Cannabinoids are a class of compounds interacting with cannabinoid receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors. The 3 types of cannabinoids are phytocannabinoids (naturally derived from flora), endocannabinoids (endogenous), and synthetic cannabinoids (artificially produced). Endocannabinoids are endogenous neuropeptide neurotransmitters found in the human nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification. Cannabinoids have a psychotropic effect, which leads to frequent recreational use, but the unique effects of cannabinoids on the CNS also provide pharmacological indications. Prescription cannabinoids treat pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia, and seizure disorders and also serve as appetite stimulants Stimulants Stimulants are used by the general public to increase alertness and energy, decrease fatigue, and promote mental focus. Stimulants have medical uses for individuals with ADHD and sleep disorders, and are also used in combination with analgesics in pain management. Stimulants.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the psychoactive component of cannabis:
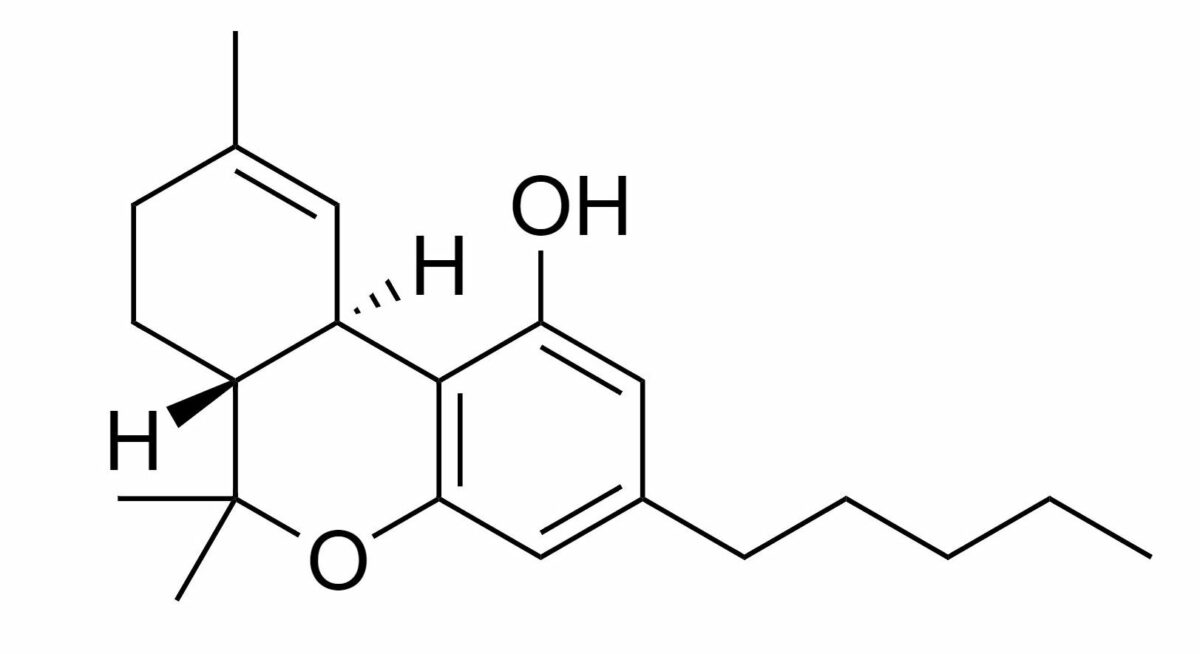
The structure of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): the psychoactive component of cannabis
Image: “THC” by Harbin. License: Public DomainCannabinoids bind BIND Hyperbilirubinemia of the Newborn to peripheral and central receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors:
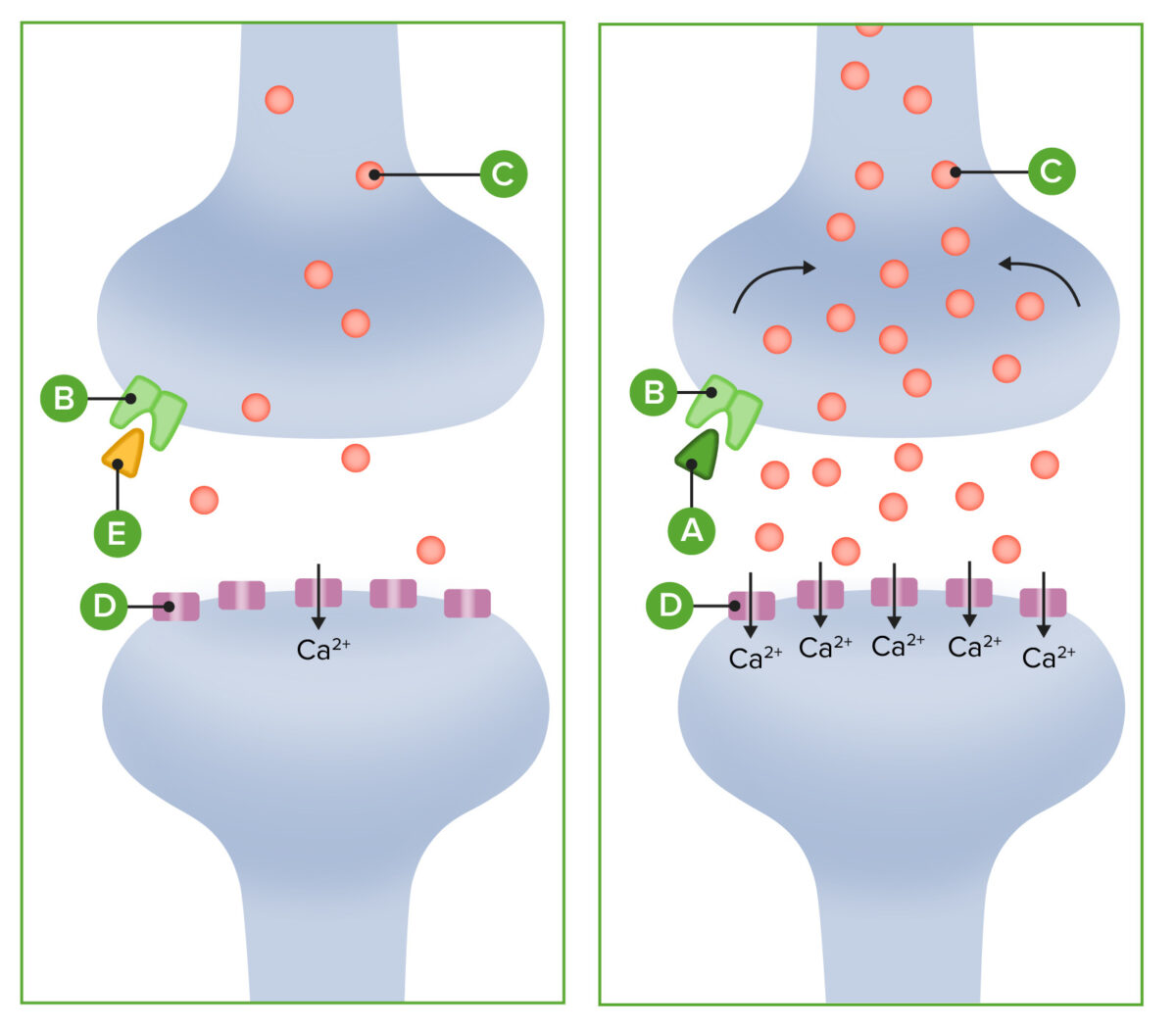
Cannabinoids form a connection with cannabinoid receptors:
Neurotransmitters (including dopamine) flood into the synaptic cleft, causing calcium to be pumped into the postsynaptic neuron at higher levels than observed in healthy natural stimuli. The higher amount of neurotransmitters gives the “high” associated with cannabis. Acting through cannabinoid receptors, THC activates the reward system of the brain. Tetrahydrocannabinol also disrupts functioning of the cerebellum and basal ganglia, which regulate balance, posture, coordination, and reaction time.
The 1st diagram shows normal activity and the 2nd diagram shows activity with the addition of THC.
A: THC
B: CB1 receptors
C: neurotransmitters
D: postsynaptic receptors
E: cannabinoid
Additional potential drug interactions with cannabinoids include:
| Drug | Notes on formulations | Indications |
|---|---|---|
Dronabinol:
|
|
|
| Nabilone: oral capsule Capsule An envelope of loose gel surrounding a bacterial cell which is associated with the virulence of pathogenic bacteria. Some capsules have a well-defined border, whereas others form a slime layer that trails off into the medium. Most capsules consist of relatively simple polysaccharides but there are some bacteria whose capsules are made of polypeptides. Bacteroides Cesamet® | / |
|
| Cannabidiol: oral solution Epidiolex® |
|
Refractory childhood-onset
seizures
Seizures
A seizure is abnormal electrical activity of the neurons in the cerebral cortex that can manifest in numerous ways depending on the region of the brain affected. Seizures consist of a sudden imbalance that occurs between the excitatory and inhibitory signals in cortical neurons, creating a net excitation. The 2 major classes of seizures are focal and generalized.
Seizures in individuals ≥ 2 years of age due to:
|
THC (Dronabinol and Nabilone):
Cannabidiol (Epidiolex®):
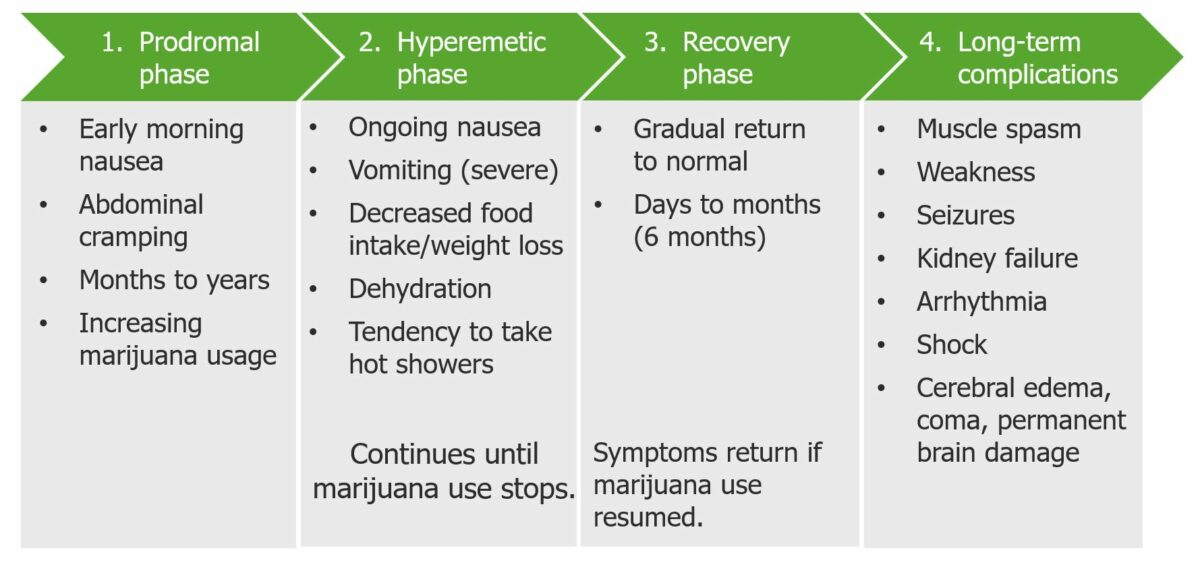
Phases of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS)
Image by Lecturio.| Drugs | Warnings | Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation | Drug interactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dronabinol |
|
|
|
| Nabilone | / |
|
CNS depressants |
| Cannabidiol ( CBD CBD Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes) (Epidiolex®) |
|
Allergic to sesame seed oil |
|