Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation Transformation Change brought about to an organism's genetic composition by unidirectional transfer (transfection; transduction, genetic; conjugation, genetic, etc.) and incorporation of foreign DNA into prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells by recombination of part or all of that DNA into the cell's genome. Bacteriology of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Genetic factors, age, and hormonal and environmental influence contribute to the progression of the disease. The most common histologic type is infiltrating ductal carcinoma, which is > 75% of all breast cancers. Screening Screening Preoperative Care mammography Mammography Radiographic examination of the breast. Breast Cancer Screening is recommended for early disease detection. Diagnosis is by core needle biopsy Core Needle Biopsy Fibrocystic Change, with biologic factors determined by immunohistochemical testing. Surgery, systemic treatment ( chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma, biologic therapy, endocrine therapy), and radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy (RT) are part of the early-stage and locally advanced disease management. In metastatic breast cancer, systemic treatment is utilized with palliative measures.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Unmodifiable factors that increase the risk:
Modifiable risk factors:
Mnemonics:
“BReast- CA CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)ncer 1 and 2” = Mutated genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure are the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure.
Non-invasive:
Invasive:
Other clinical forms:
Based on expression of:
Molecular types:
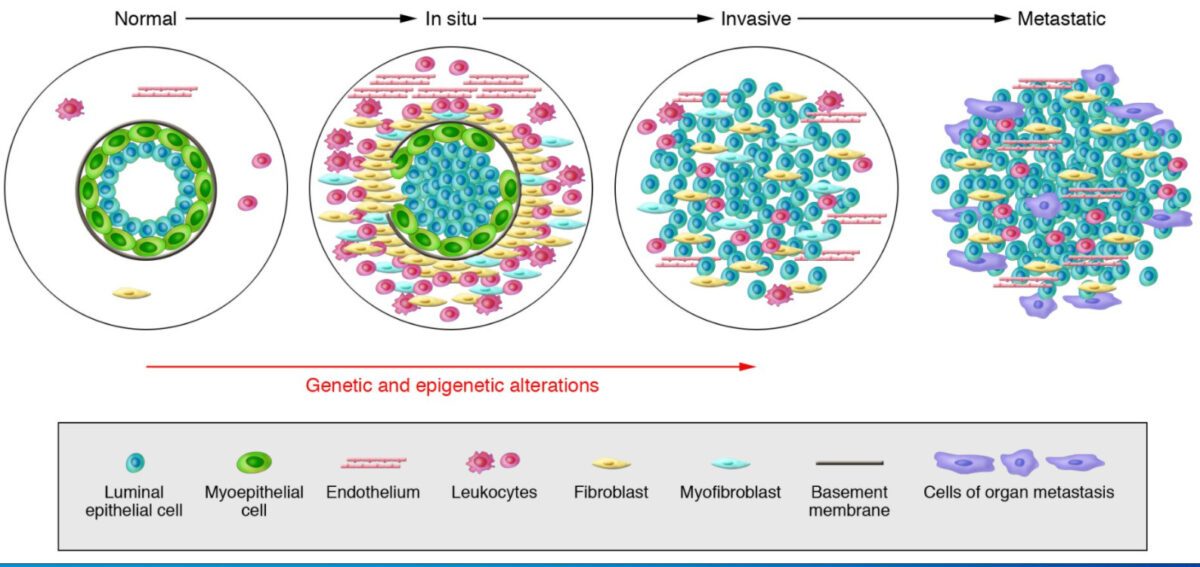
Model of breast tumor progression
From left to right: Normal breast ducts are composed of the basement membrane and a layer of luminal epithelial and myoepithelial cells. The stroma includes various leukocytes, fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and endothelial cells. In in situ carcinomas: The myoepithelial cells are epigenetically and phenotypically altered and their number decreases, potentially due to degradation of the basement membrane. The stromal fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, lymphocytes, and endothelial cells increase. In invasive carcinomas, there is a loss of myoepithelial cells and basement membrane, in which tumor cells can invade surrounding tissues. The tumor cells migrate to distant organs, eventually leading to metastases.
In areas with established breast cancer screening Screening Preoperative Care: Most cases of cancer are diagnosed by having an abnormal mammogram Mammogram Fibrocystic Change.
