The bones of growing children exhibit unique characteristics. These characteristics, combined with the unique mechanisms of injury seen in children, result in fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures patterns that differ significantly from those that are common in adults. When axial Axial Computed Tomography (CT) loads are applied, particularly to long bones Long bones Length greater than width. Bones: Structure and Types in children, compressive forces may result in buckling of the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types without disruption of the periosteum Periosteum Thin outer membrane that surrounds a bone. It contains connective tissue, capillaries, nerves, and a number of cell types. Bones: Structure and Types. These fractures are called buckle or torus fractures and are considered generally stable, requiring only immobilization Immobilization Delirium.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A buckle, or torus, fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures is a fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures that primarily affects growing metaphyseal bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types secondary to a compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma load, in which the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types buckles or compresses.
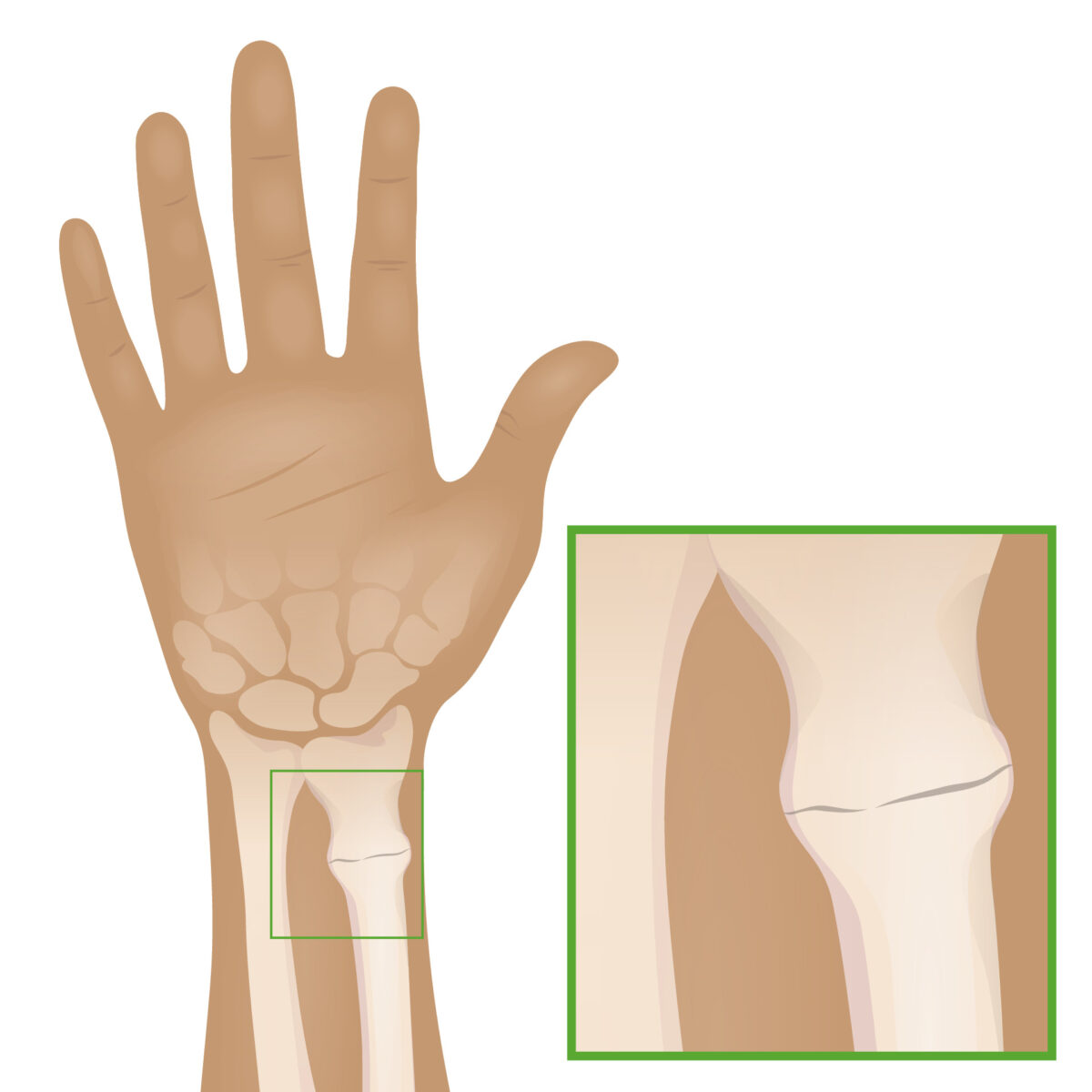
Buckle (torus) fracture:
Caused primarily by an axial load, a buckle fracture is a common injury seen primarily in the pediatric population. The fracture features disrupted cortices but intact periosteum, appearing as a bulge or prominence, generally with little angulation.
The clinical presentation of pediatric patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with buckle fractures is similar to patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with other pediatric fractures.
