Campylobacter ("curved bacteria") is a genus of thermophilic, S-shaped, gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella. There are many species of Campylobacter, with C. jejuni and C. coli most commonly implicated in human disease. The mode of transmission is primarily through the consumption of undercooked food contaminated with Campylobacter. Infection is most often associated with self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis and is also a major cause of bloody diarrhea Bloody diarrhea Diarrhea, especially in children. Two associated complications of Campylobacter gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis are Guillain-Barré syndrome Guillain-Barré syndrome Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), once thought to be a single disease process, is a family of immune-mediated polyneuropathies that occur after infections (e.g., with Campylobacter jejuni). Guillain-Barré Syndrome and reactive arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis.
Last updated: Jan 26, 2025
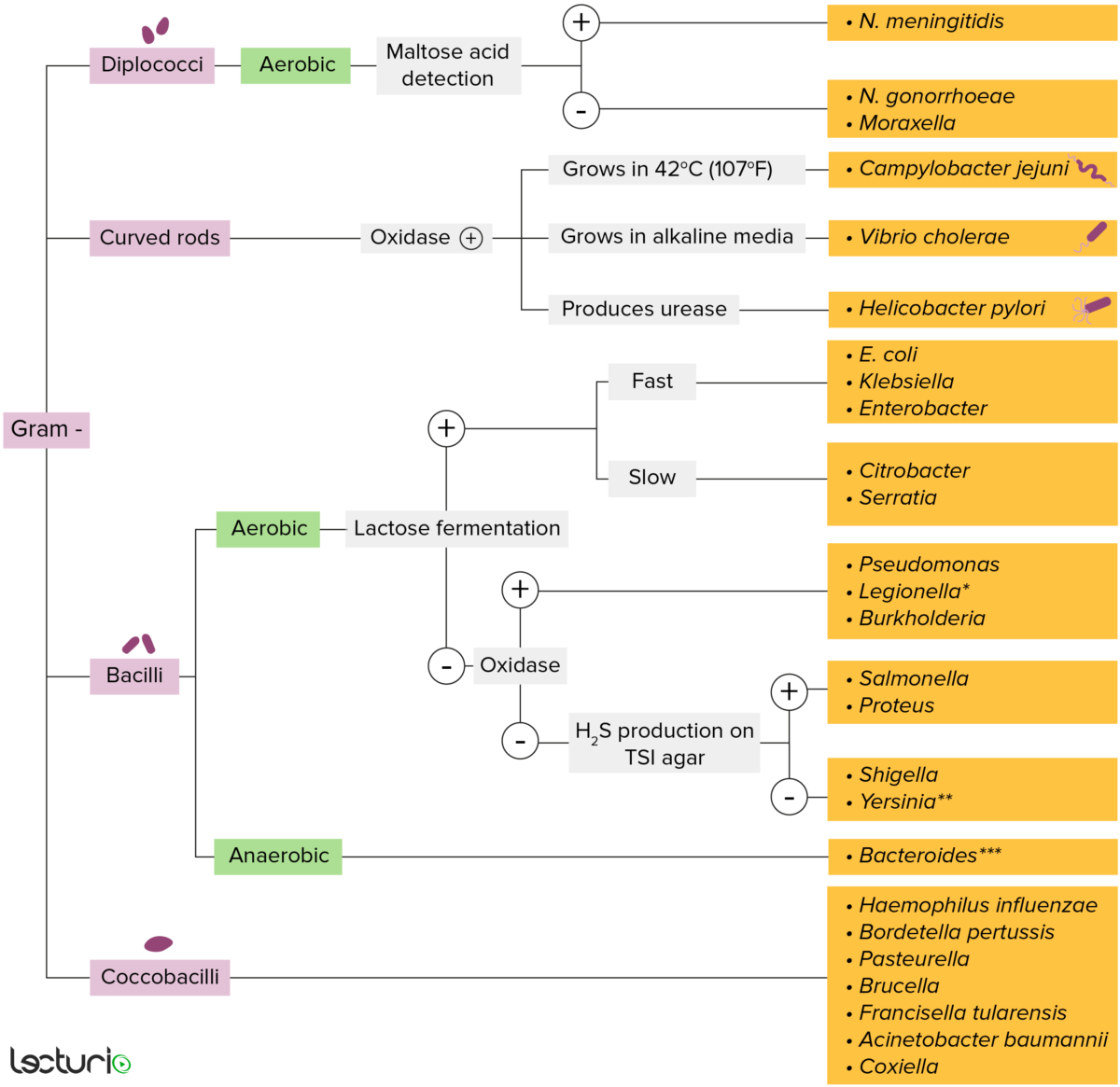
Gram-negative bacteria:
Most bacteria can be classified according to a lab procedure called Gram staining.
Bacteria with cell walls that have a thin layer of peptidoglycan do not retain the crystal violet stain utilized in Gram staining. These bacteria do, however, retain the safranin counterstain and thus appear as pinkish-red on the stain, making them gram negative. These bacteria can be further classified according to morphology (diplococci, curved rods, bacilli, and coccobacilli) and their ability to grow in the presence of oxygen (aerobic versus anaerobic). The bacteria can be more narrowly identified by growing them on specific media (triple sugar iron (TSI) agar) where their enzymes can be identified (urease, oxidase) and their ability to ferment lactose can be tested.
* Stains poorly on Gram stain
** Pleomorphic rod/coccobacillus
*** Require special transport media
General characteristics of Campylobacter species include:
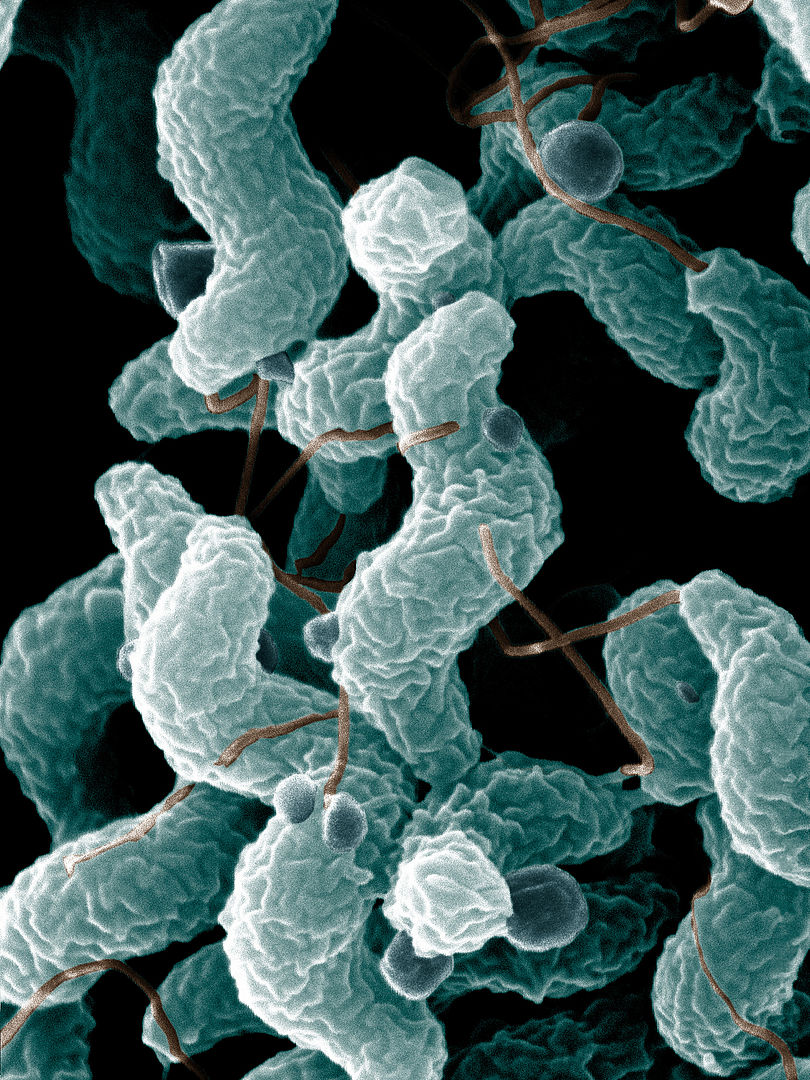
Campylobacter bacteria
Scanning electron micrograph depicts an S-shaped organism with a single, polar flagella.
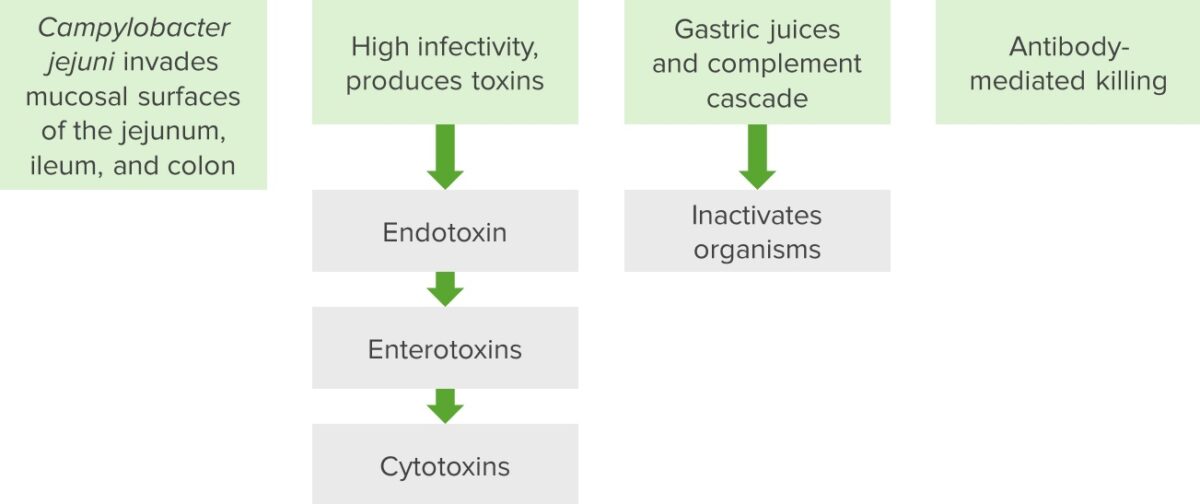
Campylobacter pathogenesis
When pathogens are embedded in the mucosal surfaces, they produce a variety of toxins which include endotoxin, enterotoxins, and cytotoxins. The body reacts by activating the complement cascade which results in the inactivation of organisms. The humoral immune system reacts by creating antibodies, which then target the Campylobacter and cause molecular mimicry to the human neurological and musculoskeletal systems. This results in an autoimmune response.