Complement component 3 (C3) deficiency is the absence, reduction, or dysfunction of complement factor C3 and its fragments, C3a and C3b. Complement factors are key components of the innate immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs. Reduced levels of C3b increase the probability Probability Probability is a mathematical tool used to study randomness and provide predictions about the likelihood of something happening. There are several basic rules of probability that can be used to help determine the probability of multiple events happening together, separately, or sequentially. Basics of Probability of developing infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease with encapsulated Encapsulated Klebsiella organisms (e.g., Pneumococcus, Haemophilus Haemophilus Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative coccobacilli, all of whose strains require at least 1 of 2 factors for growth (factor V [NAD] and factor X [heme]); therefore, it is most often isolated on chocolate agar, which can supply both factors. The pathogenic species are H. influenzae and H. ducreyi. Haemophilus influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza, Neisseria meningitidis Neisseria meningitidis A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria. It is a commensal and pathogen only of humans, and can be carried asymptomatically in the nasopharynx. When found in cerebrospinal fluid it is the causative agent of cerebrospinal meningitis. It is also found in venereal discharges and blood. There are at least 13 serogroups based on antigenic differences in the capsular polysaccharides; the ones causing most meningitis infections being a, b, c, y, and w-135. Each serogroup can be further classified by serotype, serosubtype, and immunotype. Neisseria), especially respiratory infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, due to reduced opsonization. Individuals with C3 deficiencies are also more susceptible to type III hypersensitivity reactions because a reduced clearance of antigen-antibody C3b complexes from the circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment causes an increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Complement component 3 (C3) deficiency is part of the larger category of complement deficiencies:
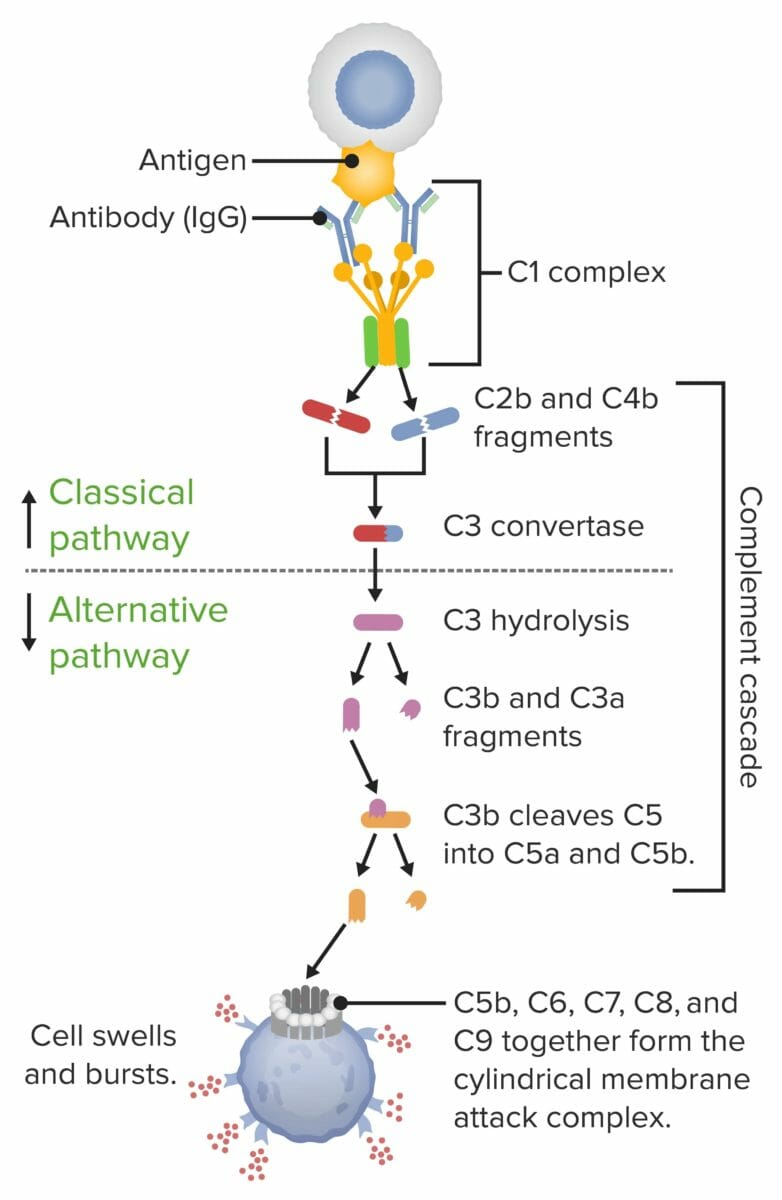
Membrane attack complex (MAC) formation:
When the 1st protein in the complement series is activated (typically by an antibody locked onto an antigen), a domino effect is set into motion. Each component takes a turn in a precise chain of steps known as the complement cascade. The end product is the cylindrical MAC, which inserts into and punctures a hole in the cell’s wall. With fluids and molecules flowing in and out, the cell swells and bursts.
Clinical testing directed by pattern of infection:
Management of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with C3 deficiency centers on prevention of illness.