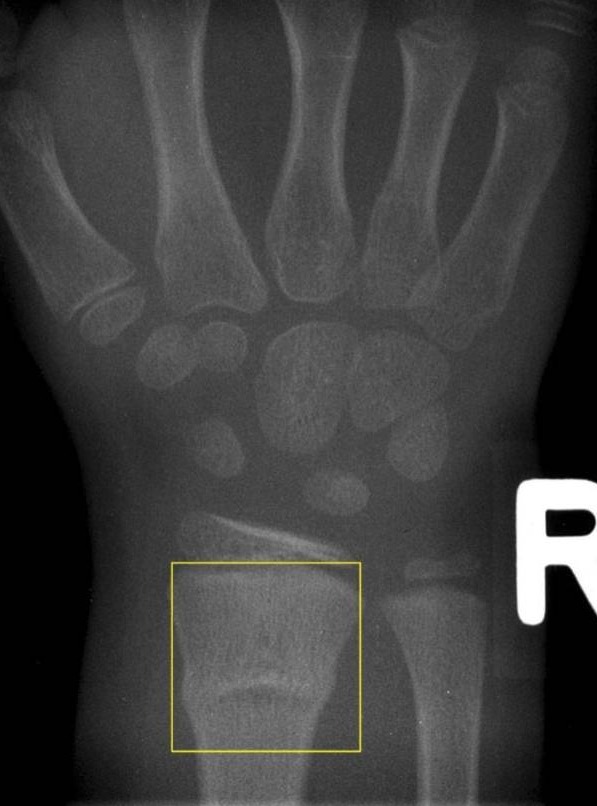
Buckle fracture of the distal radius:
Buckle fractures of the distal radius are common in children. X-ray findings may be subtle, but they often include visible buckling on both sides of the bone.
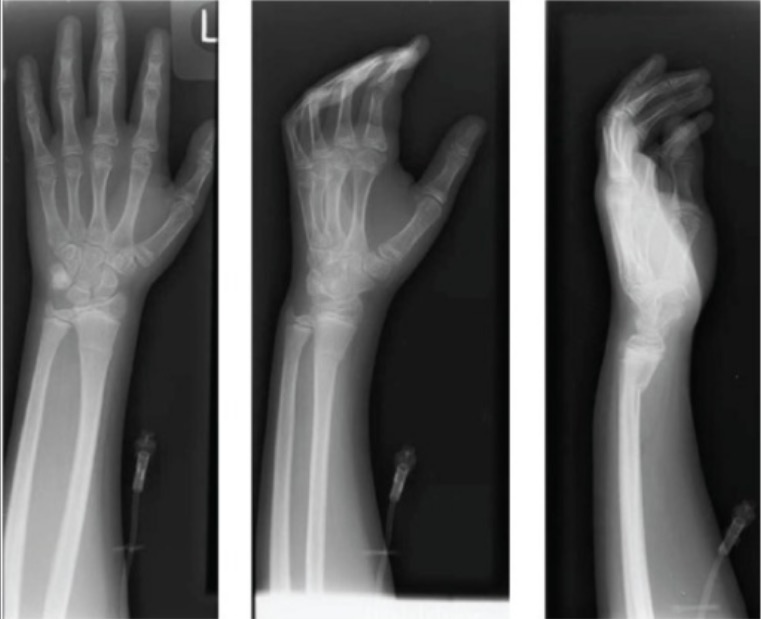
Radiographs of left wrist showing apex-dorsal distal radius buckle fracture
Image: “Radiographs of left wrist showing apex-dorsal distal radius buckle fracture” by Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Maimonides Medical Center, 927 49th Street, 2nd floor, Brooklyn, NY 11219, USA. License: CC BY 3.0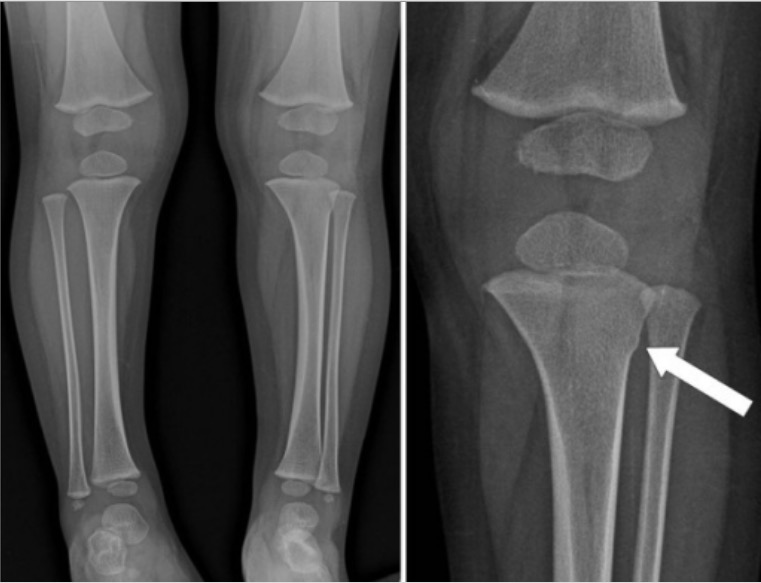
Whole lower extremity radiograph showing a metaphyseal torus fracture of the left tibia (arrow)
Image: “Whole lower extremity radiograph” by American Hospital, Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Istanbul, Turkey. License: CC BY 2.0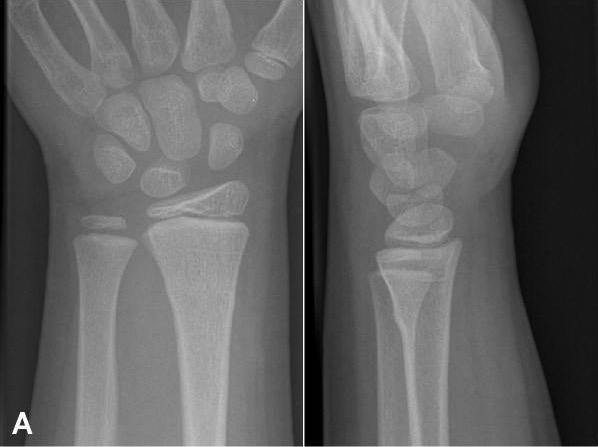
Buckle fracture of distal wrist:
Imaging findings of buckle fractures may be subtle. Here, slight bowing of the cortical bone of the radius indicates the fracture.
The majority of buckle fractures are stable and treated with immobilization Immobilization Delirium.
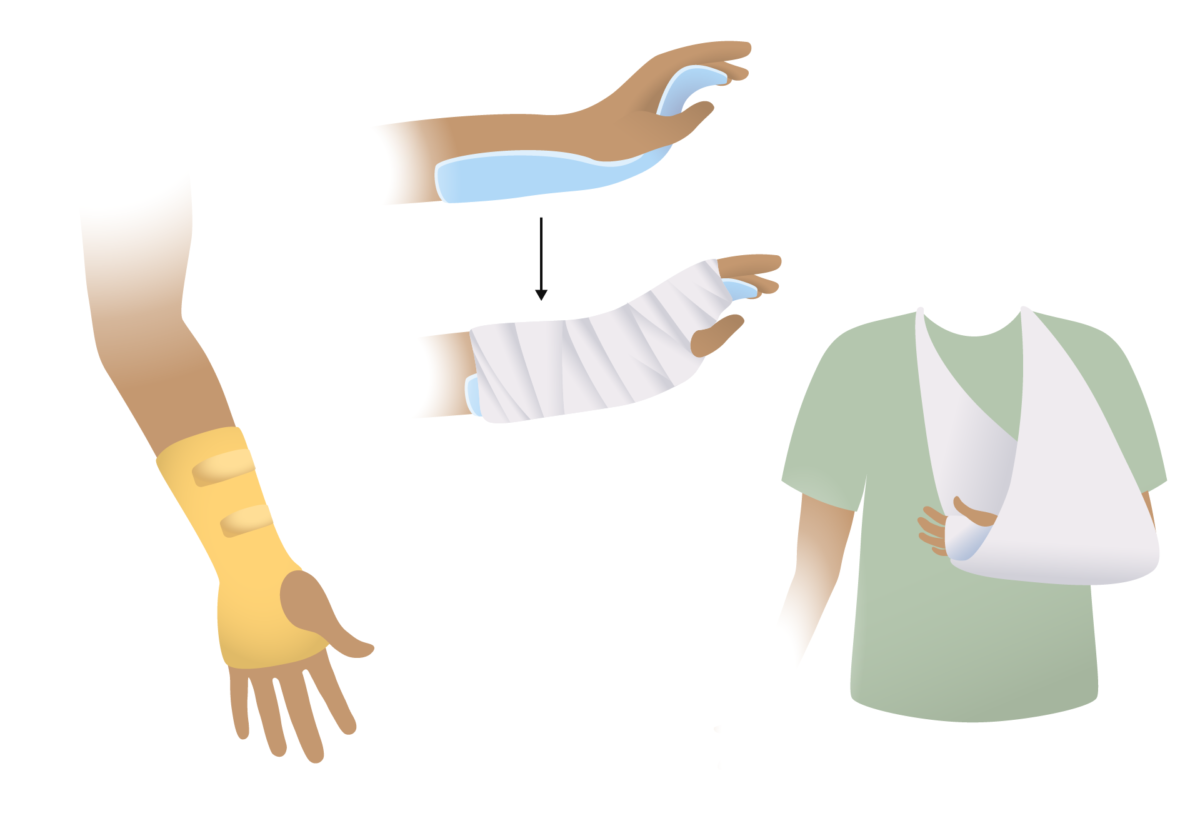
Splinting options for forearm:
In many patients, pediatric fractures of the forearm will heal with simple splinting.
Additional important pediatric skeletal injuries: