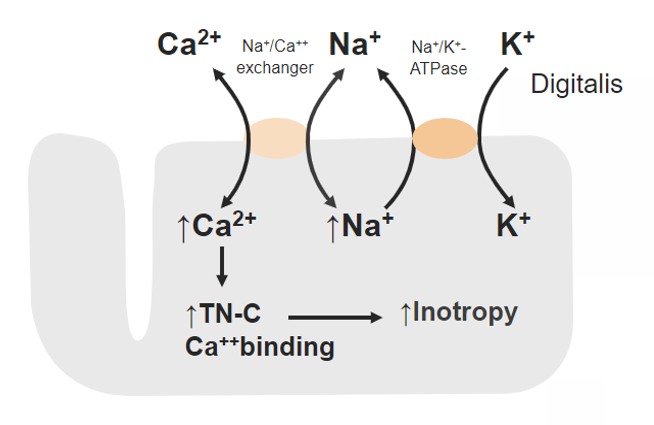
Mechanism of action of digoxin:
Inhibition of sodium (Na+)-potassium (K+) ATPase leads to increased intracellular Na+, which lowers the exchange of the Na+-calcium (Ca2+) antiporter and inhibits the efflux of Ca2+.
More intracellular Ca2+ can bind to contractile proteins (such as troponin (TN-C)), resulting in increased cardiac contractility.
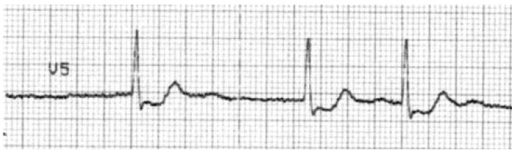
Typical “scooped” ST-depression resulting from digoxin use.
Image: “F15: An ECG with characteristic scooping ST segment depressionin a patient taking Digoxin.” by Christopher Yates and Alex F Manini. License: CC BY 2.5Digoxin is indicated for rate control when other therapies are ineffective or contraindicated:
Digoxin has a very narrow therapeutic window Therapeutic Window Dosage Calculation and several signs of toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation:
Drug interactions may lead to: