Breastfeeding is often the primary source of nutrition for the newborn Newborn An infant during the first 28 days after birth. Physical Examination of the Newborn. During pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care, hormonal stimulation causes the number and size of mammary glands in the breast to significantly increase. After delivery, prolactin Prolactin A lactogenic hormone secreted by the adenohypophysis. It is a polypeptide of approximately 23 kd. Besides its major action on lactation, in some species prolactin exerts effects on reproduction, maternal behavior, fat metabolism, immunomodulation and osmoregulation. Breasts: Anatomy stimulates milk production, while oxytocin stimulates milk expulsion through the lactiferous ducts Lactiferous ducts Breasts: Anatomy, where it is sucked out through the nipple Nipple The conic organs which usually give outlet to milk from the mammary glands. Examination of the Breast by the infant. Breastfeeding has many benefits for the mother and baby, including a decreased risk of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, GI distress, and atopic disease for the infant; and a decreased risk of anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, cardiovascular disease, and breast and ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor arising from the ovarian tissue and is classified according to the type of tissue from which it originates. The 3 major types of ovarian cancer are epithelial ovarian carcinomas (EOCs), ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs), and sex cord-stromal tumors (SCSTs). Ovarian Cancer for the mother. True contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation to breastfeeding exist but are quite rare. Important clinical conditions associated with breastfeeding include engorgement Engorgement Mastitis, mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis, galactocele Galactocele Benign Breast Conditions, breast abscess Breast Abscess Benign Breast Conditions, and infant jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice.
Last updated: Jan 2, 2024
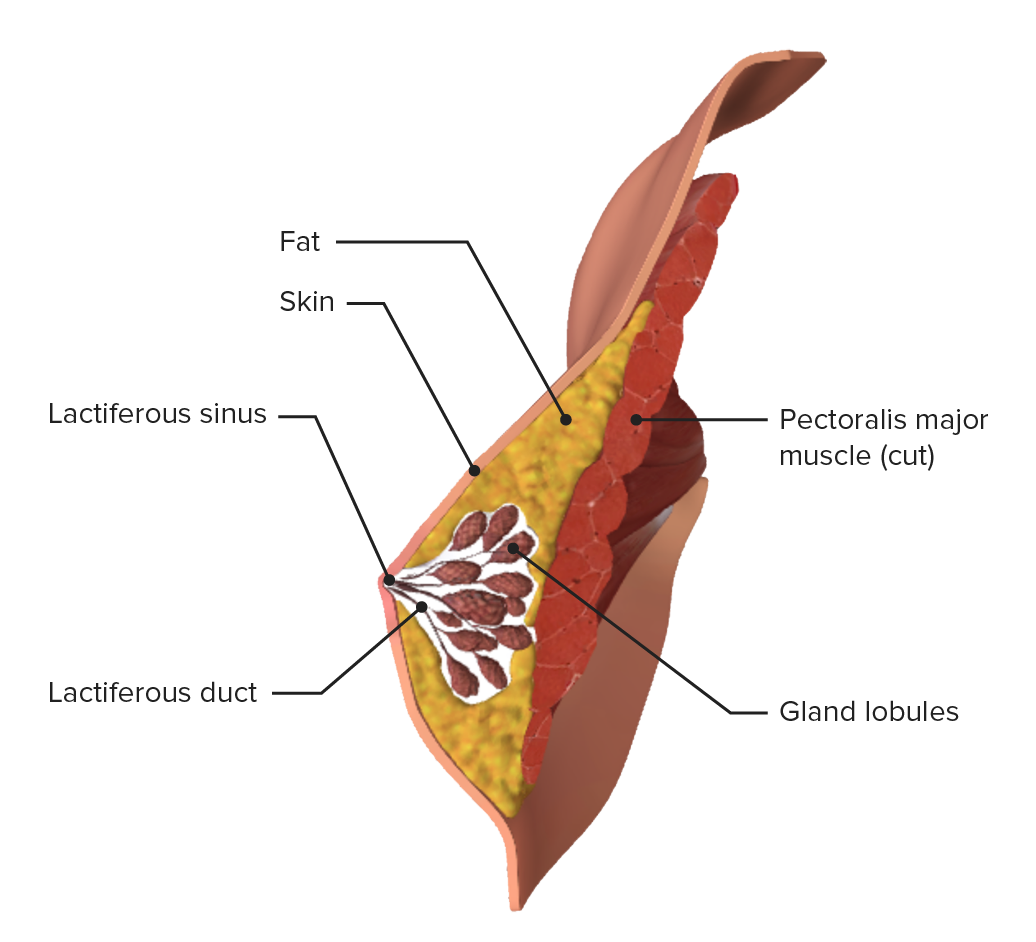
Diagram of a sagittal cross-section of the breast
Image by Lecturio.Significant growth and maturation of the breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy occur during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care as a result of hormonal secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies by the placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity.
Ejection of milk requires the pituitary Pituitary A small, unpaired gland situated in the sella turcica. It is connected to the hypothalamus by a short stalk which is called the infundibulum. Hormones: Overview and Types hormone oxytocin.
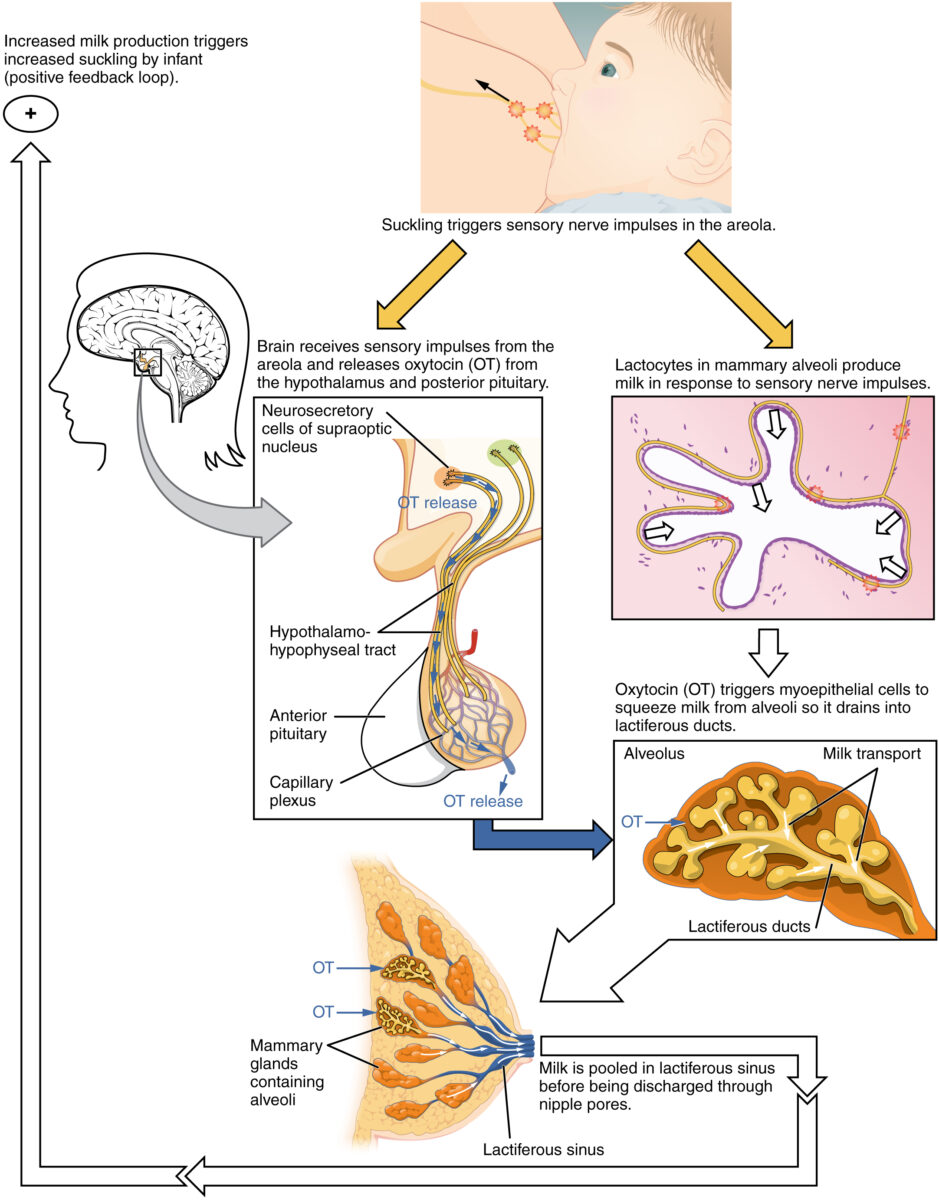
The let-down reflex
Image: “A positive feedback loop ensures continued milk production as long as the infant continues to breastfeed” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 4.0There are 2 stages of lactogenesis:
Although usually “breast is best,” there are cases when breastfeeding is not recommended, in which case, “fed is best.” These cases include:
True contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation to breastfeeding are rare, but include:
Breastfeeding is recommended by the WHO, US CDC, and United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF). Specifically, these organizations recommend the following:
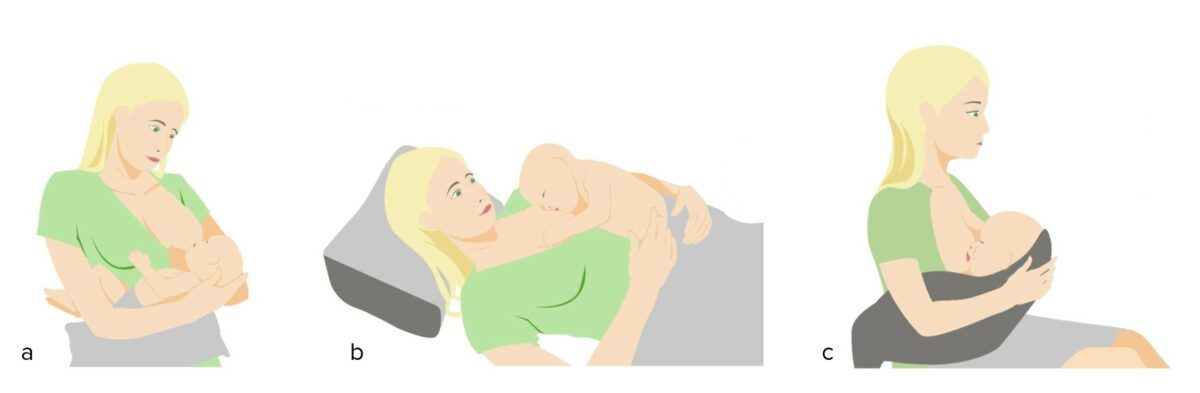
Breastfeeding positions:
a. Cross-cradle position
b. Supine position
c. Football hold
Two types of infantile jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice are associated with breastfeeding: