Carcinoid tumors are small, well-differentiated, slow-growing neuroendocrine tumors Neuroendocrine tumors Tumors whose cells possess secretory granules and originate from the neuroectoderm, i.e., the cells of the ectoblast or epiblast that program the neuroendocrine system. Common properties across most neuroendocrine tumors include ectopic hormone production (often via apud cells), the presence of tumor-associated antigens, and isozyme composition. Gastrinoma (NET). Carcinoid syndrome describes the signs and symptoms associated with unregulated vasoactive hormone production by neuroendocrine tumors Neuroendocrine tumors Tumors whose cells possess secretory granules and originate from the neuroectoderm, i.e., the cells of the ectoblast or epiblast that program the neuroendocrine system. Common properties across most neuroendocrine tumors include ectopic hormone production (often via apud cells), the presence of tumor-associated antigens, and isozyme composition. Gastrinoma. Carcinoid tumors are most commonly found in the GI and bronchopulmonary tracts. Vasoactive substances produced by NET of the GI tract do not cause carcinoid syndrome until the tumors metastasize to the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy. Symptoms of carcinoid syndrome include flushing, diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea, and wheezing Wheezing Wheezing is an abnormal breath sound characterized by a whistling noise that can be relatively high-pitched and shrill (more common) or coarse. Wheezing is produced by the movement of air through narrowed or compressed small (intrathoracic) airways. Wheezing. Treatment consists primarily of surgical tumor Tumor Inflammation resection and therapy with somatostatin Somatostatin A 14-amino acid peptide named for its ability to inhibit pituitary growth hormone release, also called somatotropin release-inhibiting factor. It is expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems, the gut, and other organs. SRIF can also inhibit the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone; prolactin; insulin; and glucagon besides acting as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. In a number of species including humans, there is an additional form of somatostatin, srif-28 with a 14-amino acid extension at the n-terminal. Gastrointestinal Secretions analogs. Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas depends on the tumor Tumor Inflammation location, aggressiveness, and overall disease burden.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Carcinoid tumor Tumor Inflammation is a neuroendocrine tumor Tumor Inflammation arising from enterochromaffin cells, typically in the GI and bronchopulmonary tracts.
The rule of 1/3s can be used to recall the characteristics of carcinoid tumors:
Biological behavior:
Classification based on embryonic origin:
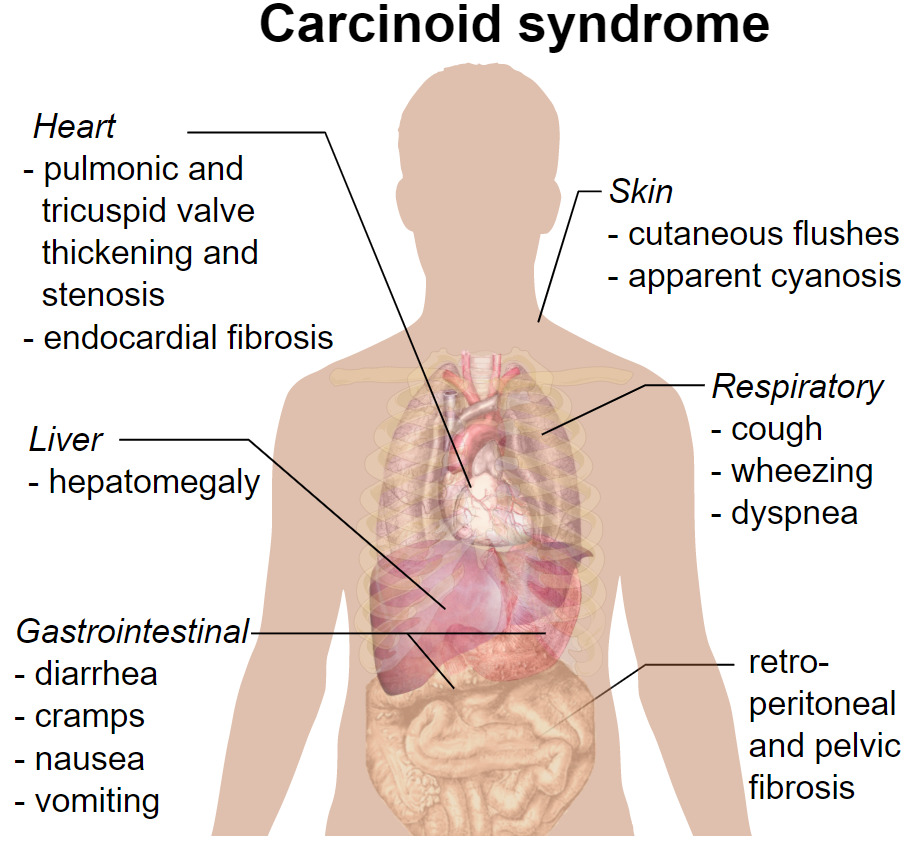
Clinical presentation of carcinoid syndrome
Image: “Carcinoid syndrome presentation” by Mikael Häggström. License: CC0 1.0, edited by Lecturio.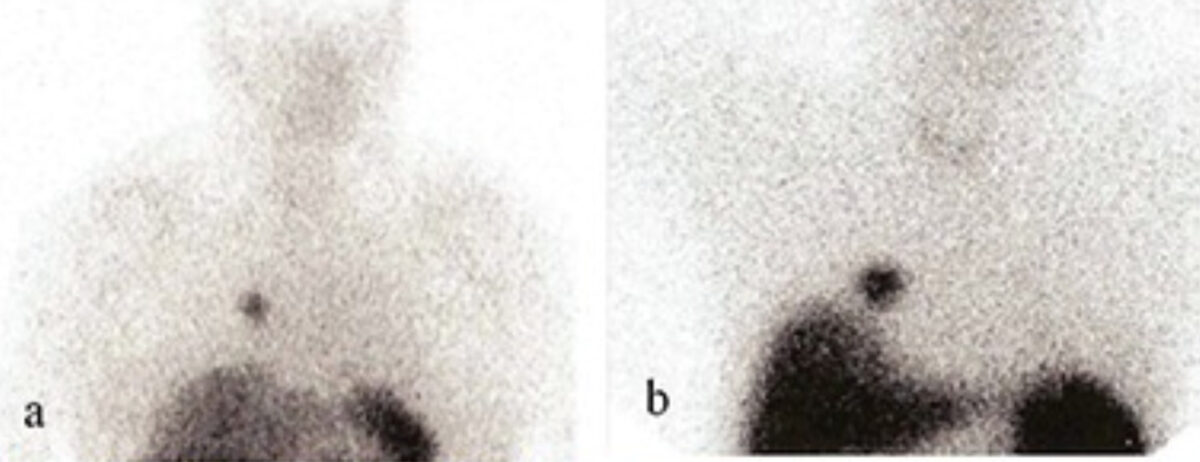
Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy of pulmonary carcinoids:
Most carcinoid tumors express somatostatin receptors. Using scintigraphy, a detailed whole-body scan can be performed to identify masses.
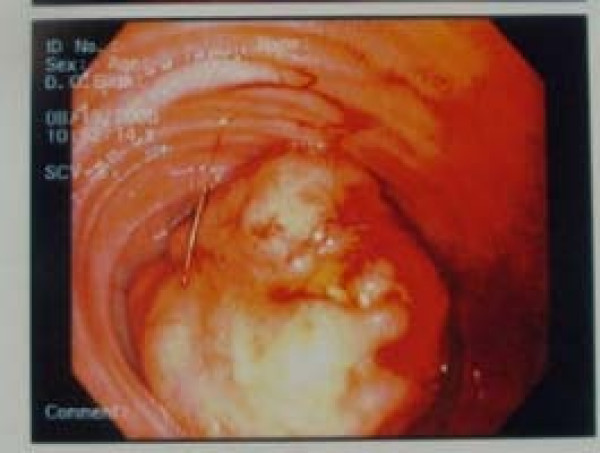
Endoscopic view of the carcinoid tumor of the ileum:
Endoscopy is an important tool in the diagnosis and staging of carcinoid tumors. Upper and lower endoscopies should be performed if a metastatic carcinoid lesion is detected but the primary mass has not been identified.
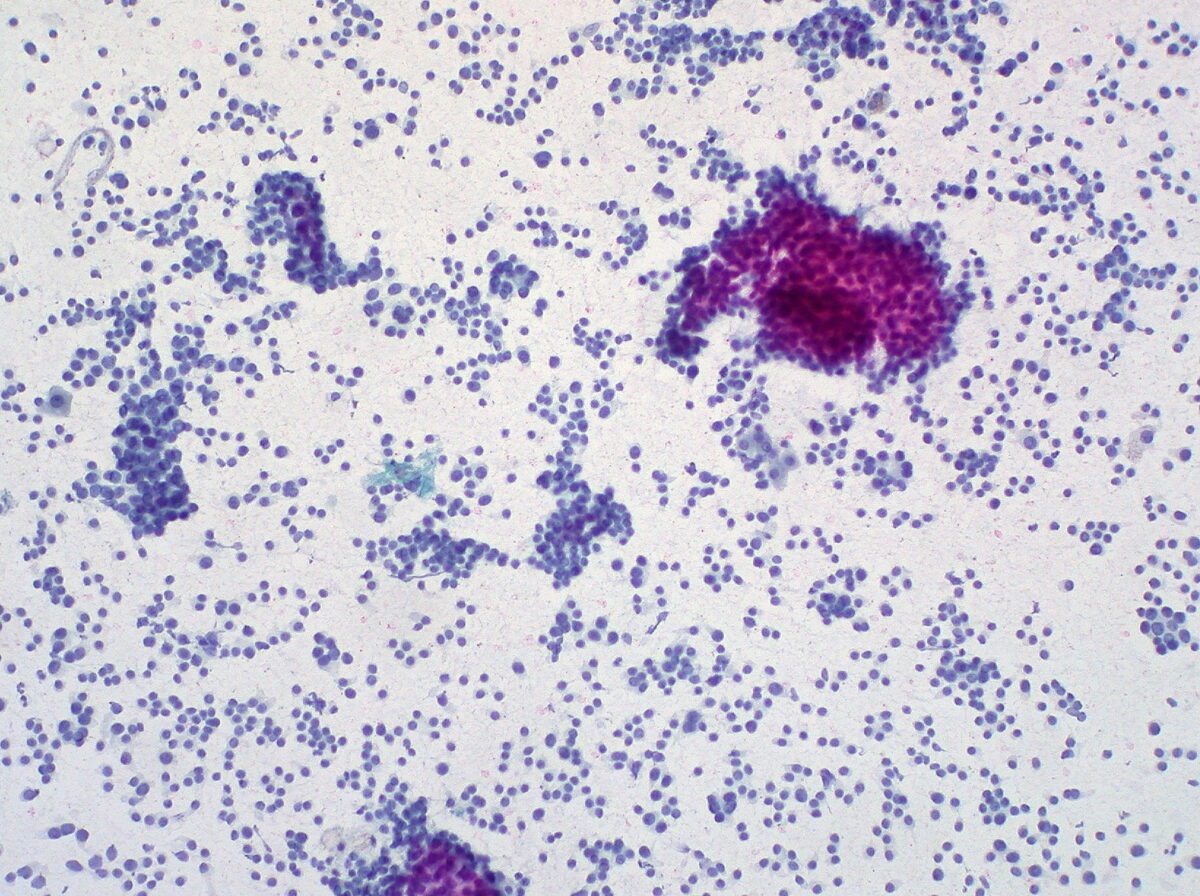
Fine-needle aspiration of the liver showing metastatic carcinoid
Image: “Carcinoid Tumor, Metastatic to Liver, FNA (1)” by Ed Uthman. License: CC BY 2.0Surgical resection is the definitive treatment for non-metastatic tumors.
Medical management of carcinoid syndrome focuses on the use of somatostatin Somatostatin A 14-amino acid peptide named for its ability to inhibit pituitary growth hormone release, also called somatotropin release-inhibiting factor. It is expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems, the gut, and other organs. SRIF can also inhibit the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone; prolactin; insulin; and glucagon besides acting as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. In a number of species including humans, there is an additional form of somatostatin, srif-28 with a 14-amino acid extension at the n-terminal. Gastrointestinal Secretions analogs to inhibit serotonin Serotonin A biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid l-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies.
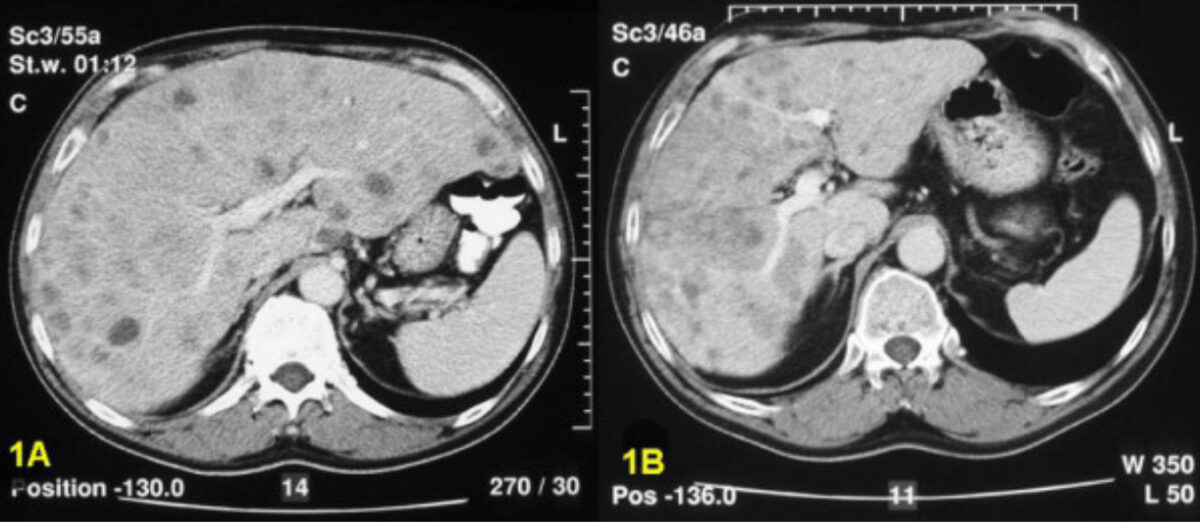
Computed tomography scan showing multiple metastatic carcinoid lesions of the liver before hepatic artery embolization (1A) and after (significant reduction in total liver volume and confluence of metastases (1B))
Image: “Local treatment in unresectable hepatic metastases of carcinoid tumors: Experiences with hepatic artery embolization and radiofrequency ablation” by Meij V, Zuetenhorst JM, van Hillegersberg R, Kröger R, Prevoo W, van Coevorden F, Taal BG. License: CC BY 2.0