Female breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy, made of glandular, adipose, and connective tissue Connective tissue Connective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix. Connective Tissue: Histology, are hormone-sensitive organs that undergo changes along with the menstrual cycle Menstrual cycle The menstrual cycle is the cyclic pattern of hormonal and tissular activity that prepares a suitable uterine environment for the fertilization and implantation of an ovum. The menstrual cycle involves both an endometrial and ovarian cycle that are dependent on one another for proper functioning. There are 2 phases of the ovarian cycle and 3 phases of the endometrial cycle. Menstrual Cycle and during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy may be affected by various diseases, in which different imaging methods are important to arrive at the correct diagnosis and management. Mammography Mammography Radiographic examination of the breast. Breast Cancer Screening is used for breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer screening Screening Preoperative Care and diagnostic evaluation of various breast-related symptoms. Ultrasonography is rarely used for screening Screening Preoperative Care, but it is typically used for diagnostic workup and during procedures (e.g., breast biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma). MRI of the breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy is used as a supplementary screening Screening Preoperative Care tool for those at high risk for developing breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer. Additionally, in individuals with breast implants, inconclusive mammographic and/or breast ultrasound Breast Ultrasound Fibrocystic Change findings, and diagnosed breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer needing evaluation pretreatment and posttreatment, MRI is an important breast radiologic tool.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
There are no absolute contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation, but there are relative ones (owing to adverse effects of radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma exposure).
| Views | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard views | Mediolateral oblique (MLO) view | Better view of the superior lateral quadrant of the breast Quadrant of The Breast Examination of the Breast and axilla Axilla The axilla is a pyramid-shaped space located between the upper thorax and the arm. The axilla has a base, an apex, and 4 walls (anterior, medial, lateral, posterior). The base of the pyramid is made up of the axillary skin. The apex is the axillary inlet, located between the 1st rib, superior border of the scapula, and clavicle. Axilla and Brachial Plexus: Anatomy |
| Craniocaudal view (CC) |
|
|
| Specialized views | Spot compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma | Better visualization of suspicious masses, calcifications, or asymmetric breast tissue |
| Magnification | ||
| XCCL (exaggerated CC lateral) view | Modified CC view, focused on the lateral part of breast | |
| XCCM (exaggerated CC medial) view | Modified CC view, focused on the medial part of the breast | |
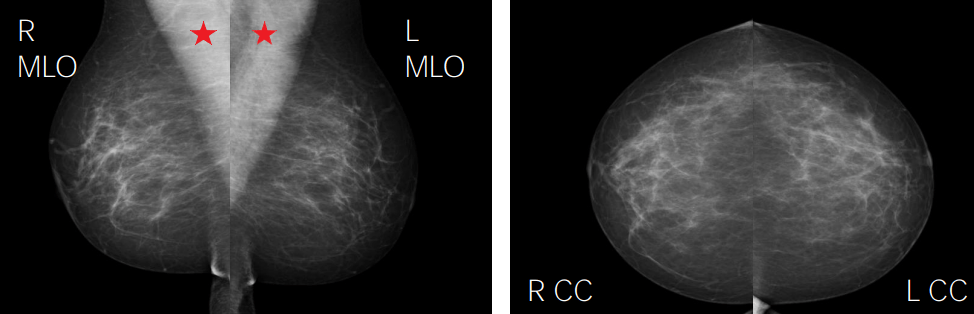
Normal mammogram, depicting fibroglandular tissue:
Red stars represent pectoralis major.