Symptoms:
Signs:
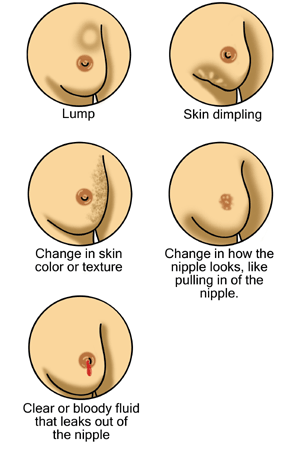
Possible signs of breast cancer
From right to left, top to bottom: a breast lump/mass, skin dimpling, change in skin color/texture, nipple changes including retraction (pulling in of the nipple), and nipple discharge
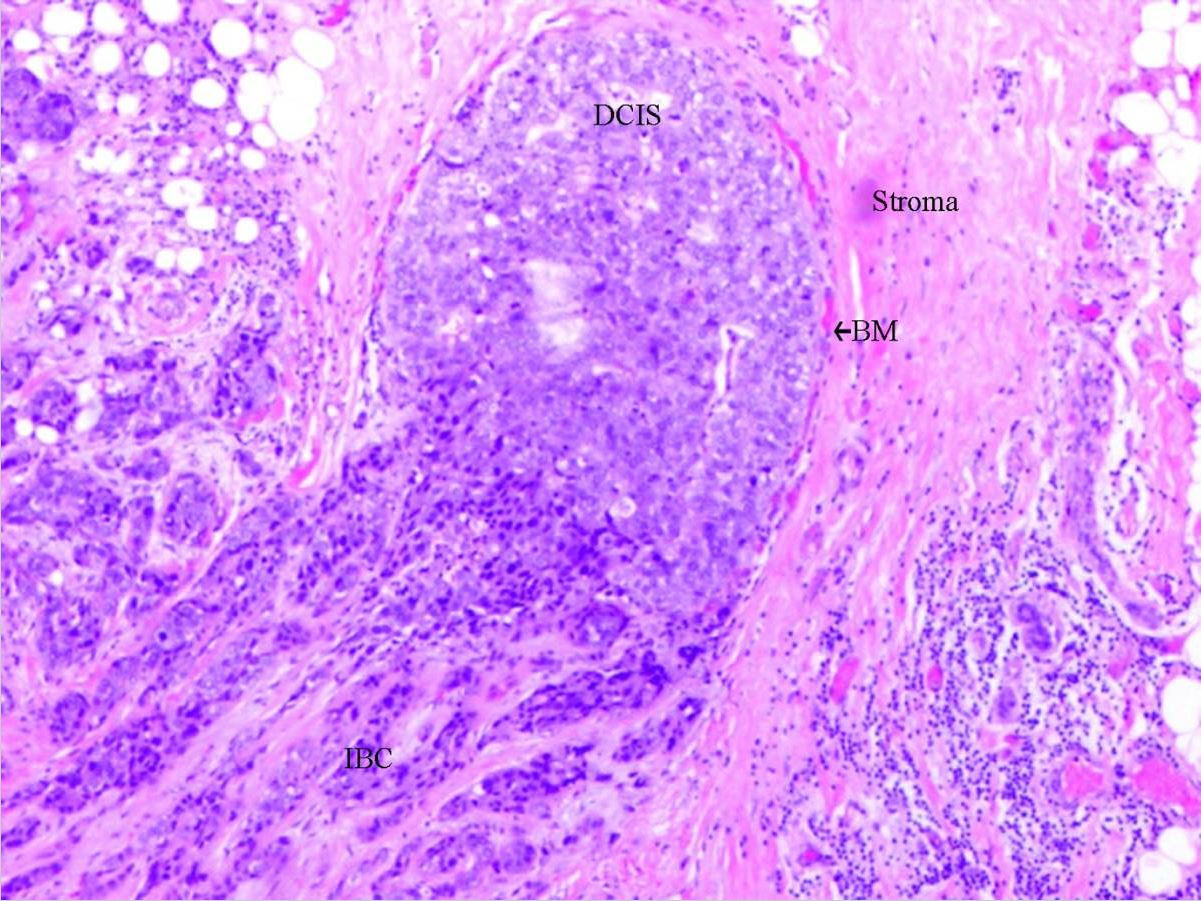
Ductal carcinoma in situ: DCIS with invasion
Abbreviations used:
DCIS: ductal carcinoma in situ
BM: basal membrane
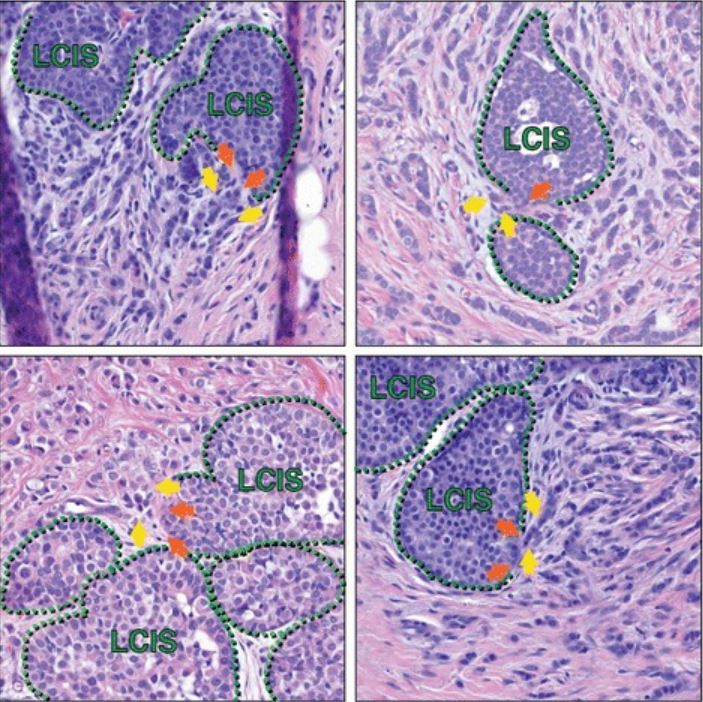
Lobular carcinoma in situ in association with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)
Histologic sections from multiple patients capture areas of LCIS that appear to have focal myoepithelial layer disruption adjacent to ILC, suggesting possible progression of LCIS to ILC at such transitions. Green hatched lines mark the myoepithelial layer; orange arrows are possible foci of myoepithelial disruption; yellow arrows highlight invasive cells. In addition to the cells marked by yellow arrows, additional ILC cells are present in each image throughout the stroma, surrounding the areas of LCIS.
| DCIS | LCIS | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentation | Unifocal Unifocal Retinoblastoma | Multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma |
| Patterns |
|
Solid |
| Calcification | Yes/no | Usually no |
| Risk of invasive breast cancer | Higher | Lower |
| Location of cancer | Ipsilateral breast | Ipsilateral or contralateral |
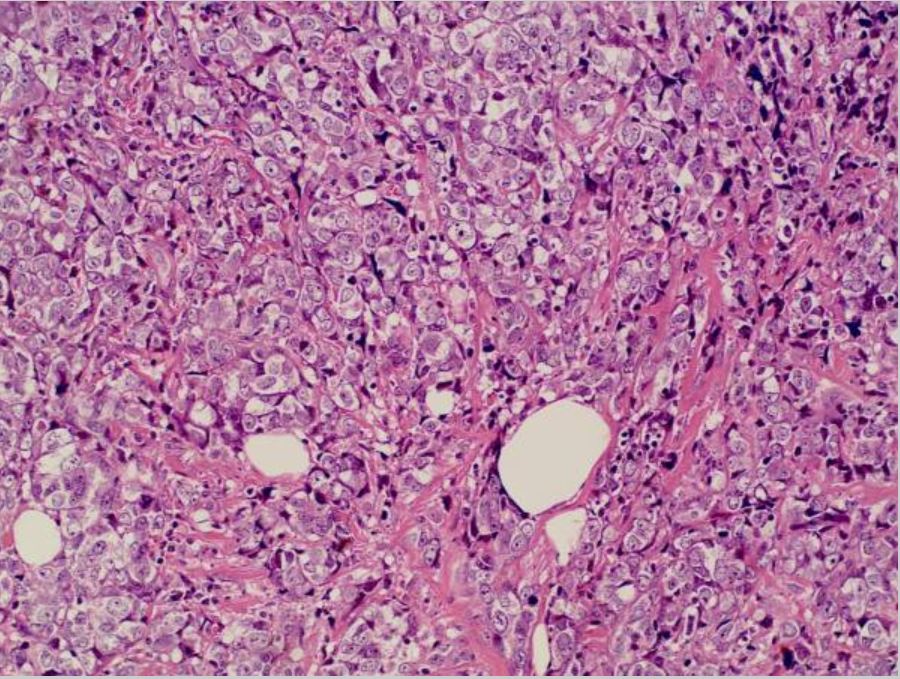
Breast cancer: invasive ductal carcinoma in the left breast
Image: “Invasive ductal breast cancer metastatic to the sigmoid colon” by Zhou XC, Zhou H, Ye YH, Zhang XF, Jiang Y. License: CC BY 2.0.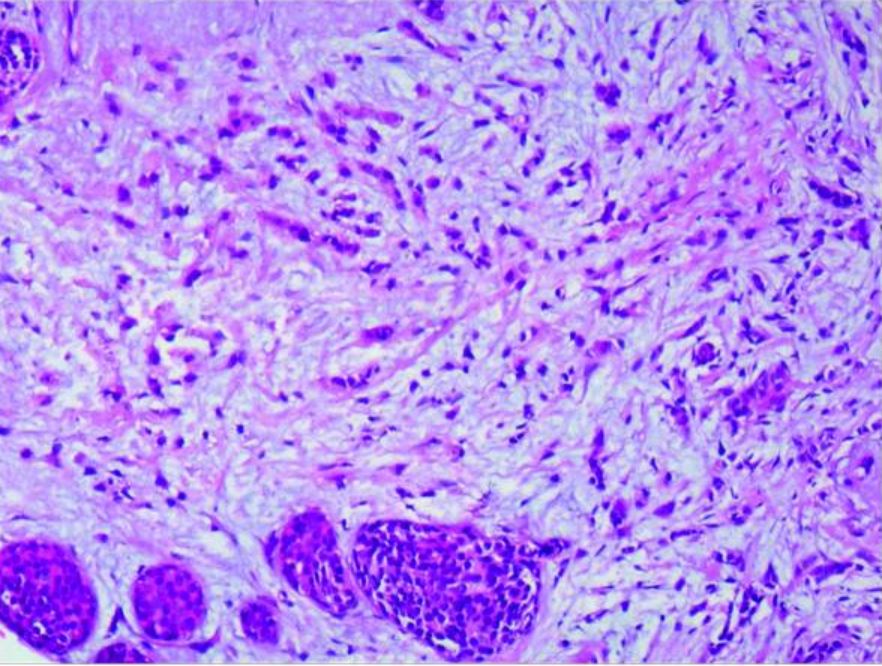
Lobular carcinoma: infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the right breast and LCIS (amplified 20×10)
Image: “Case report of small bowel obstruction caused by small intestinal metastasis of bilateral breast cancer” by Lv L, Zhao Y, Liu H, Peng Z. License: CC BY 3.0.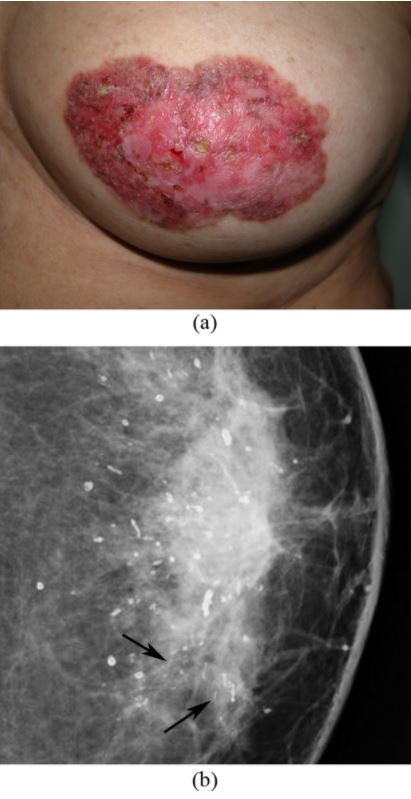
Paget’s disease of the breast: left nipple areolar changes
(a) Photograph of the left breast shows skin thickening, redness, erythema, erosion of the nipple, and scaling around the nipple-areola area.
(b) Mammogram shows scattered rod-like calcifications and groups of pleomorphic, fine, linear microcalcifications in the inner quadrant (arrows). Simple mastectomy revealed DCIS and secretory calcifications in the breast and Paget’s disease of the nipple.
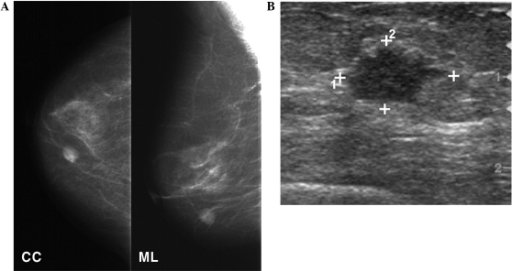
Mammography and breast ultrasound
A: Mammography shows a round, high-density mass in the lower inner quadrant of the right breast.
B: Ultrasonography follow-up shows a 1.3-cm irregularly shaped, hypoechoic mass in the breast.