CC: craniocaudal
MLO: mediolateral oblique
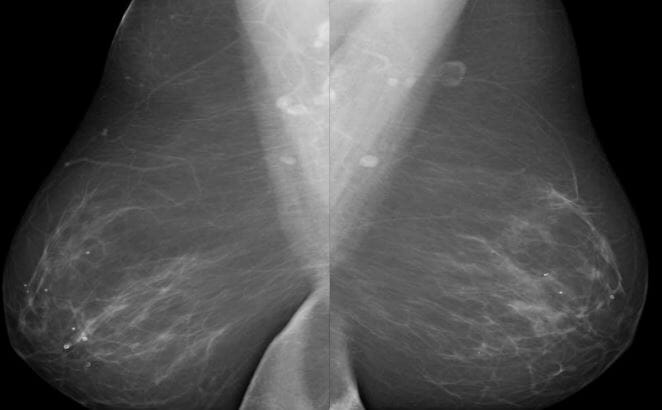
Breast density, almost entirely fatty
Image by Hetal Verma.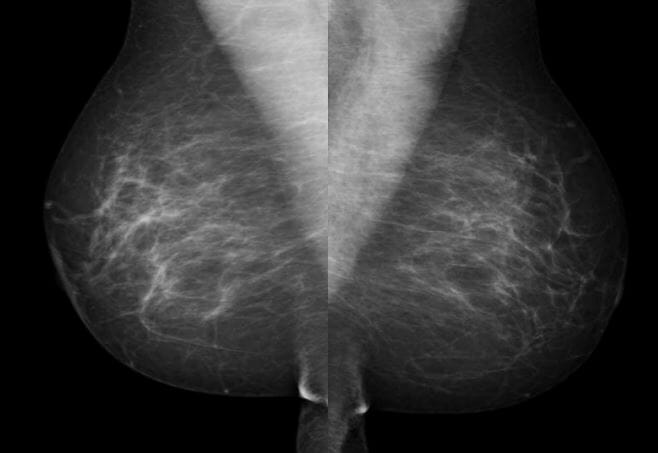
Breast density, scattered fibroglandular
Image by Hetal Verma.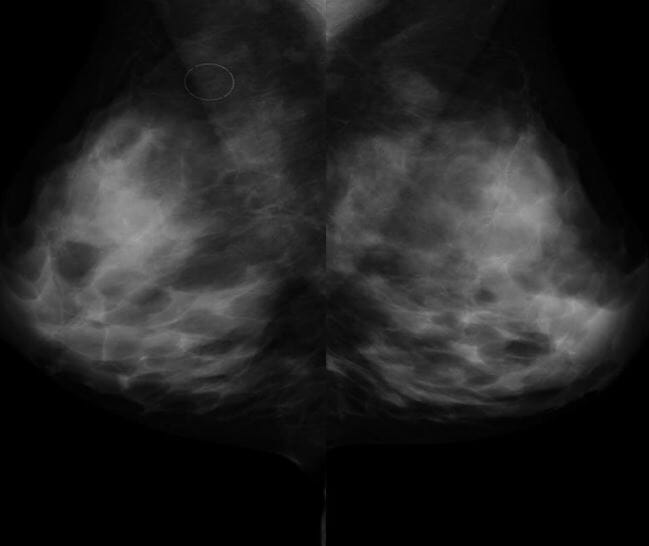
Breast density, heterogeneously dense
Image by Hetal Verma.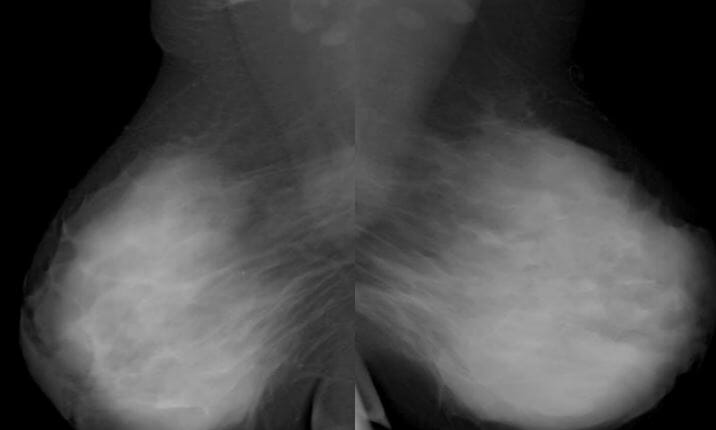
Breast density, extremely dense
Image by Hetal Verma.| Category | Assessment | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| BI-RADS 0 | Incomplete assessment | Additional mammography Mammography Radiographic examination of the breast. Breast Cancer Screening views or ultrasound follow-up needed |
| BI-RADS 1 | Negative | Continue with routine screening Screening Preoperative Care |
| BI-RADS 2 | Benign Benign Fibroadenoma findings | Continue with routine screening Screening Preoperative Care |
| BI-RADS 3 | Probably benign Benign Fibroadenoma findings | Diagnostic mammography Mammography Radiographic examination of the breast. Breast Cancer Screening or ultrasound in 6 months |
| BI-RADS 4 | Suspicious abnormality | Biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma should be considered. |
| BI-RADS 5 | Highly suggestive of malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax | Biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma should be performed. |
| BI-RADS 6 | Biopsy-proven malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax | Management for breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer |
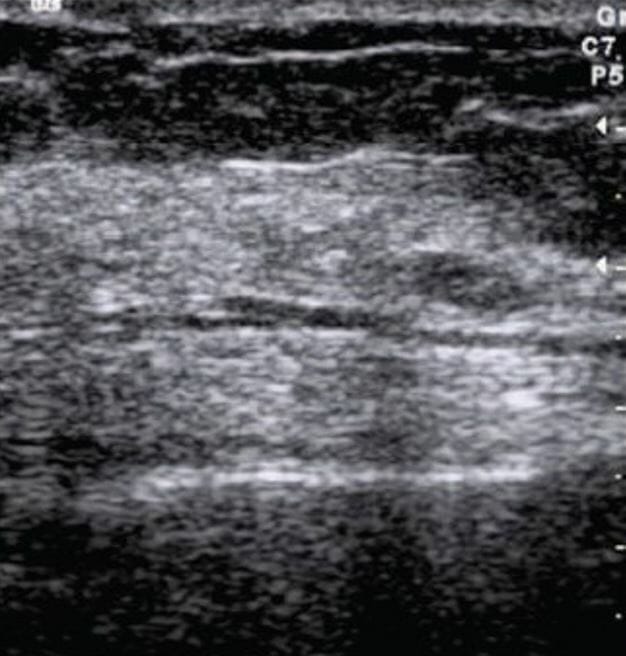
Ultrasound image of a normal breast:
The fibroglandular parenchyma is echogenic and surrounded by hypoechoic fat.
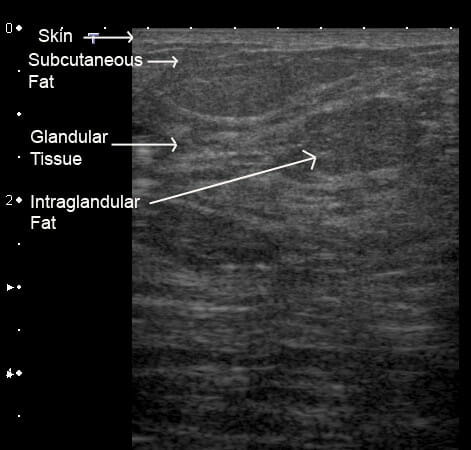
Ultrasound image of a lactating breast:
The skin is displayed as an echogenic line. The glandular tissue is hyperechoic, with lines representing the epithelial lining, and the fat is slightly more hypoechoic.
Radiologic technique that uses magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses to produce highly detailed images of the breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy.
A breast MRI is contraindicated in MRI-incompatible hardware or anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis An acute hypersensitivity reaction due to exposure to a previously encountered antigen. The reaction may include rapidly progressing urticaria, respiratory distress, vascular collapse, systemic shock, and death. Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction to gadolinium Gadolinium An element of the rare earth family of metals. It has the atomic symbol gd, atomic number 64, and atomic weight 157. 25. Its oxide is used in the control rods of some nuclear reactors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Findings are grouped into 3 categories:
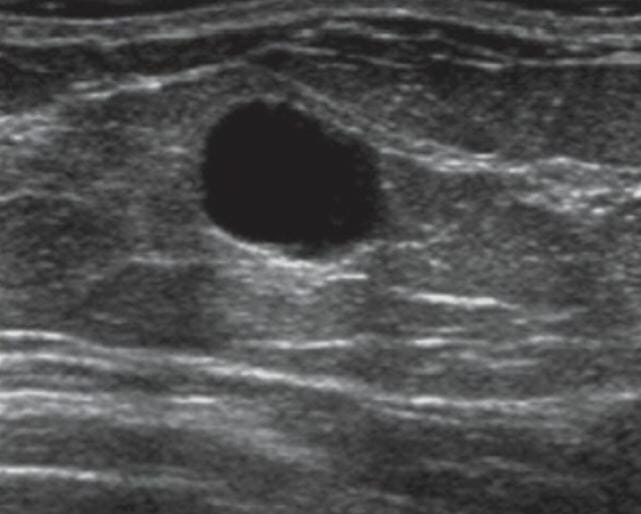
Ultrasound image shows a well-defined oval anechoic mass with imperceptible walls and posterior acoustic enhancement consistent with a simple cyst.
Image: “A 37-year-old female with a palpable breast mass” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Nguyen JQ. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.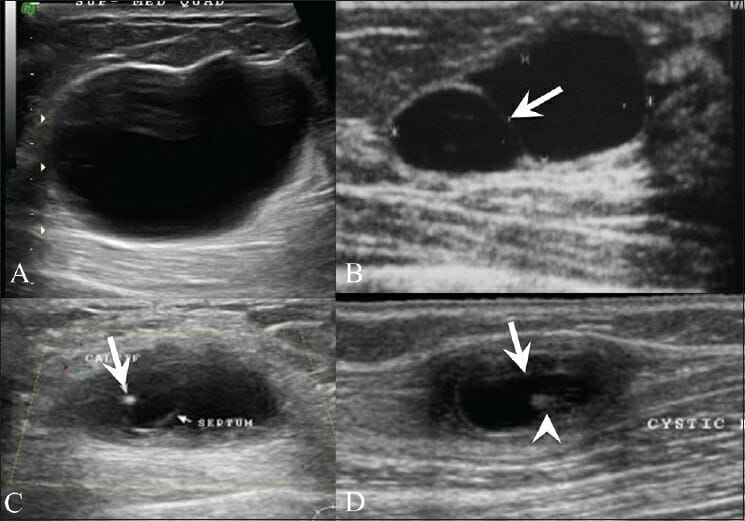
Breast ultrasound (US) shows a simple cyst (A), presenting as an anechoic lesion with posterior enhancement and a cyst (B) with a septum (arrow).
Breast US (C) in a 26-year-old woman with a painless palpable lump in her left breast shows a complex cyst, with an eccentrically placed echogenic focus (arrow) representing the scolex of a cysticercus granuloma.
She also had a similar swelling in the right upper arm, a US (D) of which also revealed a cyst (arrow) with an echogenic scolex (arrowhead) within.
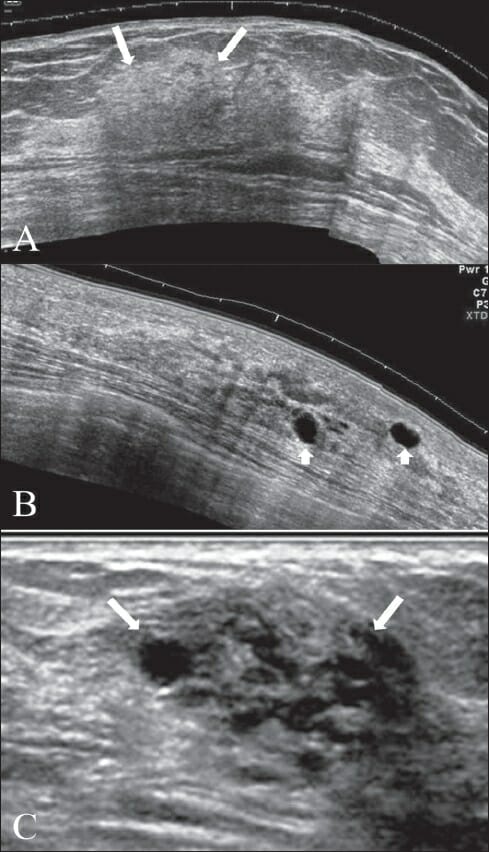
Ultrasound image showing a focal area of thickening with patchy appearance (A, arrows), scattered, discrete, thin-walled cysts (B, arrowheads), and a cluster of tiny cysts (C, arrows)
The characteristics of these lesions suggest fibrocystic changes.
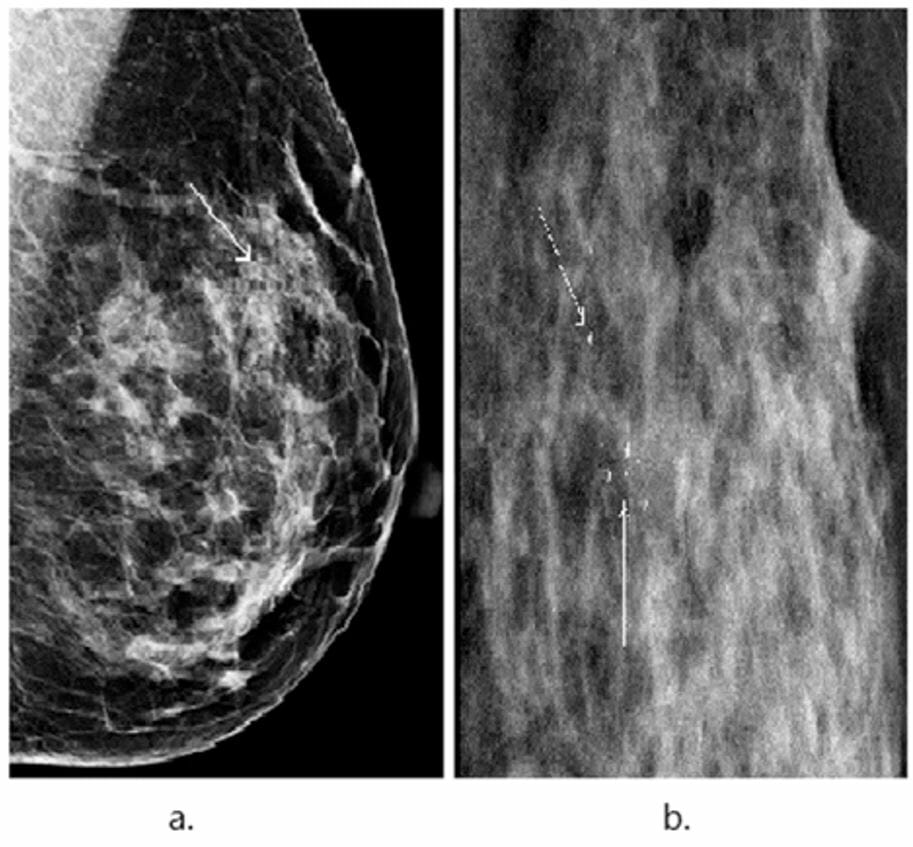
Mammogram showing focal microcalcifications (thin arrows) with surrounding dense parenchyma, suggestive of fibrocystic changes
Image: “An illustrative example showing segmentation of microcalcifications in a mammogram” by Wang J, Yang X, Cai H, Tan W, Jin C, Li L. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.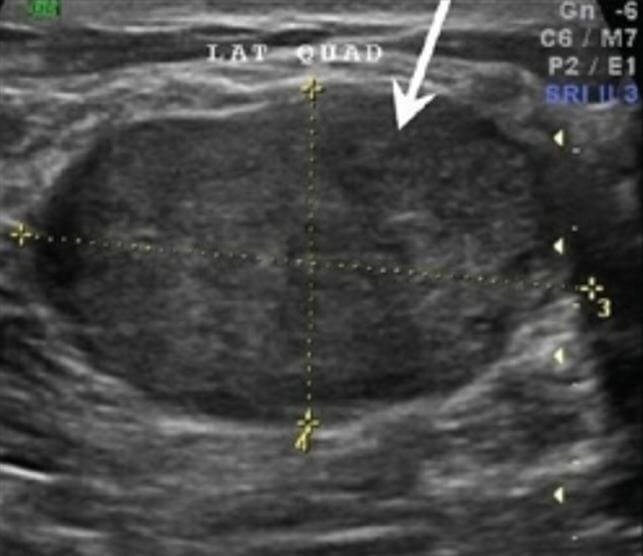
Ultrasound image showing a homogeneous, hypoechoic mass that is oval-shaped and has a greater transverse diameter, suggesting a fibroadenoma