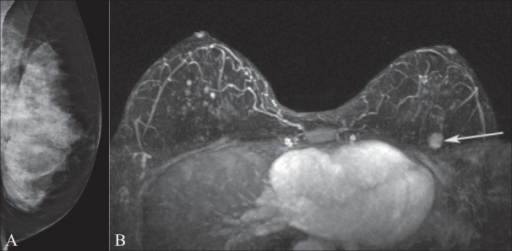
Mammography and breast MRI
Image A shows mammography of the left breast in a BRCA1 gene mutation carrier. Note the extremely dense breast tissue.
MRI image B demonstrates an enhancing mass (arrow) in the upper left breast that was occult on the mammogram.
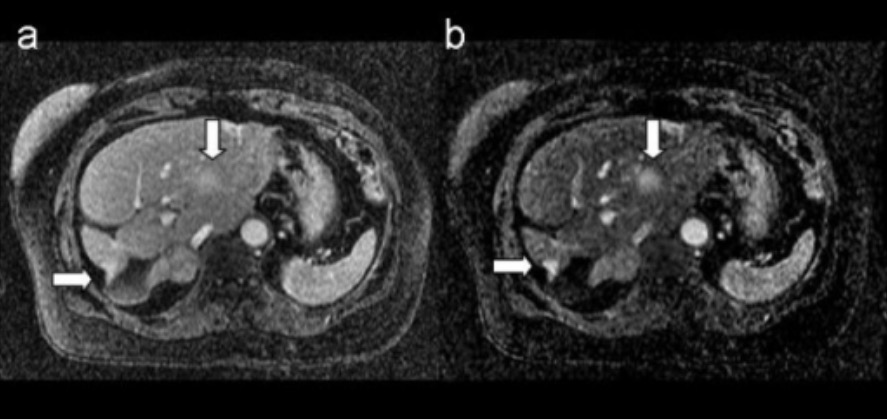
MRI of breast metastasis: images show metastatic breast lesions in the liver
A. T1-weighted 3D postcontrast image
B. corresponding 3D subtraction image
Arrows indicate the metastatic lesions.
| Tumor Tumor Inflammation stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Tx | Primary tumor Tumor Inflammation unable to be assessed |
| T0 | No evidence of primary tumor Tumor Inflammation |
| Tis |
|
| T1 | ≤ 20-mm tumor Tumor Inflammation in greatest dimension |
| T2 | > 20-mm but ≤ 50-mm tumor Tumor Inflammation in greatest dimension |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | > 50-mm tumor Tumor Inflammation in greatest dimension |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Tumor Tumor Inflammation of any size, with direct extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs to the chest wall Chest wall The chest wall consists of skin, fat, muscles, bones, and cartilage. The bony structure of the chest wall is composed of the ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae. The chest wall serves as armor for the vital intrathoracic organs and provides the stability necessary for the movement of the shoulders and arms. Chest Wall: Anatomy and/or skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions ( ulceration Ulceration Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers or macroscopic nodules) |
| Node stage | Description |
|---|---|
| cNX | Regional LNs cannot be assessed. |
| cN0 | No regional LN metastases |
| cN1 | Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to movable ipsilateral level I, II axillary LNs |
| cN2 |
|
| cN3 |
|
| Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis | Description |
|---|---|
| M0 | No evidence of distant metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis (clinical or radiographic) |
| M1 | Detectable metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis |
| Stage | Substages | Tumor Tumor Inflammation | Node | Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tis | N0 | M0 | |
| I |
|
T0-T1 | N1 | M0 |
| II |
|
T0-T3 | N0-N1 | M0 |
| III |
|
T0-T3 | N1-N2 | M0 |
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 |
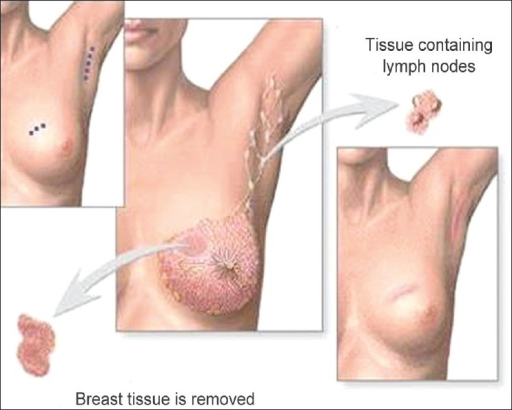
Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy): excision of the tumor to the negative margins and axillary lymph node evaluation
Image: “Phantom breast syndrome” by the Indian Journal of Palliative Care. License: CC BY 2.0.