Image: “Fibroadenoma” by Shah G, Jankharia B. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.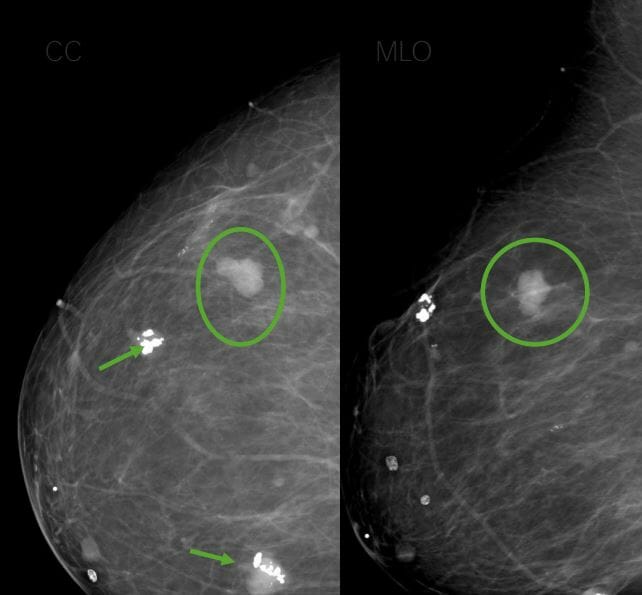
Mammogram showing popcorn calcifications (arrows) and upper lateral mass (circle), suggestive of fibroadenomas
Image by Hetal Verma.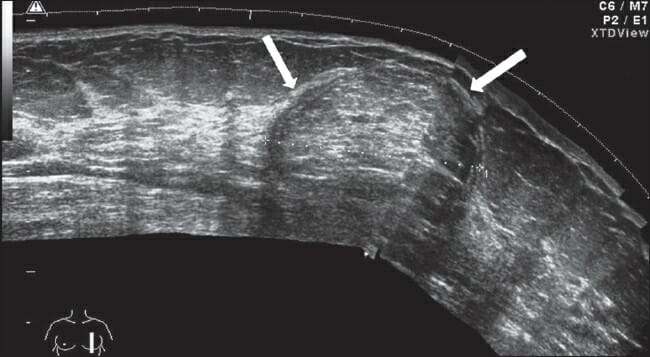
Ultrasound image of a well-defined subtly echogenic mass (lipoma) with a lamellar pattern and a well-defined, thin capsule (arrows)
Image: “Lipoma” by Gokhale, S. License: CC BY 2.0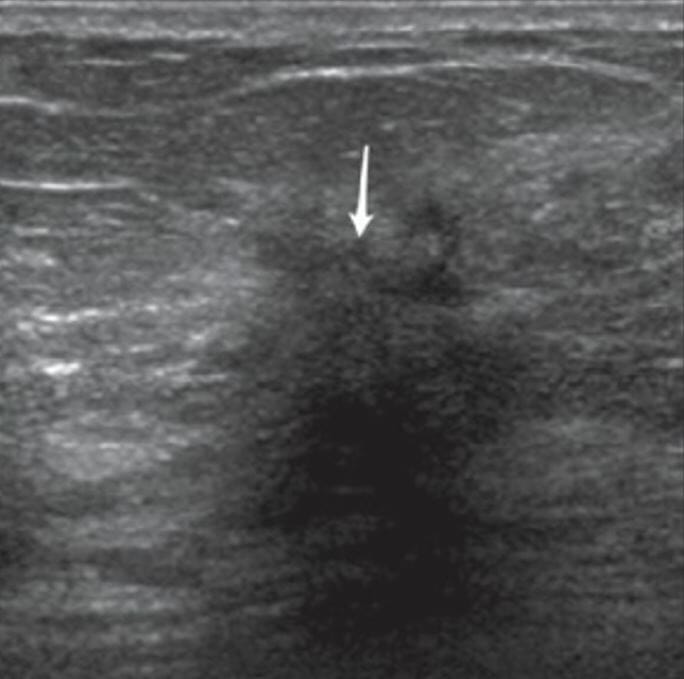
Ultrasound image of a hypoechoic mass with irregular borders, spiculated margins, and posterior acoustic shadowing (arrow)
Characteristics of the mass suggest a malignant tumor.
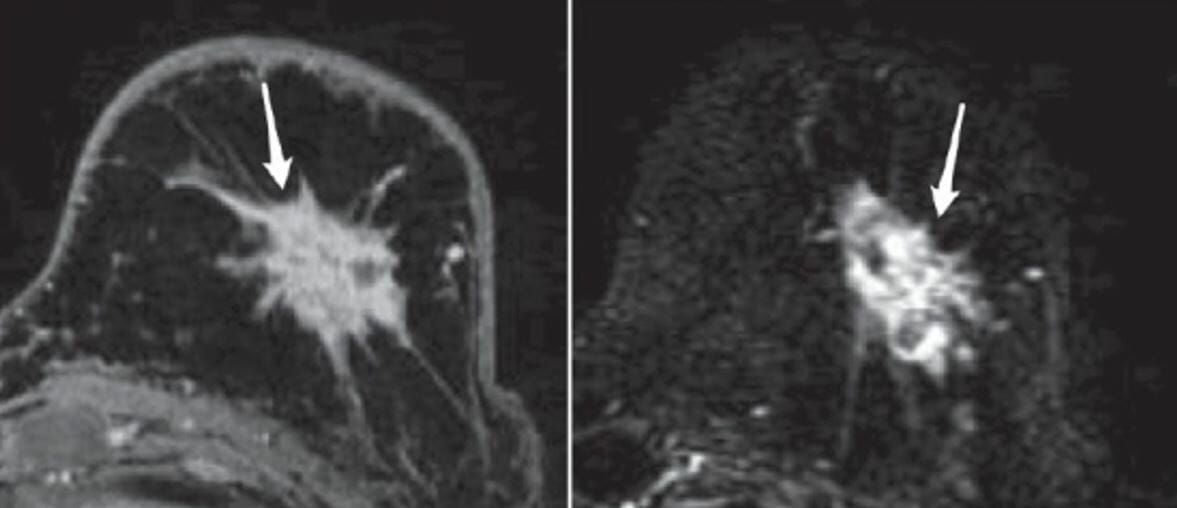
MRI with contrast shows a heterogeneously enhancing irregular mass with spiculated margins, suggestive of breast cancer.
Image: “A 55-year-old woman with a palpable abnormality” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Nguyen JQ. License: CC BY 2.0, cropped by Lecturio.
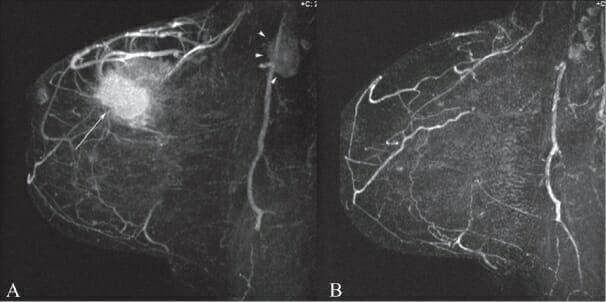
A: MRI of breast shows a primary tumor (thin arrow) and axillary lymphadenopathy (arrowheads).
B: Postchemotherapy MRI of breast shows resolution of the mass and lymphadenopathy.
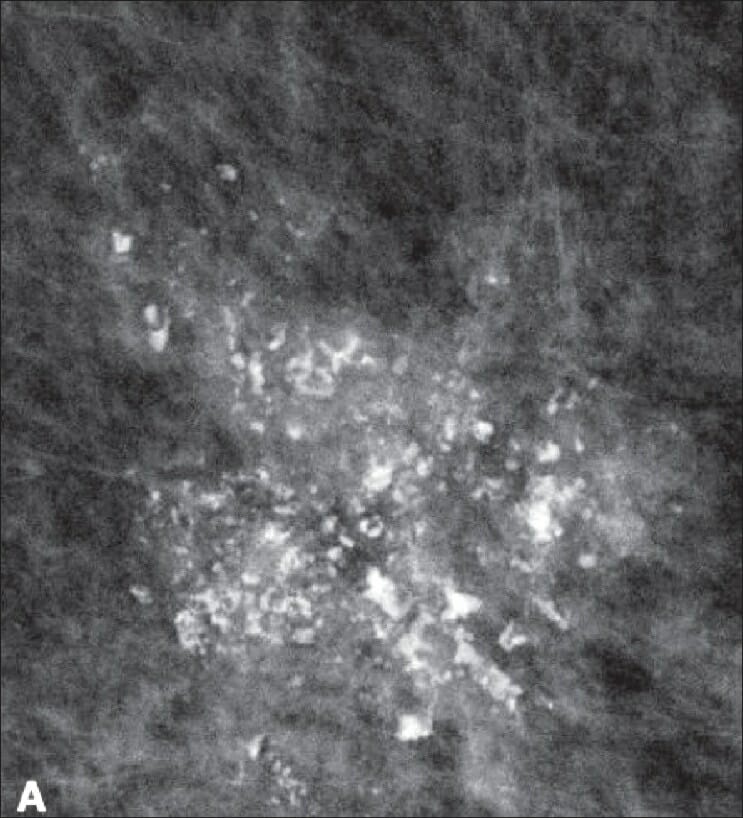
Mammogram showing a group of pleomorphic microcalcifications, suggestive of breast cancer
Image: “Screening mammogram in a 63-year-old woman” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Nguyen JQ. License: CC BY 2.0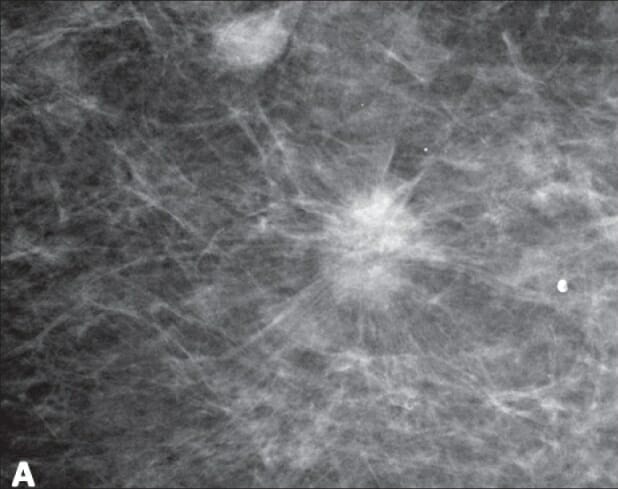
Mammogram showing a spiculated mass, suggestive of breast cancer
Image: “Screening mammography in a 67-year-old woman” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Nguyen JQ. License: CC BY 2.0
Ultrasound image showing a lesion of mixed echogenicity, reported as fat necrosis/oil cyst
Biopsy confirmed fat necrosis.
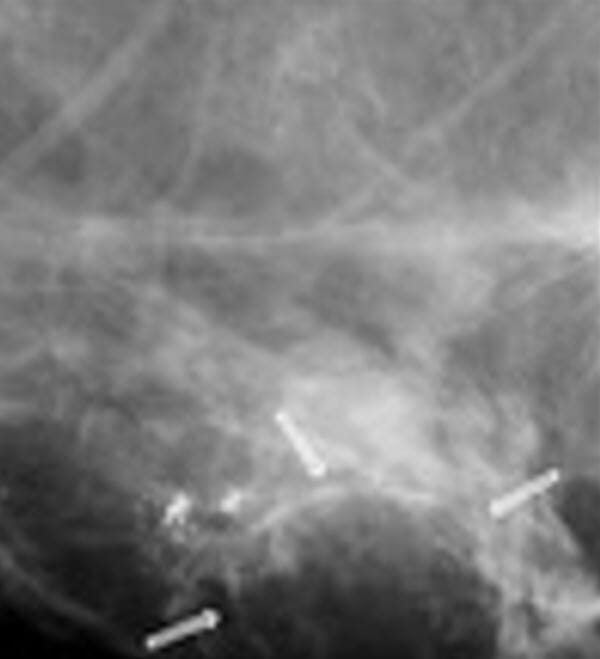
Mammogram showing well-circumscribed lesion (arrows) with soft border and several calcifications near the lesion, suggestive of an oil cyst
Image: “VA, US and mammography images” by Alizad A, Mehrmohammadi M, Ghosh K, Glazebrook KN, Carter RE, Karaberkmez LG, Whaley DH, Fatemi M. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.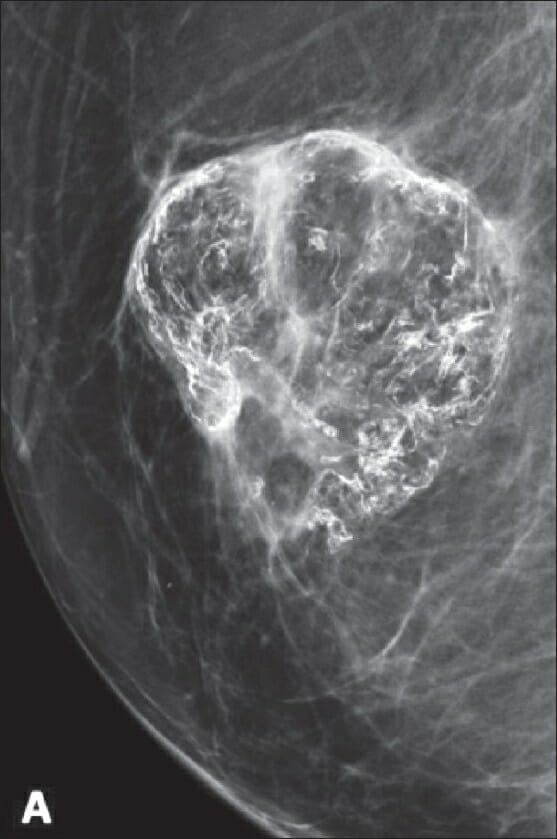
Mammogram showing coarse and eggshell calcification, suggestive of fat necrosis
Image: “A 52-year-old woman presented with a palpable abnormality following breast reduction surgery” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Nguyen JQ. License: CC BY 2.0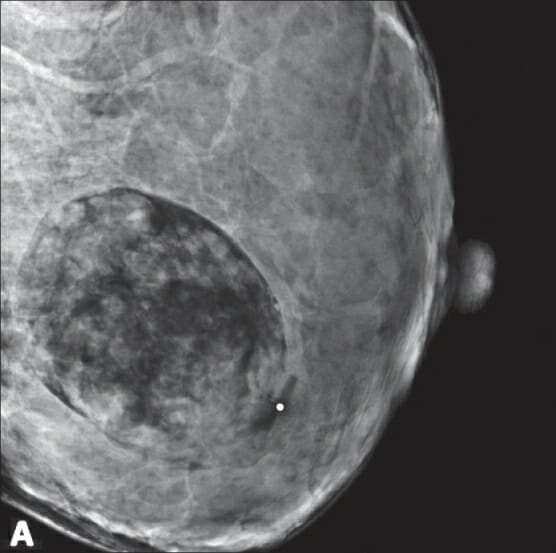
Mammogram showing a fat-containing oval mass, suggestive of hamartoma
Image: “A 26-year-old pregnant female with a new palpable mass” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Nguyen JQ. License: CC BY 2.0